Researchers in this study found that though SBRT use more than doubled from 2010 to 2015 in patients with prostate cancer, it only accounted for less than 10% of all patients undergoing radiotherapy.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Researchers in this study found that though SBRT use more than doubled from 2010 to 2015 in patients with prostate cancer, it only accounted for less than 10% of all patients undergoing radiotherapy.

This study found that men with low baseline PSA levels could be screened less frequently, while men with higher baseline levels would benefit from more intensive screening strategies.
Given these data, the researchers indicated that physicians screening for this cancer type should account for strong age dependence.
The investigation of darolutamide plus ADT in men with non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer indicated a significant improvement in overall survival in this patient population.
A study of the Veterans Affairs health system found that, despite trends suggesting otherwise, African American men with prostate cancer had similar survival outcomes, compared with non-Hispanic white men.

This study suggested that along with pelvic floor underactivity, men who had a prostatectomy and experienced stress urinary incontinence as a result have pelvic floor overactivity as well.

This research found that combining family history and a genetic risk score could better stratify inherited risk for developing prostate cancer.

The FDA granted priority review to rucaparib for the treatment of adult patients with BRCA1/2-mutant recurrent, metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
A recent study shows the importance of information regarding adverse events of cancer treatment for prospective patients.
When treatment decisions were made using a prostate genomic classifier after radical prostatectomy in men with prostate cancer, patient outcomes significantly improved.
Single dose radiotherapy may be as effective as 5 doses for patients with spinal canal compression from metastatic cancer.
Researchers indicated that among men age ≥66 with prostate cancer, organ transplant is associated with higher overall mortality but no observable difference in prostate cancer-specific mortality.

The FDA approved enzalutamide for the treatment of patients with metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer.
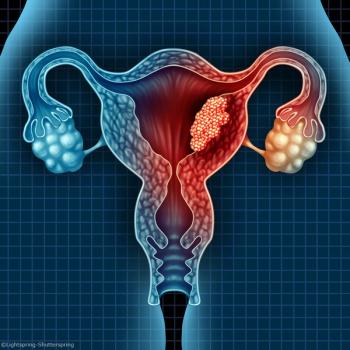
Patients with endometrial cancer pose a very high risk of dying from cardiovascular diseases in the year after diagnosis, suggesting the necessity of early involvement of cardiologists for these patients.

Myovant announced that their phase III HERO study of relugolix met its primary efficacy end point and all 6 secondary endpoints in men with advanced prostate cancer.
An international study of prostate cancer clinical trials discovered that opioid use appears to differ by region, implying that a variability should be considered.

Fewer biopsies among men receiving antidiabetic medications may explain the lower prostate cancer risk in men with diabetes.

MCLA-128 showed radiological and clinical responses in patients with certain types of cancer who harbored neuregulin 1 gene fusions.

Metastasis-directed therapy with stereotactic ablative radiotherapy has emerged as a promising complementary technique for the management of low-volume metastatic prostate cancer.

The addition of apalutamide to androgen deprivation therapy is well tolerated and significantly improves survival while maintaining health-related quality of life in men with prostate cancer.
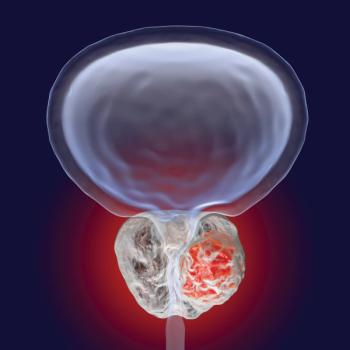
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy can relieve symptoms of late radiation cystitis in patients who underwent radiotherapy of the pelvic region for prostate cancer.

The agency granted breakthrough therapy designation to niraparib for the treatment of men with BRCA1/2-mutant positive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.

Despite prolonged progression-free duration, a 25% reduction in risk of death associated with anti-androgen agent apalutamide fell short of statistical significance in patients with non-metastatic, high-risk castration-resistant prostate cancer.
The findings of a trial presented at ESMO 2019 may be a breakthrough when it comes to molecularly targeted treatment for prostate cancer.