Articles by Anna Azvolinsky

The results of the 2-year follow-up of the dasatinib DASISION phase III trial show the continued superiority of the drug compared to imatinib. The results provide further support for treatment of first-line chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients that harbor the Philadelphia chromosome.

A large cohort study shows that women on antiestrogen therapy have a lower risk of melanoma. In a study of 7360 women diagnosed with breast cancer between 1980 and 2005, 54% were given supplemental antiestrogen therapy. The rate of cutaneous melanoma was 60% higher for those women not taking antiestrogen supplements compared with the expected rate of melanoma incidence based on age and other factors.

Inherited mutations in the ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) gene increase the odds of developing pancreatic cancer according to a new study. While there is predisposition for pancreatic cancer with up to 10% of cases occurring among families with a history of the disease, the genetic basis for this had not been previously discovered.
A new finding suggests that inhibiting the cytokine interleukin-17A, produced by inflammatory cells of the immune system, may be a novel approach in the treatment of lung tumors.
A study has identified a gene fusion from a never-smoker lung cancer patient that may act as a driver in a subset of lung cancer cases. The results suggest that the newly identified fusion is not that rare and that the mutation exists in primary lung adenocarcinomas.

A study published in the journal Cancer shows that breast cancer survivors can experience problems with specific mental abilities up to several years after treatment.

The results of a study presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS) prompted enough controversy to warrant a statement from 3 major medical societies and an expert panel teleconference on December 14, 2011 to discuss the analysis of data presented by the MD Anderson Cancer Center physicians.
Results of the phase III SWOG S0016 trial comparing 2 chemotherapy regimens for follicular lymphoma (FL), presented this week at ASH, show no statistically significant differences in either progression-free survival (PFS) or overall survival. Both regimens produced “excellent” results, according to the presenter.

The phase III randomized RESORT (ECOG Protocol E4402) trial asked whether a maintenance schedule of rituximab every 3 months would lead to a superior disease control outcome compared to retreatment upon progression. The answer, presented this week at ASH, is no.
Researchers presented a late-breaking abstract reporting activity in a metastatic lymphoma mouse model of two monoclonal antibodies combined with CpG, a short synthetic oligonucleotide agonist of TLR9, that mimic bacterial and viral DNA and facilitates a pro-inflammatory immune response.
The first plenary session at this year’s ASH was kicked off by the presentation of a study that showed that when stem cells come from donors unrelated to the patient there is no difference in patient survival between the use of cells sourced from peripheral blood or bone marrow.

The phase III trial comparing the use of gemtuzumab ozogamicin combined with chemotherapy to chemotherapy alone in newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients provides evidence that the combination treatment may be promising in this patient population.

At this year’s San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, new data results from four different clinical trials of bisphosphonate usage in patients with breast cancer will be presented and discussed.

The San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium brings together basic science researchers and clinicians for the latest breast cancer research-related progress. The symposium has evolved from a 1-day local conference to a 5-day international meeting focusing on clinical, preventive, diagnostic, translational, and basic research.
Is estrogen plus progestin better than estrogen alone for symptom relief in menopausal women? For women who have not had a hysterectomy, adding progestin to estrogen therapy counteracts the increased risk of uterine cancer from estrogen monotherapy. However, the progestin and estrogen combination increases breast cancer risk. The combination treatment also comes with its own side effects, including breast tenderness, which ranges from 8% to 15% of patients in randomized clinical trials.

Coffee is emerging as a protective agent against a number of diseases, including cancer. A study published last week shows that women who drank more than four cups of coffee per day cut their risk of endometrial cancer by 25% compared with those who drank less than one cup per day.

