
At the 2021 American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting, CancerNetwork® spoke with Tanios S. Bekaii-Saab, MD, to discuss recent updates in the treatment of gastrointestinal malignancies.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


At the 2021 American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting, CancerNetwork® spoke with Tanios S. Bekaii-Saab, MD, to discuss recent updates in the treatment of gastrointestinal malignancies.
Patients with HCC who received atezolizumab/bevacizumab experienced a positive quality of life and improved disease symptoms vs sorafenib.
The combination of cabozantinib plus atezolizumab resulted in improved progression-free survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma whose disease has not previously been treated vs sorafenib monotherapy.

At the 2021 American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting, CancerNetwork® spoke with Tanios S. Bekaii-Saab, MD, about genomic drivers in cholangiocarcinoma.
The Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee has decided to wait until more results from a clinical trial of retifanlimab are available to make a final decision about approval in squamous cell carcinoma of the anal canal.
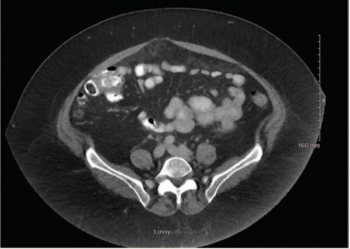
Mehmet Sitki Copur, MD, and colleagues examine the case of a 65-year-old patient with appendiceal mucinous neoplasms of the appendix who was treated with cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy.

Data from a phase 1b trial of the combination of regorafenib plus pembrolizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma display safety and early efficacy.
Adding toripalimab and hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy to lenvatinib yielded robust, durable responses for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.

Objective response data from a phase 2 trial supported the FDA’s decision to grant infigratinib accelerated approval to treat patients with certain a certain type of cholangiocarcinoma.

Adjuvant nivolumab for resected esophageal or gastroesophageal junction cancer was granted full approval by the FDA based on statistically significant improvements in disease-free survival over placebo in a phase 3 trial.

According to an economic evaluation, the use of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab is not cost effective versus sorafenib for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma when considering life-years gained and willingness-to-pay thresholds.

In patients with gastrointestinal cancers, factors such as younger age and comorbidities, among others, were significantly associated with a greater likelihood of sleep disturbance.

Based on response data from a randomized phase 3 trial, the FDA granted accelerated approval to pembrolizumab plus trastuzumab and chemotherapy for the treatment of HER2-positive gastric tumors.

Based on results of a phase 3 study, the IDH1-targeted agent ivosidenib will be considered by the FDA as therapy for cholangiocarcinoma following prior treatment.

By a close decision, the FDA’s Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee voted against upholding the accelerated approval of nivolumab monotherapy to treat patients with hepatocellular carcinoma following sorafenib.
Young women with gastrointestinal cancers who received the FOLFIRI or FOLFOX chemotherapy regimens experienced a benefit in terms of reduced nausea and vomiting with the combination of aprepitant plus palonosetron and dexamethasone.
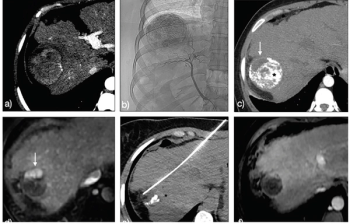
A thought-provoking installment of Clinical Quandaries is presented by Alejandro Gabutti, MD; and Tommaso Cascella, MD, of a 36-year-old patient with hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis and a subsequent diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Based on positive results of the phase 2 FIGHT trial, the FDA has granted the investigation antibody bemarituzumab plus FOLFOX6 breakthrough therapy designation for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic gastric and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma with FGFFR2b overexpression in the frontline setting.
Twenty percent of patients with resectable hepatocellular carcinoma experienced significant tumor necrosis when treated with neoadjuvant cemiplimab-rwlc, according to data from a phase 2a open label.
The addition of nivolumab to either chemotherapy or ipilimumab improved overall survival among patients with unresectable advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, according to data from the phase 3 CheckMate-648 trial.

Phase 2 trial data support the FDA breakthrough therapy designation for futibatinib in cholangiocarcinoma tumors positive for FGFR2 gene fusions and rearrangements.

The phase 3 CheckMate 577 trial is the first to show a checkpoint inhibitor in the adjuvant setting after trimodality therapy demonstrate a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in disease-free survival in patients with resected esophageal and gastroesophageal junction cancer.

Based on positive overall and progression-free survival data from the phase 3 KEYNOTE-590 trial, pembrolizumab was approved by the FDA for use in patients with metastatic or locally advanced esophageal or gastroesophageal junction carcinoma.

In order to properly utilize cancer therapies for personalized care, adequate molecular testing must be performed in patients who are eligible for these therapies, with this necessity becoming more and more prevalent in the treatment of gastrointestinal malignancies.

A selective internal radiation therapy from Boston Scientific Corporation, TheraSphere Y-90 Glass Microspheres, was granted FDA approval for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.