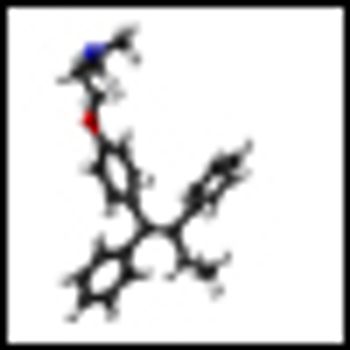
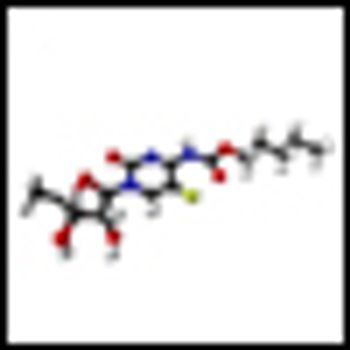
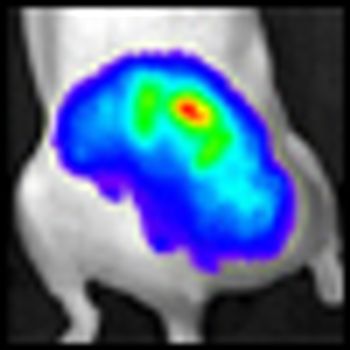
Combining histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors with PARP inhibitors or cisplatin has the potential to be an effective treatment for triple-negative breast cancer, according to preclinical research presented this week at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.