
The US Preventive Services Task Force recently issued an updated statement recommending against screening for thyroid cancer in asymptomatic adults.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


The US Preventive Services Task Force recently issued an updated statement recommending against screening for thyroid cancer in asymptomatic adults.

In this interview we discuss a study that found that survivors of thyroid cancer diagnosed with the disease at a young age had an increased risk of late effects from therapy.

Preoperative testing of thyroid nodules for RAS mutations showed that nodules that tested positive for HRAS and NRAS were associated with a substantial risk for cancer.

Patient age was found to be significantly associated with mortality from papillary thyroid cancer in a linear fashion with no apparent age cut point.

Undergoing a lobectomy for thyroid nodules suspicious for papillary thyroid cancer on fine-needle aspiration was more cost effective and was associated with greater effectiveness compared with total thyroidectomy.

Identifying certain characteristics of BRAF-positive and RAS-positive thyroid cancers may help define a molecular profile for the disease.

Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center’s experience shows that selected patients with low-risk papillary thyroid cancer can safely defer surgery in favor of active surveillance.

In this interview we discuss which distant metastases in thyroid cancer are appropriate targets for I-131 treatment, appropriate dosing, and more.

Dual inhibition of PI3K signaling and histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) enzymes with CUDC-907 slowed thyroid tumor cell proliferation, tumor progression and metastasis, according to a preclinical study.

Mitochondrial glycerophosphate dehydrogenase (mGPDH) is overexpressed in differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) tissue, and metformin, which downregulates mGPDH, is associated with slowed growth in metastatic DTC tumors in mice.

The risk of immunotherapy-related destructive thyroiditis requires close patient monitoring and can cause permanent hypothyroidism.

Five years after treatment, low-dose postsurgical radioiodine (I-131) ablation for low-risk thyroid cancer offers outcomes equivalent to those seen following higher-dose ablation, according to a long-term follow-up analysis by French researchers.

As part of our coverage of the 2016 American Thyroid Association Annual Meeting we discuss active surveillance vs immediate lobectomy or thyroidectomy in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma.

A MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry (MassARRAY) mutation-detection panel shows promise for improving the presurgical diagnosis of thyroid cancers with fine needle aspirations, according to a pilot study.

In this interview on medullary thyroid carcinoma we discuss treatment strategies, prognostic biomarkers, surveillance following treatment, and more.
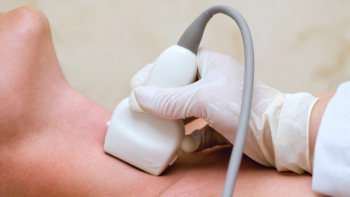
High-risk ultrasound findings strongly indicate that thyroid nodules are malignant, even when nodules are cytologically indeterminate following find needle aspiration.

Researchers have established estimates of occult nodal disease risk in patients after surgery for papillary thyroid cancer, using primary tumor stage and the number of lymph nodes examined.

Results of a phase II study indicated that the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib was active in patients with BRAF V600E–mutated papillary thyroid cancer who were refractory to radioactive iodine.

Radioguided sentinel lymph node biopsy detected occult cervical lymph node metastases in about one-half of patients with thyroid nodules suspicious for papillary thyroid carcinoma, altering the management of their disease.

The multi-target RTK inhibitor anlotinib yielded a high response rate and was well tolerated in patients with advanced medullary thyroid carcinoma.

The addition of lenalidomide to cediranib failed to improve progression-free survival outcomes in patients with iodine 131–refractory differentiated thyroid cancer.

This management guide of endocrine malignancies covers the risk factors, diagnosis, screening, and treatment of both thyroid and parathyroid cancers.
Selumetinib has received Orphan Drug Designation status by the US Food and Drug Administration to be used as an adjuvant treatment in patients with stage III or IV differentiated thyroid cancer.

A new study is calling for a change in name for certain thyroid tumors. Patients diagnosed with what is currently known as noninvasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma have a very low risk for recurrence and therefore, researchers have suggested renaming the condition.
Despite a large increase in the diagnosis of thyroid cancer during the last few decades, a new study indicates that thyroid cancer incidence may be leveling off.