Prostate Cancer
Latest News
Latest Videos
CME Content
More News
Rencsok and colleagues found that the proportion of white participants in the clinical trials studied has primarily remained above 80% since 1990.
Researchers detailed methods and processes that may be useful for additional research and validation of computational hematoxylin and eosin staining deep learning models and the images generated by them.

Payment models with shared-savings components, such as the Oncology Care Model, may be associated with fewer visits and lower costs in certain cancer settings in the first year.
This study found that regional- and distant-stage prostate cancer incidence continues to increase in US men aged ≥50 years.

The FDA approved olaparib for the treatment of adult patients with deleterious or suspected deleterious germline or somatic homologous recombination repair gene-mutated metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
A recent examination of older adults with cancer found accelerated losses in differing sarcopenia measures existed before and after a cancer diagnosis.

The FDA approved rucaparib for the treatment of adult patients with a deleterious BRCA mutation-associated metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
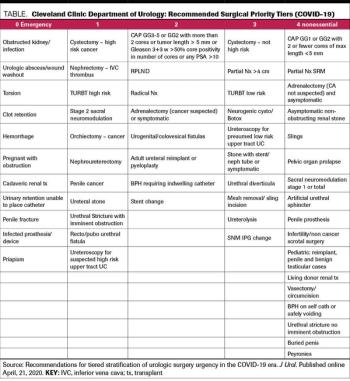
The chairman of the Glickman Urological & Kidney Institute at the Cleveland Clinic provides commentary and an adjacent perspective to the Duke Cancer Institute report.
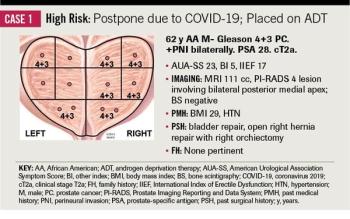
Experts from the Duke Cancer Institute outline their current approach to stratifying surgical management of patients with prostate cancer.

A recent study found that the proportion of men with high-risk prostate-specific antigen levels at diagnosis was decreased in association with Medicaid expansion states.
Olaparib was found to be associated with longer progression-free survival and improved measures of response and patient-reported end points than either enzalutamide or abiraterone in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
In a webinar, a multidisciplinary team from Duke Cancer Center came together to discuss the differences in treating patients with genitourinary cancer as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.

A recent study led by led by King's College London and Public Health England examined 1.4 million patients of cancer via the National Cancer Registry and found that early GP referrals led to longer survival rates for patients.
The model was able to use data from each treatment cycle to estimate intratumor subpopulations and accurately predict the outcomes in each subsequent cycle.

Results from the trial showed a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in overall survival with olaparib versus enzalutamide or abiraterone in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer selected for BRCA1/2 or ATM gene mutations.

A prognostic survival model, titled PROVIEW, was able to accurately predict changing cancer survival risk over time and may have the potential to be a useful prognostic tool that can be completed by patients.
The prostate cancer expert discussed guidelines that he and his colleagues culminated for triaging patients with prostate cancer during the COVID-19 pandemic.
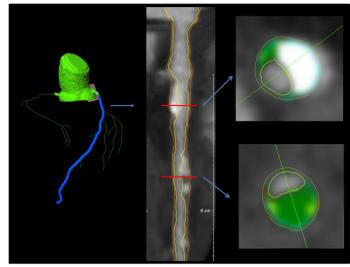
Experts discuss the case of a 69-year-old man with a history of metastatic prostate cancer previously treated with androgen deprivation therapy with leuprolide.

A recent study found that a group of patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer responded positively to treatment with ipilimumab, prolonging survival after treatment in the “favorable” cohort.

An international team of researchers created a framework of recommendations to help patients and healthcare professionals make decisions regarding radiation treatment for patients with prostate cancer during the COVID-19 pandemic.

A recent study analyzed response to treatment of oligometastatic prostate cancer with stereotactic ablative radiotherapy and found improved oncologic outcomes among men.

Prostate-specific membrane antigen PET/CT was found to be a suitable replacement for conventional imaging in patients with prostate cancer, providing superior accuracy to the combined findings of CT and bone scanning.

In this study, polypharmacy during the 6-month time period pre-IV chemotherapy was highly predictive of post-chemotherapy inpatient hospitalization.

These data suggest that clinicians should prescribe a short-term exercise program at the beginning of ADT to attenuate these important treatment-related side-effects.
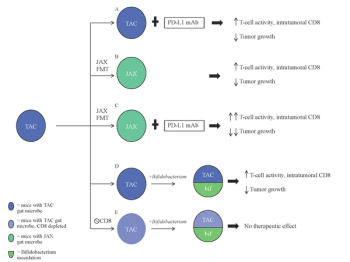
This review article discusses the concepts of a tumor microenvironment and a gut microbiome and their effects on responses to checkpoint inhibitors (CPIs). It also reviews recent research investigating these 3 topics, and how it can be applied to using CPIs in prostate cancer.