Gastrointestinal Cancer
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
Neoadjuvant botensilimab plus balstilimab appears to be safe and effective in patients with colorectal cancer regardless of mismatch repair status in the phase 2 NEST-1 trial.
Real-world data suggest a role for noncytotoxic chemotherapy treatments such as EGFR inhibitors beyond the frontline setting for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer.
Duration of response results with pembrolizumab plus lenvatinib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma appear to be ‘promising’ in the phase 3 LEAP-002 trial.
Results from the phase 3 CheckMate-8HW trial highlight that the safety of frontline nivolumab plus ipilimumab in microsatellite instability–high or mismatch repair deficient is comparable with prior reports.
Real-world data may elucidate the characteristics and factors that influence long-term remission with regorafenib among patients with metastatic colorectal cancer.
Data from the phase 3 NETTER-2 trial support the frontline use of Lutetium Lu 77 dotatate well-differentiated gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.
Data from the phase 2 NAVIGATE trial support the wider adoption of next-generation sequencing panels including NTRK gene fusions in the treatment of those with gastrointestinal cancers.
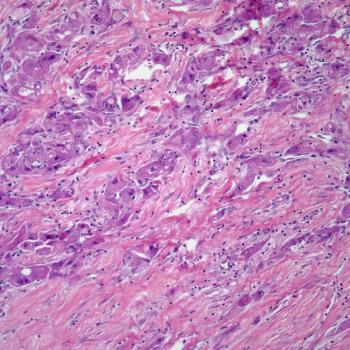
Durvalumab plus bevacizumab and TACE may be a new standard of care in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma eligible for embolization, according to Riccardo Lencioni, MD.
Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and Child-Pugh-B liver function appear to have worse overall survival following treatment with regorafenib in the REFINE trial.
Treatment-emergent adverse effects following therapy with fostrox plus lenvatinib among those with hepatocellular carcinoma appear to be manageable in a phase 1a/2a study.
Investigators observe a benefit with durvalumab plus neoadjuvant chemotherapy among subgroups of patients regardless of microsatellite instability status in the phase 3 MATTERHORN trial.
Findings from the phase 3 FRESCO-2 trial support fruquintinib’s potential to provide an improved survival benefit and quality of life for those with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer.
The DeFianCe trial is using DKN-01 plus bevacizumab and chemotherapy to determine if a clinical benefit would occur in patients with microsatellite stable colorectal adenocarcinoma.
Data from the phase 3 SKYSCRAPER-08 trial may support tiragolumab plus atezolizumab and chemotherapy as an alternative frontline treatment option for those with locally advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Neoadjuvant camrelizumab plus chemotherapy may hold promise as a standard of care in locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, according to Yin Li, MD.
Combining ASKB589 with capecitabine, capecitabine, and sintilimab leads to no treatment discontinuation due to adverse effects among patients with gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer in a phase 1/2 trial.
In the overall population and in patients with a PD-L1 CPS of 5 or greater who received nivolumab plus chemotherapy, overall survival and progression-free survival improved when compared with chemotherapy alone.
Results from an observational study found nivolumab plus chemotherapy helped enhance overall survival and progression-free survival for patients with advanced or metastatic gastric cancer, gastroesophageal junction cancer, or esophageal adenocarcinoma.
An overview of NRG1 fusion–positive tumors was given by experts in the gastrointestinal and lung cancer space in a recent Frontline Forum.
Sugemalimab is now approved for managing esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in China following results from the phase 3 GEMSTONE-304 study.
Investigators indicate that, although treatment with adjuvant/neoadjuvant pembrolizumab results in an absolute decrease in risk of an event, the benefit was not statistically significant in those with untreated, locally advanced gastric/GEJ cancer.

In Europe, pembrolizumab is now available as a treatment in combination with fluoropyrimidine-/platinum-containing chemotherapy for HER2-negative gastric or GEJ adenocarcinoma, as well as in combination with gemcitabine/cisplatin for locally advanced biliary tract carcinoma.

First-line pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy has been approved by the FDA for patients with HER2-negative gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma.

Approval of PD-L1 IHC 22C3 pharmDx may also identify patients with non–small cell lung cancer and other malignancies who may benefit from treatment with pembrolizumab.

Only patients with PD-L1–positive tumors may receive treatment with pembrolizumab plus trastuzumab and chemotherapy for HER2-positive gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma following the FDA’s amendment.