
All News



Oncologists and their patients are facing disruptive changes in healthcare, research, and communication. This dramatic increase in the quantity and quality has changed our lives forever. However, many of us remain frustrated with our inability to control this information overload.

Radium-223 is a promising agent that represents a new class of alpha pharmaceuticals that gets down to the site of bony metastases. The limited side-effect profile potentially allows for repeat administration to increase durability of pain control, and for its use in combination with novel biologic and chemotherapeutic agents.

One would hope that survival data from at least one more phase III or phase IV clinical trial will convincingly show a prolongation of survival due to treatment with Alpharadin. This will not be inexpensive therapy.

In this article, we endeavor to clarify the role of radiation therapy and chemotherapy in the treatment of ATC; we note important contributions of the historical literature, and we review more contemporary strategies adopted by several renowned institutions.

This article will present current information about alpha-pharmaceuticals, a new class of targeted cancer therapy for the treatment of patients with CRPC and bone metastases. It will review preclinical and clinical studies of the experimental radiopharmaceutical radium-223 chloride (Alpharadin).

Just over a year ago, Alex Trebek introduced the world to Watson. IBM insists that Watson is a decision-support tool, meant to assist and not supplant physicians. Could it work as an oncology support?
Scientists in Germany have potentially found a way to indirectly target the MYC oncogene-an elusive cancer therapy target to date, discovering that cancer cells with upregulated levels of MYC are dependent on AMPK-related kinase 5 to stay alive. Inhibition of ARK5 causes these MYC-dependent cells to die.
Scotland will soon begin a large prospective trial of early screening for lung cancer in high-risk patients using a simple blood test. The test, called EarlyCDT-Lung, has been in use and trials in the United States for more than two years.

Treatment with tremelimumab stabilized patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma due to chronic hepatitis C infection for more than 12 months, according to data from a phase II clinical trial presented at the AACR annual meeting.
A combination of cixutumumab, a type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor inhibitor, and temsirolimus, a mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor, showed evidence of activity in refractory Ewing’s sarcoma tumors as well as small-round-cell tumors in a phase I multicenter clinical study.

Of all the sad pronouncements that oncologists deliver, this may be the one that stings the most. If you were expecting hope from your doctor, how would you react to these words? Would you sit with quiet disbelief, or storm out of the office?


CancerNetwork brings exclusive coverage of the AACR Annual Meeting, held March 31-April 4, 2012 at McCormick Place in Chicago, Illinois. The meeting will highlight the best and latest findings in all major areas of cancer research. This year's theme is “Accelerating Science: Concept to Clinic,” reflecting the progress and emphasizing the synergy between basic, clinical, and translational research that will continue to lead to effective cancer therapies and prevention strategies. Check below for the most important news to come out of this year's event.

Rationale for prostate cancer screening continues to be debated as an update to a large European trial reconfirms a reduction in death rates from prostate cancer in men who are screened for the disease. The study, however, found no significant difference in overall mortality between the two arms of the trial.

Given the abundance of breast cancer data, this review will focus on breast cancer–related lymphedema. However, the principles and controversies discussed are relevant regardless of the type of malignancy to which the lymphedema is attributed.

Combined-modality therapy has rendered disease-free an increasing number of patients who were previously considered to be incurable. Still, despite myriad advances in imaging, and in surgical and therapeutic modalities, many patients who undergo resection of limited metastatic disease with curative intent ultimately relapse.

The development of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathway inhibitors and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors for the treatment of renal cancer is a real success story.

The etiology and risk factors of breast cancer–related lymphedema (BCRL) are multifactorial and not fully understood.

It is ironic that we were asked to comment on the article by Dr. McLaughlin in this issue of ONCOLOGY. A few months ago, one of us (LKJ) was attending a patient in the breast clinic who had recovered well from a lumpectomy with sentinel node biopsy followed by completion axillary lymph node dissection (ALND).


The surge in availability of apps for every possible purpose is not limited to Apple but has also occurred with apps for the BlackBerry, for Google's Android platform, and for a number of other devices. The authors discuss their experience with apps that are relevant, directly or indirectly, to the oncology practice for both the iPhone and Android smartphones.
Researchers have reported cases of brain tumors among cardiologists and radiologists that work in cardiac catheterization laboratories. In addition to support from the literature, documenting 5 cases of brain tumors, a new study reports 4 new cases of brain malignancies, all in the left hemisphere of the brain.
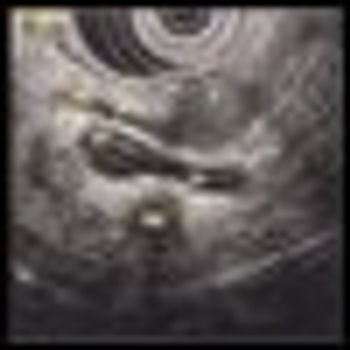
A combined dual inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and c-MET is showing promise in preventing tumor invasion and metastasis. The data thus far are in a laboratory model of pancreatic neuroendocrine cancer.

Reporting interim findings from a multi-institutional assessment of more than 50,000 people 50 to 69 years of age, COLONPREV Study Group investigators from Spain have concluded colonoscopy is better than fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) at detecting adenomas.

CancerNetwork presents exclusive coverage of the 29th Annual Miami Breast Cancer Conference. We speak with nationally recognized breast cancer specialists and bring you their insights into the optimal multidisciplinary management of patients with breast cancer and the application of innovative approaches to practice. As always, we encourage feedback and suggestions on how we can better serve your clinical cancer information needs. Please check your inbox for reports from the 29th Annual Miami Breast Cancer Conference, and watch here for our editorial staff’s coverage during the meeting.

The treatment of cancer is shifting to increasingly more oral pills. Most oncology drug labels recommend taking the pills while fasting though often there is evidence that food increases bioavailability of the medication as much as four-fold.

In this interview, Christopher-Paul Milne and Kenneth Kaitin, Tufts Center for the Study of Drug Development. discuss the current challenges of the US Food and Drug Administration review process as it relates to oncology therapeutics and upcoming changes to the Prescription Drug User Fee Act.
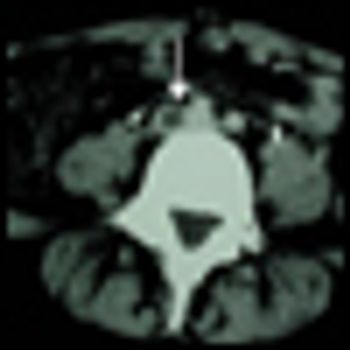
Semuloparin, an ultra-low molecular weight heparin reduces the probability that a cancer patient undergoing chemotherapy has a thromboembolic event by 64%. The results from the phase III trial also show that the benefit is not accompanied by an increase in major bleeding, a potential side effect of semuloparin.
