Articles by Anna Azvolinsky
A large-scale study of US women between the ages of 20 and 44 shows that using the injectable contraceptive, depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA), is associated with a two-fold increase in the risk of invasive breast cancer when the contraceptive is used for at least one year.
Results from a phase II trial of vemurafenib for metastatic melanoma show a significant number of patients exhibiting a prolonged and durable response and a median overall survival of 16 months.
Scientists in Germany have potentially found a way to indirectly target the MYC oncogene-an elusive cancer therapy target to date, discovering that cancer cells with upregulated levels of MYC are dependent on AMPK-related kinase 5 to stay alive. Inhibition of ARK5 causes these MYC-dependent cells to die.

Researchers at the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, Canada have sequenced and analyzed over 100 triple-negative breast tumors at the time of diagnosis, the first in-depth genomic analysis of this heterogeneous breast cancer subtype.
Researchers have identified a marker of DNA damage that may be able to predict a patient’s response to platinum-based chemotherapy agents such as cisplatin and carboplatin.
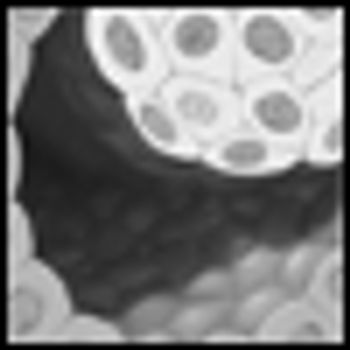
A wide negative margin during breast-conserving surgery should be attempted for women with ductal carcinoma in situ–this is the conclusion from an analysis published today in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.

Three papers published today show that aspirin, taken daily, may prevent cancer, and could even treat certain cancers.
Typically women who are likely to be treated with systemic therapy before surgery have bulky disease. But should all breast cancer patients receive systemic neoadjuvant therapy?

Reasons for recurrence after treatment for early breast cancer are still not well understood. Lifestyle and other longer-term factors are likely at play, but the subject is difficult to study. The best advice for cancer patients is exercise and a healthy diet.

Endocrine-therapy resistant HER2-negative breast cancer is the most common cause of breast cancer death. The basis for this resistance is heavily studied to identify new ways to treat these patients.
What are the latest advances in the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer? Are there new ways to molecularly characterize breast cancer tumors to identify specific mutation targets and increase the chance of response in this disease?
Breast cancer tumors that have a loss of function in DNA-repair genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2 may be particularly sensitive to PARP inhibitors such as olaparib.
Over the past several months, the results of four randomized bisphosphonate adjuvant trials in a range of different patients have been released, two of these trials showed a survival benefit for the addition of a bisphosphonate to standard systemic therapy. ER-positive patients who are postmenopausal and have had no chemotherapy seemed to benefit the most.

Rationale for prostate cancer screening continues to be debated as an update to a large European trial reconfirms a reduction in death rates from prostate cancer in men who are screened for the disease. The study, however, found no significant difference in overall mortality between the two arms of the trial.
Women who received estrogen while part of the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) trial had lower rates of invasive breast cancer compared to those who received placebo, and they were less likely to die of the disease compared to women who never took the hormone replacement therapy.

Two studies published today help clarify how to interpret CYP2D6 genetic testing and the results will likely affect the current trend of CYP2D6 genotyping prior to tamoxifen usage in early-stage ER-positive breast cancer patients.
Researchers have reported cases of brain tumors among cardiologists and radiologists that work in cardiac catheterization laboratories. In addition to support from the literature, documenting 5 cases of brain tumors, a new study reports 4 new cases of brain malignancies, all in the left hemisphere of the brain.
A combined dual inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and c-MET is showing promise in preventing tumor invasion and metastasis. The data thus far are in a laboratory model of pancreatic neuroendocrine cancer.

The treatment of cancer is shifting to increasingly more oral pills. Most oncology drug labels recommend taking the pills while fasting though often there is evidence that food increases bioavailability of the medication as much as four-fold.
Semuloparin, an ultra-low molecular weight heparin reduces the probability that a cancer patient undergoing chemotherapy has a thromboembolic event by 64%. The results from the phase III trial also show that the benefit is not accompanied by an increase in major bleeding, a potential side effect of semuloparin.

Researchers at Vanderbilt University Medical Center have found that eating omega-3 fatty acids regularly can result in prevention of colon polyp formation. The 33% reduced risk of colorectal adenomas was seen in women, but not in men.
The new drug, MDV3100, extended overall survival by 4.8 months (P < .001) and reduced the risk for death by 37% as compared to placebo in men with castration-resistant prostate cancer who had progressed after treatment with docetaxel.

Four publications on cancer treatment during pregnancy were published last week in the journal Lancet, serving as new treatment guidelines for chemotherapy and surgery in pregnant patients with solid tumors and hematologic malignancies.

Initial results of a multicenter trial show that 2 biomarkers, PCA3 and T2-ERG, are found at high levels in prostate cancer compared to noncancerous prostate cells and correlate well with 2 indicators of aggressive prostate cancer, tumor volume and Gleason score.
It is still difficult to gauge the probability that a low-risk prostate cancer patient may be upgraded to a higher prostate cancer stage. Researchers at Vanderbilt University Medical Center have now determined that smaller prostates were more likely to evolve into more serious, aggressive disease.

Metastatic melanomas that harbor the V600E mutation in the BRAF gene respond rapidly to vemurafenib (Zelboraf), the BRAF V600E inhibitor. But While vemurafenib results in a response in about 80% of melanoma patients, the clinical response among CRC patients is not greater than 5%.

A study published earlier this month in the New England Journal of Medicine, identifies specific colorectal tumors that are less responsive to chemotherapy. Researchers at the University of Magdeburg show that the hypermethylation of the transcription factor AP-2 epsilon (TFAP2E) gene results in lower expression of the TFAP2E protein and upregulation of the DKK4 gene, a gene which has been previously associated with resistance to the chemotherapy fluorouracil.

Breast cancer survivorship continues to rise, but the long-lasting psychosocial and quality-of-life changes that occur after treatment need to be studied, as treatment outcomes can lead to negative side effects that outlast the treatment.

Researchers in Sweden who analyzed several prospective studies found an increased risk of pancreatic cancer associated with processed meat consumption. They also found that eating red meat is linked to pancreatic cancer among men.

A new study has made a step forward toward better characterization of sporadic ovarian tumors by identifying their DNA repair protein expression profile.






























