
Eric Singhi, MD, joins the Oncology Brothers, Rahul Gosain, MD, and Rohit Gosain, MD, to discuss the treatment algorithm for patients with limited-stage small cell lung cancer (SCLC), highlighting the ADRIATIC study.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Eric Singhi, MD, joins the Oncology Brothers, Rahul Gosain, MD, and Rohit Gosain, MD, to discuss the treatment algorithm for patients with limited-stage small cell lung cancer (SCLC), highlighting the ADRIATIC study.

The phase 2 DELLphi-301 trial showed durable response rates when tarlatamab was used to treat extensive-stage small cell lung cancer.
Treatment with SNB-101 previously demonstrated tolerability among patients with solid tumors in a phase 1 trial.

Treatment with durvalumab raises no new safety signals among patients with limited-stage small cell lung cancer in the phase 3 ADRIATIC trial.

Practices are on the cusp of better understanding small cell lung cancer that in turn can help to advance treatment strategies for patients, says Gregory Peter Kalemkerian, MD.

The use of novel agents like tarlatamab may be “interesting” among patients with small cell lung cancer in the relapsed setting, says Gregory Peter Kalemkerian, MD.

Prophylactic cranial irradiation may not be worthwhile for treating patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer based on conflicting data, according to Gregory Peter Kalemkerian, MD.

FDA-approved immunotherapy options such as atezolizumab and durvalumab have produced substantial benefits in certain groups of patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer, says Gregory Peter Kalemkerian, MD.
A post hoc analysis of lurbinectedin showed an improvement in the overall response rate compared with topotecan for patients with small cell lung cancer.
The FDA sets a Prescription Drug User Fee Act date of June 12, 2024, for tarlatamab as a therapy for patients with advanced small cell lung cancer.
Investigators are assessing BI 764532 in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer and other neuroendocrine carcinoma as part of the phase 2 DAREON-5 study.

Findings from the phase 3 SKYSCRAPER-02 trial support outcomes following atezolizumab plus chemotherapy for patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer.
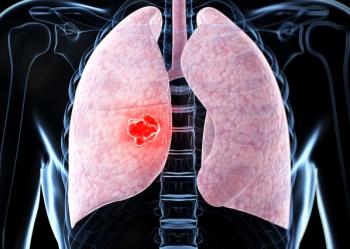
Patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer who receive trilaciclib appear to experience lower rates of hematologic adverse effects than those who are not treated with the agent.
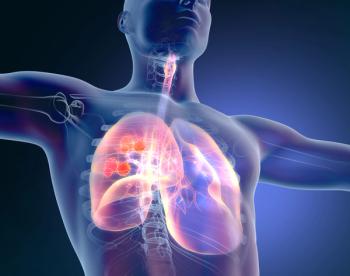
The phase 2 TROPiCS-03 trial helped elicit responses and disease control in patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer who received second-line sacituzumab govitecan.
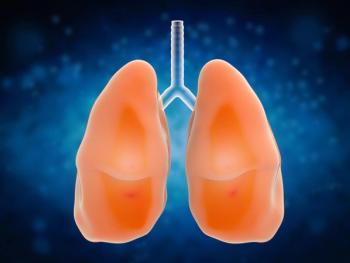
Tarlatamab may represent a new immunotherapeutic approach for patients with small cell lung cancer, according to the investigators of the phase 2 DeLLphi-301 trial.
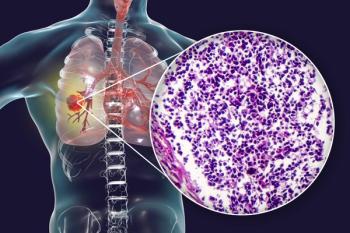
Developers plan to assess onvansertib plus standard of care as a frontline treatment for patients with metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in an investigator-initiated trial.
Data from a phase 1 trial highlight a clinically acceptable safety profile for BI 764532 in patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer and extrapulmonary neuroendocrine carcinomas.
Alisertib will be assessed in patients with small cell lung cancer as part of the phase 2 Study PUMA-ALI-4201.

Treatment with BI 764532 produces a manageable safety profile among those with small cell lung cancer and neuroendocrine carcinoma in a phase 1 trial.
Benmelstobart plus anlotinib and chemotherapy produce survival benefits in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer across all patient subgroups in the phase 3 ETER701 trial.
Investigators of the phase 1/2 Acclaim-3 trial will assess quaratusugene ozeplasmid in combination with atezolizumab as a treatment for those with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer.

Findings from the CROSS-FIRE study may inform individualized decision-making regarding stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with small cell lung cancer, according to Chad Rusthoven, MD.
The reduction of hematologic adverse effects with trilaciclib may improve clinical outcomes in patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer, according to Jerome Goldschmidt, MD.

Thoracic radiotherapy appears to be tolerable and effective in a real-world cohort of patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer.

Findings from a retrospective review suggest that stereotactic radiosurgery alone may be an effective option vs whole brain radiation therapy among those with small cell lung cancer with brain metastases.