
Researchers have found that tumors with multiple cancer genomes and the downregulation of the LRP1B gene are associated with chemotherapy resistance among patients with the high-grade serous ovarian cancer.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Researchers have found that tumors with multiple cancer genomes and the downregulation of the LRP1B gene are associated with chemotherapy resistance among patients with the high-grade serous ovarian cancer.

CancerNetwork speaks with Dr. Sara Hurvitz, director of the breast cancer program at the University of California in Los Angeles. Dr. Hurvitz is actively involved in translational phase I/II breast cancer clinical trials as well as in research to better define distinct types of breast tumors to better design novel targeted therapies.

The proposition that a consumer smartphone could somehow become part of the diagnostic toolkit of an oncologist may seem ridiculous. There are, however, many researchers and start-ups that would disagree.

Schrader and colleagues provide four compelling examples of the power of genetic testing to impact medical management for probands and their family members.

In this article, we use a case-based approach to focus on the hereditary aspects of the most common GI cancers, including pancreatic, gastric, and colon cancer.

In this review, we will present the current data on commercially available molecular profiling assays in breast cancer and discuss the challenges surrounding their incorporation into routine clinical practice as prognostic and predictive tools.
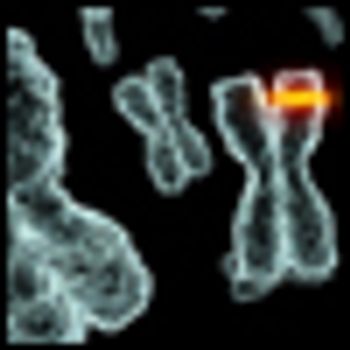
A study published today details a scoring system that may predict which ovarian cancer patients responded to first-line platinum chemotherapy based on a DNA-repair pathway-focused score. The score is based on a gene expression profile of 23 DNA-repair genes that normally function to repair platinum-induced DNA damage.

Selumetinib, a small-molecule MEK inhibitor, controlled recurrent low-grade serous ovarian cancer in 81% of patients treated. Current first-line defense against this disease (surgery followed by cytotoxic chemotherapy) has met with limited success.
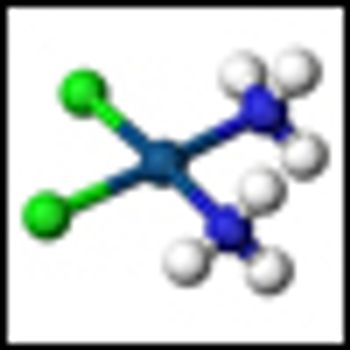
Researchers have identified a marker of DNA damage that may be able to predict a patient’s response to platinum-based chemotherapy agents such as cisplatin and carboplatin.

Cancer Network interviews two prominent ovarian cancer researchers from both sides of the Atlantic on the role of PARP inhibitors and the challenges of developing ovarian cancer therapies.

Following a large survey of more than 22,000 US women, researchers from H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center, in Tampa, Florida, have concluded that a significant proportion of female cancer survivors have poor health behaviors, compared with women who have not had cancer.

This article reviews the trials that have been conducted with PARP inhibitors in epithelial ovarian cancer, fallopian tube cancer, and primary peritoneal cancer, and places the impact of those results in the larger context of PARP inhibitor development.

Four publications on cancer treatment during pregnancy were published last week in the journal Lancet, serving as new treatment guidelines for chemotherapy and surgery in pregnant patients with solid tumors and hematologic malignancies.

The development of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors as a new class of anticancer agents has created a tremendous amount of hope in the ovarian cancer community, especially in the high-risk, difficult-to-screen, hereditary ovarian cancer population.

Ovarian cancers account for more than 50% of gynecologic cancer deaths. This is attributable to the late stage of the disease at diagnosis.

Tanner et al provide a concise review of lung cancer screening, including discussion of past failed attempts, the success of the National Lung Screening Trial (NLST), and promising new avenues for improving on the NLST results.

A new study has made a step forward toward better characterization of sporadic ovarian tumors by identifying their DNA repair protein expression profile.

The past year in oncology was highlighted by the continuation of breakthroughs in targeted therapies-with new treatments receiving US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for non–small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), lymphoma, and melanoma.

Coffee is emerging as a protective agent against a number of diseases, including cancer. A study published last week shows that women who drank more than four cups of coffee per day cut their risk of endometrial cancer by 25% compared with those who drank less than one cup per day.

The US Food and Drug Administration announced today that it has revoked the approval of bevacizumab for breast cancer due to the potentially life-threatening side effects associated with the treatment. It was approved for metastatic breast cancer in February 2008, but data later showed that along with an increase in side effects, there was no increase in overall survival.
Breast and ovarian cancer patients with limited tumor burden and minimal prior chemotherapy appear to have benefited from a novel vaccine.

In September 2011, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved marketing of the HE4 Test (Fujirebio Diagnostics, Malvern, Pennsylvania) along with the CA-125 test in the Risk of Ovarian Malignancy Algorithm, called ROMA, to determine the likelihood of finding malignancy at surgery in premenopausal or postmenopausal women presenting with an ovarian adnexal mass.

Counseling women at high risk for ovarian and uterine cancer is a complex process, from genetic diagnosisto the management of at-risk women. Rimes andcolleagues have presented these challenging issues, andsuggested ways to manage them, very well.

Patient education and counseling are essential in women at increased risk for ovarian and endometrial cancer. Women must be educated regarding the signs, symptoms, and risks associated with these cancers.

The aim of this article is to review the preclinical data and rationale for PARP inhibitor use in the aforementioned settings, as well as the current status of the clinical development of these agents in the treatment of breast cancer, along with future directions for research in this field.