The new diagnostic test to detect KRAS gene mutations, will facilitate speedier assessment of the KRAS mutation status of a patient’s tumor to allow for an earlier treatment decision to use cetuximab or to go on with another treatment.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


The new diagnostic test to detect KRAS gene mutations, will facilitate speedier assessment of the KRAS mutation status of a patient’s tumor to allow for an earlier treatment decision to use cetuximab or to go on with another treatment.

The FDA has approved a new strategy to evaluate the risk and safety of both extended-release and long-acting opioid analgesic, called a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS). The drug class are synthetic versions of opium, that have had a long history of regulated control to mitigate their abuse and illegal distribution.

Young women in Southern and Midwestern states have seen death rates from lung cancer decline more slowly than elsewhere in the country, or even increase, over the last several decades, according to a new study.
A new study finds cutaneous human papillomavirus infection can increase the risk of squamous-cell carcinoma, a nonmelanoma skin cancer.
A new noninvasive blood test for prostate cancer detection won the approval of the FDA last month. The manufacturer believes the test will provide better detection and a decrease in costs.
One of the largest whole-exome sequencing analyses in breast cancer is published this week in Nature, identifying a new gene fusion among a subset of triple-negative breast cancers.

Researchers at the Roswell Park Cancer Institute believe that cancer studies should take into account the tobacco and smoking habits of participants-something that rarely happens. Whether a trial participant uses tobacco products can affect cancer treatment, say the group of investigators.

Pertuzumab has been approved in combination with trastuzumab (Herceptin) and docetaxel chemotherapy for women whose breast cancer overexpress the HER2 receptor and who have not received prior systemic treatment.

Researchers have found that circulating tumor cells can predict early recurrence and decreased overall survival in nonmetastatic breast cancer patients who have not yet been treated with chemotherapy.
Two studies demonstrate that a “liquid biopsy”, using plasma or blood samples can be used to detect the acquired resistance and potentially measure disease progression.

The results of a randomized phase III trial show paclitaxel beat two newer chemotherapies, nab-paclitaxel and ixabepilone in the treatment of metastatic breast cancer patients who have not had prior systemic therapies.
Women previously treated for HER2-positive breast cancer have lower rates of relapse when given a novel peptide vaccine. The AE37 vaccine showed a 43% risk reduction in these patients after 22 months of follow-up in a phase IIb clinical trial.

Women with metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer treated with a taxane-based chemotherapy in combination with trastuzumab as a first-line of treatment have a longer progression-free survival compared to chemotherapy in combination with lapatinib (Tykerb)
A 13-gene signature can predict the development of brain metastasis among patients with advanced HER2-positive breast cancer who have estrogen-receptor (ER)-negative tumors. The results were presented at a breast cancer session at the 2012 meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.

Results of a large phase III trial shows that a new oncology therapy, trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1), significantly delays progression of disease in women with HER2-positive advanced breast cancer previously treated with a taxane chemotherapy and trastuzumab (Herceptin).
A new study shows that obese patients are more likely to have advanced papillary thyroid cancer and for the cancer to be of an aggressive subtype.

Researchers have shown that patients who use nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like aspirin and ibuprofen are less likely to develop three types of skin cancer.
A new study has identified independent risk factors for the development of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) including high fetal growth, older age of the mother, low birth order, and male sex. A family history of NHL in either parent or sibling was found to be the strongest risk factor.

The first randomized, controlled clinical trial testing the effect of weight loss on sex hormone levels in overweight, postmenopausal women shows a benefit with moderate weight loss.
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania have identified a protein that could be targeted to turn off B-cell lymphomas. The protein, CD19, was found to be a major regulator of B-cell neoplastic growth driven by the MYC oncogene.
Three studies published this week show that lenalidomide improves progression-free and overall survival as a maintenance therapy in multiple myeloma, despite its link to other primary cancers.
Melanoma has become the poster cancer for genomic research. The identification of a driver mutation in the BRAF gene found in approximately 40% of metastatic melanoma patients and the subsequent approval last year of the targeted BRAF inhibitor, vemurafenib, has resulted in a surge of both clinical and laboratory research.

A new study from the National Cancer Institute shows that physical activity is associated with lower mortality rates in patients with breast and colon cancers.

An abstract presented at the 13th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Breast Surgeons suggests that women who are at high risk for recurrence may not need a mastectomy.
New data presented at the 13th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Breast Surgeons shows radiofrequency ablation can prevent local breast cancer recurrence just as effectively as radiation therapy. Compared to radiation therapy, radiofrequency ablation showed superior cosmetic results and poses little risk to healthy tissue.
A study published today shows that whole-breast irradiation fares better than brachytherapy for women with breast cancer.
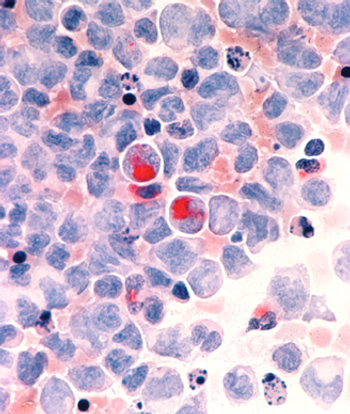
Two researchers from the Mayo Clinic have published an editorial calling for new approaches in the treatment of AML, arguing that "using the same old drugs in different doses or different schedules is not going to cut it."
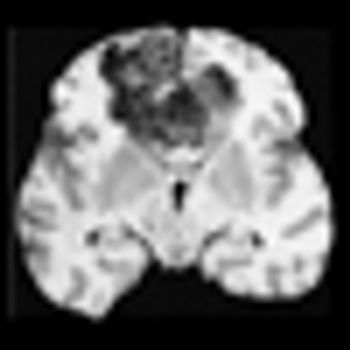
Results from a phase II clinical trial with HSPPC-96 (vitespen), an autologous heat shock protein-peptide vaccine, have shown promise in patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme.
Researchers from the United Kingdom and Canada have released new data genetically characterizing over 2,000 breast tumors. The work provides a framework to understand how gene copy-number aberrations affect gene expression in breast cancer and reveals novel subgroups that could be targets of future investigations.
A study published today details a scoring system that may predict which ovarian cancer patients responded to first-line platinum chemotherapy based on a DNA-repair pathway-focused score. The score is based on a gene expression profile of 23 DNA-repair genes that normally function to repair platinum-induced DNA damage.