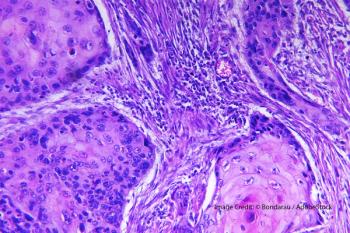
Researchers evaluated whether treatment with calcipotriol plus 5-fluorouracil aided in reducing the risk of squamous cell carcinoma.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Researchers evaluated whether treatment with calcipotriol plus 5-fluorouracil aided in reducing the risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
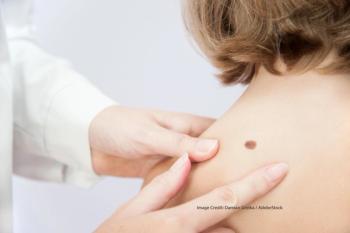
The association between the presence of several viruses and non-melanoma skin cancer was investigated in a recent study.

Cancer Network spoke with Ryan J. Sullivan, MD, about the efficacy and safety of entinostat plus pembrolizumab in patients previously treated with immunotherapy.

A review published in Experimental Dermatology examined the safety and efficacy of nicotinamide in reducing non-melanoma skin cancers.
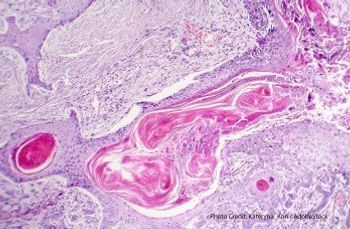
Survival rates in patients with cSCC receiving high-dose chemoradiotherapy vs conventional radical surgery were compared.
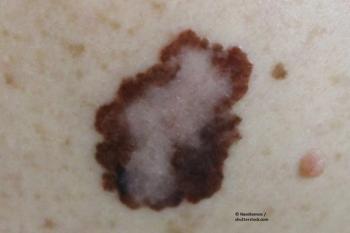
The CheckMate 511 phase IIIb/IV trial investigated raising the nivolumab dose to 3 mg/kg and lowering the ipilimumab dose to 1 mg/kg.
A recent review article highlighted developments in the treatment of non-melanoma skin cancers, from new chemoprevention agents to telemedicine.

A new meta-analysis offers compelling evidence on the causal relationship between indoor tanning and skin cancer risk.

The findings of a systematic review may help standardize reflectance confocal microscopy terminology, which is used to describe non-melanocytic lesions.
Researchers studied whether the mechanistic target of mTORC2 directs UVB–induced apoptosis by regulating the expression of NOXA downstream of FOXO3a.

Cancer Network speaks with Dr. Ryan J. Sullivan about adjuvant therapies in development for melanoma patients.
A new study in Cancer Research evaluated the function of TRIM29 in regulating keratin distribution and migration/invasion of SCC.

Researchers evaluated the efficacy of 5-florouracil vs imiquimod in preventing site-specific keratinocyte carcinoma.
A recent study examined the literature on whether immune checkpoint molecules improve overall survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma.

Guy Ben-Betzalel, MD spoke with Cancer Network about the emerging role of targeted BRAF+MEK inhibition in antitumor immunity.
Investigators shared results of an interim analysis evaluating antitumor activity and safety in patients with mMCC receiving avelumab monotherapy.

The American Academy of Dermatology published new clinical practice guidelines with recommendations for the treatment of primary cutaneous melanoma.
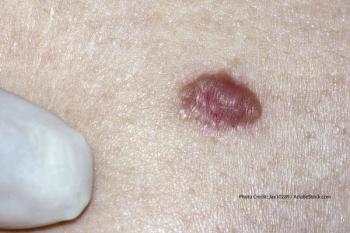
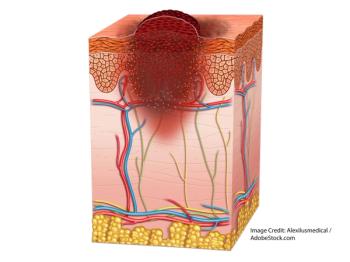
Cemiplimab (Libtayo), approved for advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, is intended for those not eligible for curative surgery or radiation.
The percentage of patients with pediatric melanoma is 6-fold to the 28-fold higher when compared with the general population of patients with melanoma.
The combination of encorafenib and binimetinib resulted in longer overall survival compared with vemurafenib in patients with BRAF V600–mutant melanoma.

In this article, we review the role of baseline tumor size in response and survival on traditional and contemporary therapies for the treatment of locoregional and distant melanoma recurrences.
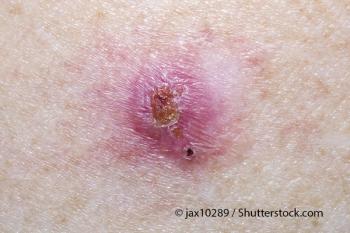
Individuals who develop frequent basal cell carcinomas may have an increased prevalence of germline mutations in DNA repair genes and an increased malignancy risk.
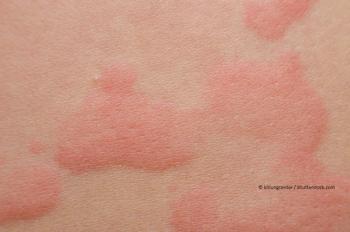
Mogamulizumab (Poteligeo) is indicated for relapsed or refractory mycosis fungoides or Sézary syndrome following at least one prior systemic therapy.
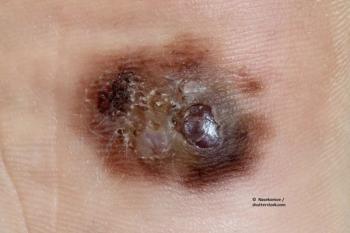
The combination of pembrolizumab and a TLR9 agonist known as SD-101 showed promising activity in patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma.