
A new meta-analysis indicated that people with diabetes are not only at an increased risk of developing breast and colon cancer, but are also at an increased risk of dying from the diseases.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!



A new meta-analysis indicated that people with diabetes are not only at an increased risk of developing breast and colon cancer, but are also at an increased risk of dying from the diseases.

The FDA today granted pertuzumab (Perjeta) accelerated approval for the treatment of patients with HER2-positive early stage breast cancer prior to surgery who are at high risk for recurrence or metastasis.

Ten-year follow up two large randomized trials in the UK show that less frequent but higher dose radiotherapy regimen are as safe and effective as the standard regimen of more frequent lower doses for women with early breast cancer post-surgery.

In order for malignancies to establish in metastatic sites, cancer cells must acquire attributes of those sites; specifically how this occurs in many cancers is relatively unknown, but a new study implicates the stroma of certain breast cancer tumors in the development of bone metastases.

Clearly there is no single therapy for all patients with TNBC, given the molecular heterogeneity of this subtype. However, new insights from further genomic analysis of TNBC suggest approaches to rational clinical trial design, and patients will undoubtedly benefit as we define the most appropriate therapeutic targets in management of this aggressive disease.

Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) remains a very challenging entity today, but with the identification of new targets and further optimization of therapy, the landscape for TNBC may not look so negative. In the future, “TNBC” may be considered an antiquated misnomer, as we will have identified various breast cancer subgroups based on what they “are” rather than what they “are not.”

With regard to potential research strategies relevant to the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer/basal-like breast cancer, potential targets include PTEN, INPP4B, PIK3CA, KRAS, BRAF, EGFR, FGFR1, FGFR2, IGFR1, KIT, MET, PDGFRA, and the HIF1-α/ARNT pathway. Many of these will be discussed further in this review article.

Combining four cycles of docetaxel and cyclophosphamide with 1 year of trastuzumab may be a viable treatment option for women with HER2-amplified early-stage breast cancer regardless of their TOP2A status, according to the results of a phase II study.

About 40% of women experienced a change in at least one biomarker from primary to residual breast cancer after undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy, according to the results of a study presented at the ASCO Breast Cancer Symposium.

Two studies presented at the ASCO Breast Cancer Symposium 2013 focused on studying cognitive function in women with early-stage breast cancer, focusing on the relationship between perceived and measurable cognitive decline, and factors that may help to predict cognitive decline.

The exposure of the heart to radiation during radiotherapy for ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) did not increase cardiovascular mortality or morbidity, according to a study by researchers in the Netherlands.

More than 90% of women about to undergo a mammography were unable to accurately quantify their risk for breast cancer, either over- or underestimating their risk, according to the results of a large-scale survey presented at the ASCO Breast Cancer Symposium 2013.

Expert radiologists were able to screen magnetic resonance images and rule out breast cancer diagnosis with a negative predictive value of about 99% using an abridged breast MRI protocol in a single-center study presented Saturday at the ASCO Breast Cancer Symposium 2013.

As part of our coverage for the ASCO Breast Cancer Symposium 2013, we spoke with Dr. Susan K. Boolbol, chief of the division of breast surgery at the Appel-Venet Comprehensive Breast Service at Beth Israel Medical Center in New York City, who is chairing a general session panel discussion on the overdiagnosis of breast cancer.

Results of the PrefHer study indicated that when given the option between subcutaneous trastuzumab and intravenous trastuzumab, significantly more patients with HER2-positive breast cancer preferred the subcutaneous administration.

A retrospective analysis of the HERA trial indicated that young age was not associated with early recurrence in women with HER2-positive breast cancer, despite previous research suggesting that young age at diagnosis might be a risk factor for recurrence and death.

To make the punishment fit the crime, you would want the decision of whether or not to use adjuvants to be informed by the degree of risk that the DCIS would recur. What factors can predict for an increased risk of recurrence, or more importantly, the risk of an invasive breast cancer occurring?
Use of calcium-channel blockers for treatment of high blood pressure for more than 10 years can increase the risk of breast cancer for women after menopause, a new study shows.

A study defining patterns of recurrence in node-negative breast cancer patients could help guide surveillance recommendations and future therapeutic approaches.
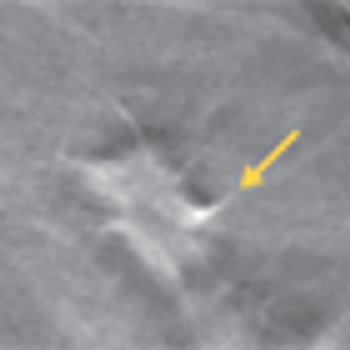
A new study shows that the combination of digital mammography plus tomosynthesis results in fewer false positive results compared with digital mammography alone. Women under the age of 50 and those with dense breasts had the greatest benefit from the combined screening approach.

Using easy-to-obtain risk factors for breast, ovarian, and endometrial cancers, researchers have come up with models that can predict an individual woman’s absolute risk for developing each type of cancer.

The combination of the chemotherapy capecitabine with external beam radiation was found to be both safe and effective in treating pain from bone metastases in patients with advanced breast cancer.
The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) has updated its guidelines on treating women at high risk of developing breast cancer with pharmacologic drugs.

Last week, the FDA announced that it would grant priority review to pertuzumab (Perjeta), as a neoadjuvant treatment for women with HER2-positive early-stage breast cancer.

The expression levels of two genes could indicate whether a woman with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer is at risk for recurrence after 5 years of tamoxifen therapy and should receive subsequent therapy.