Patients with triple-negative breast cancer experienced improved pathologic complete responses with the addition of neoadjuvant atezolizumab to chemotherapy.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Patients with triple-negative breast cancer experienced improved pathologic complete responses with the addition of neoadjuvant atezolizumab to chemotherapy.
The PARP inhibitor reduced the risk for death by 31% in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, compared with enzalutamide or abiraterone plus prednisone.
First-line treatment with the third-generation ALK TKI was also associated with higher overall and intracranial response rates in patients with ALK-positive non–small cell lung cancer.
“Dostarlimab demonstrated durable antitumor activity in both dMMR and MMRp advanced and recurrent endometrial cancer,” said Ana Oaknin, MD, PhD.
Sacituzumab govitecan-hziy induced significant activity with favorable tolerability in heavily pretreated patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma.
Data for the phase 3 COMBI-i trial showed that spartalizumab combined with dabrafenib and trametinib did not meet its primary end xpoint of investigator-assessed progression-free survival.
Frontline pembrolizumab induced clinically meaningful improvements in the health-related quality of life of patients with microsatellite instability-high and/or mismatch repair-deficient metastatic colorectal cancer.
Durvalumab, with or without tremelimumab, failed to meet its primary end point of overall survival in patients with metastatic urothelial cancer.
The combination use of nivolumab plus ipilimumab, compared with sunitinib, continued to show benefit during a 4-year follow-up in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.
“PD-L1 expression was significantly associated with pCR, which increased with higher PD-L1 expression on immune cells,” said Giampaolo Bianchini, an author of the NeoTRIPaPDL1 study.
“With expanding options for patients with advanced RCC, the overall efficacy, safety, and quality of life benefits, as well as individual patient characteristics, are very important considerations when you select appropriate therapy.”
The first-in-class inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) antagonist significantly improved overall survival in patients with LA-SCCHN.
Induction avelumab prior to standard of care led to a clinically relevant worsening of survival as the first-line treatment for patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma.
Cemiplimab demonstrated an objective response rate of 31% in patients with locally advanced basal cell carcinoma who progress on or are intolerant to hedgehog inhibitors.
A new combination may be key to improving tumor response rates and overall survival in colorectal cancer.
Despite prolonged progression-free duration, a 25% reduction in risk of death associated with anti-androgen agent apalutamide fell short of statistical significance in patients with non-metastatic, high-risk castration-resistant prostate cancer.
The findings of a trial presented at ESMO 2019 may be a breakthrough when it comes to molecularly targeted treatment for prostate cancer.
The findings of a new study presented at ESMO may offer a new treatment for non–small cell lung cancer.
Extended follow-up from the CheckMate 032 trial showed strong results with three different immunotherapy regimens involving nivolumab and ipilimumab in patients with previously treated metastatic urothelial carcinoma.
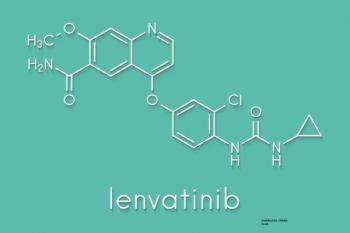
Lenvatinib offers the highest published response rate to a targeted agent for patients with advanced neuroendocrine tumors, but the agent’s precise role in this setting remains in question.
In general, NETs are considered an “immunological desert,” but a new study showed some promise for immunotherapy.

Many lung cancer patients may be unaware of the potential benefits of exercise.
Previous research showed that gefitinib can improve DFS in certain NSCLC patients, raising the possibility that EGFR-targeted TKIs could be beneficial in the neoadjuvant setting.

The combo showed improvement in disease-free survival over tamoxifen in premenopausal patients with hormone receptor (HR)-positive early breast cancer.

Researchers compared the cost effectiveness of two durations of trastuzumab in HER2+ breast cancer patients.
The SOLAR-1 trial tested whether the PI3K inhibitor alpelisib improved outcomes in HR+, HER2− breast cancer patients.

A subgroup analysis of Short-HER looked at the differences in 5-year DFS rates for 9 weeks vs 1 year of trastuzumab for HER2+ breast cancer patients.
Researchers tested whether combining chemotherapy with immunotherapy would offer improved survival for patients with triple-negative breast cancer.
Researchers tested whether immunotherapy could be safely used in HIV-positive patients with cancer.
Researchers tested whether 2 years of maintenance therapy with olaparib would improve outcomes in advanced ovarian cancer patients.