Researchers conducted the QUADRA trial to examine if niraparib could improve outcomes in heavily pretreated patients with ovarian cancer.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Researchers conducted the QUADRA trial to examine if niraparib could improve outcomes in heavily pretreated patients with ovarian cancer.
In this study, researchers aimed to further characterize differences in hospice use in a cohort of ovarian cancer patients.
The results of a post-hoc exploratory analysis of the phase III ARIEL3 trial were promising.
The TWiST analysis of the phase III ENGOT-OV16/NOVA trial evaluated the time without symptoms or toxicity for niraparib vs placebo in patients with recurrent ovarian cancer.
The phase II trial evaluated dendritic cell–based immunotherapy with concomitant administration of chemotherapy vs chemotherapy alone.
A randomized trial tested whether lymphadenectomy would improve survival outcomes in patients with advanced ovarian cancer.
Results of a phase II trial evaluating pembrolizumab in combination with bevacizumab and oral metronomic cyclophosphamide were presented at SGO 2019.
Avelumab alone or with pegylated liposomal doxorubicin did not improve survival in this phase III trial, but a subgroup analysis showed promising findings.
Early results of the WISP trial, which is evaluating risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy vs salpingectomy with delayed oophorectomy, were presented in Honolulu.

A score derived from CT imaging using a machine learning radiomics approach was able to reliably identify epithelial ovarian cancer patients with poor survival outcomes.
Researchers tested whether conservative management of adnexal masses classified as benign could lead to subsequent malignant ovarian cancer.
Two new studies found that targeting the cyclin-dependent kinases 4/6 exposed a vulnerability in SMARCA4-deficient cancers.
Researchers studied how the anti–PD-L1 agent avelumab fit into the recurrent and refractory ovarian cancer treatment landscape.

A large study looked at previously confirmed and newly discovered associations between several genes and breast cancer and ovarian cancer risk.

This study was the first in a large, unselected population to assess ovarian mass appearance and the connection to ovarian cancer risk.

In this new study involving a mouse model of ovarian cancer, researchers evaluated the effects of entinostat on adaptive immune responses.

A screening study that began more than 30 years ago looked at ultrasound screening for at-risk women for ovarian cancer and its effects on disease-specific survival.
A pooled analysis of two randomized trials found that neoadjuvant chemotherapy and upfront debulking surgery yield similar outcomes in patients with advanced tubo-ovarian cancer, except in some settings.
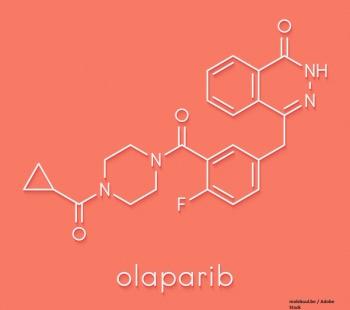
Researchers tested whether 2 years of maintenance therapy with olaparib would improve outcomes in advanced ovarian cancer patients.

Regular users of low-dose aspirin appear to have a reduced risk of developing ovarian cancer, according to a new study.
A study shows that combined hormonal contraceptive use is associated with a significant reduction in the risk of ovarian cancer.
A new proteomic analysis found that CT45 is an independent prognostic factor in patients with high-grade serous ovarian cancer, and a potential target of immunotherapies.
Certain malignancies may possess a common and targetable matrix response, which affects disease pathogeneis, according to a study in Cancer Discovery.

Dr. Dmitriy Zamarin speaks with Cancer Network about the findings of a phase II trial in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer patients.
New research examines the mechanisms underlying why most patients with high-grade serous ovarian cancer develop resistance to PARP inhibitors.