Researchers are hoping that adding a checkpoint inhibitor to the treatment armamentarium may help improve outcomes in patients with locally advanced or metastatic disease epithelial ovarian cancer.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Researchers are hoping that adding a checkpoint inhibitor to the treatment armamentarium may help improve outcomes in patients with locally advanced or metastatic disease epithelial ovarian cancer.

A large, prospective analysis showed that risk factors for ovarian cancer demonstrate substantial heterogeneity in their associations with histologic subtypes of the disease.

In this video Dr. Odunsi discusses a new study that found that higher T-cell diversity in ovarian cancer is associated with poor overall survival.

Despite hematologic toxicities and port-related adverse events, IP carboplatin plus IV dose-dense paclitaxel appears to be effective in patients with suboptimally debulked epithelial ovarian or primary peritoneal carcinoma.

Extending platinum-free interval with pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, topotecan, or gemcitabine does not improve overall survival among patients with recurrent ovarian cancer.

Baseline quality of life measures predict early cessation of chemotherapy and overall survival in women with platinum-resistant/refractory, recurrent ovarian cancer.

Hormone maintenance therapy is associated with better survival than post-treatment surveillance for women with low-grade serous carcinoma of the ovary or peritoneum.

Among women previously treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by debulking surgery for advanced epithelial ovarian cancer, adding intraperitoneal to intravenous administration of postsurgical chemotherapy appears to be associated with a lower rate of disease progression.

NEW ORLEANS – A new type of antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) platform may pave the way to help patients with ovarian cancer and non-small cell lung cancer.

Combining three markers of homologous recombination deficiency into a single score may improve treatment decisions for women with ovarian cancer, according to a study reported at the 2016 SGO Annual Meeting.

Assignment to a dose-dense regimen of paclitaxel given weekly did not prolong progression-free survival compared with paclitaxel given every 3 weeks in a group of patients with ovarian cancer treated with or without bevacizumab.
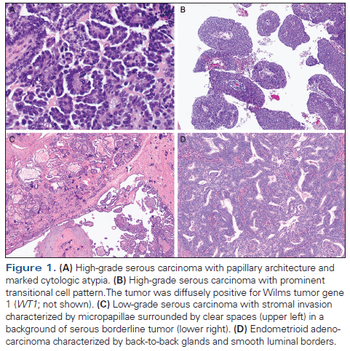
This review focuses on the clinicopathologic and molecular features of epithelial ovarian cancer, with specific attention to genetic predisposition, morphologic challenges, immunohistochemistry, and molecular features.

The movement of ovarian carcinoma histotypes from ill-defined and poorly reproducible clusters of cases to distinct disease entities clearly has beneficial implications for patient management.

A mouse study found that resveratrol has a significant antitumor effect in an ovarian cancer model, and also suppressed tumor regrowth following cisplatin.

Women older than 70 received less treatment for ovarian cancer than did their younger counterparts, according to the results of a single-center French study.

Women with chemotherapy-naive advanced ovarian cancer gained significant delays in the progression of their disease when adding nintedanib to carboplatin/paclitaxel.

A study in Great Britain found that women diagnosed with female factor infertility were at an increased risk for ovarian cancer.

Muscle attenuation assessed with preoperative CT was an independent prognostic marker in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer.

A new study at a single center in Japan found no significant differences in the rate of BRCA mutations between ovarian cancer patients with or without family histories of the mutations and recommends that BRCA1/2 testing be required for all ovarian cancer patients

A recent study that gave hormone therapy to ovarian cancer patients with severe menopausal symptoms revealed that the treatment had a beneficial survival effect.

Here we discuss the advantages and pitfalls of HIPEC in advanced ovarian cancer, as well as current data and ongoing prospective trials.

The evidence suggests that few centers offer IP therapy routinely. Why? The answer may be that oncologists simply don’t know what to do. There have been three completely distinct regimens, none of which has been used in the outpatient setting.

Based on the currently available scientific evidence, HIPEC should not be considered a standard therapeutic option after optimal cytoreduction in advanced ovarian cancer, nor should it be offered outside of a clinical trial.

A small study showed that treatment with the anti-PD-1 immunotherapy nivolumab was able to produce complete responses in patients with advanced platinum-resistant ovarian cancer.

Beta-blockers were associated with increased overall survival in women with epithelial ovarian cancer, according to a retrospective study.