The results of a trial comparing concurrent versus sequential trastuzumab and chemotherapy as adjuvant treatment of breast cancer has shown an improved efficacy without increased toxicity for the concurrent regimen.
Breast and ovarian cancer patients with limited tumor burden and minimal prior chemotherapy appear to have benefited from a novel vaccine.
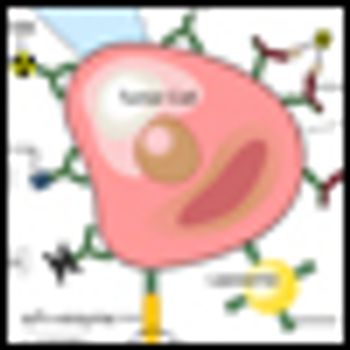
Researchers have developed a novel way to molecularly target and kill cancer cells, called photoimmunotherapy. The method uses a monoclonal antibody against the epidermal growth factor coupled to a near-infrared dye. The result is a target-specific photosensitizer that causes specific cell death of cells bound by the antibody when NIR light is applied.
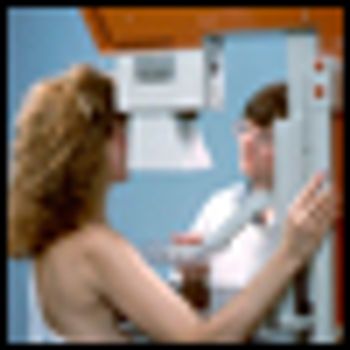
A new prospective study has shown that cancer detection using digital film mammography has outcomes similar to the much less expensive film-screen mammography technique. Sensitivity of digital mammography was found to be higher, however, for specific subpopulation cohorts.

A new study has found that cumulative alcohol consumption in women is a risk factor for breast cancer. Even low levels of drinking were found to be linked to a small increase in breast cancer risk according to research published in today’s issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA)

A study has been released that demonstrates the cost-effectiveness of Medicare-funded cancer care treatment programs.
A study published online in the Journal of Clinical Oncology analyzed triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) for distinguishing characteristics. The study compared clinical, pathological, and hormone-related lifestyle characteristics of 1469 women aged twenty to forty-nine.
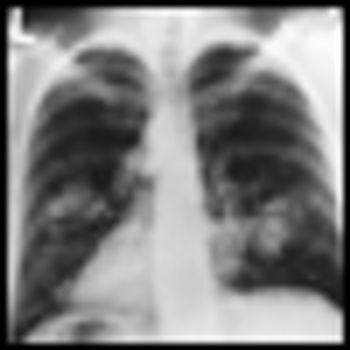
A trial of 154,901 participants between the ages of 55 and 74 sought to address whether chest radiographs as lung cancer screenings affect lung cancer incidence and mortality rates from lung cancer.

A small phase II clinical trial published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology has shown that consuming ginger root decreased harmful inflammatory prostaglandins in the colon and was tolerable and non-toxic.
Researchers have identified a novel rare, germline mutation linked to a predisposition for both melanoma and renal cell carcinoma (RCC) that results in a five-fold increased risk of developing melanoma, RCC, or both.
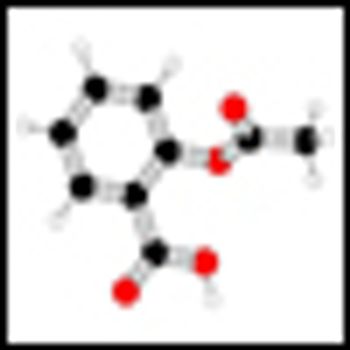
Epidemiological evidence as well as evidence from recent randomized trials suggest that aspirin may be of use in the adjuvant setting to treat cancer.

Vitamin E supplements, rather than reducing the risk of prostate cancer have been found to increase the risk of developing the disease. The findings are a 3-year follow-up to the Selenium and Vitamin E Cancer Prevention Trial (SELECT).

The mining of whole genomes from 656 Icelanders with ovarian cancer and the comparison of these genomes to 41,675 control genotyped Icelanders has led to the identification of 16 million sequence variants that were tested for their association to ovarian cancer, one of the deadliest forms of cancer among women.

Women with high-grade serous ovarian cancer who also harbor a BRCA2, but not a BRCA1 mutation tend to have a better chemotherapy response and overall survival compared with those patients who are BRCA wild type.




























