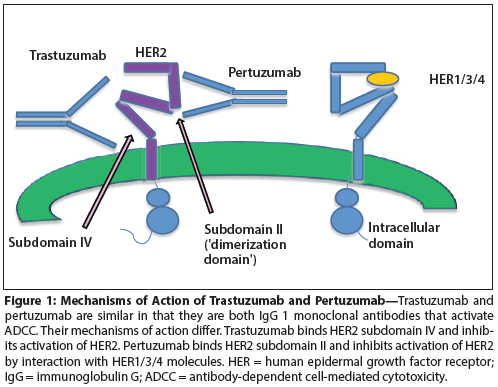
Management recommendations for breast cancer local-regional recurrence (LRR), including patient scenarios, are reviewed, and represent evidence-based data and expert opinion of the American College of Radiology Appropriateness Criteria Expert Panel on LRR.