Results from phase 1 of the RAMP 201 study shows efficacy in treating patients with recurrent low-grade serous ovarian cancer with avutometinib plus defactinib, regardless of previous treatment.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Results from phase 1 of the RAMP 201 study shows efficacy in treating patients with recurrent low-grade serous ovarian cancer with avutometinib plus defactinib, regardless of previous treatment.
Docetaxel plus standard of care may be beneficial among patients with prostate cancer and low prostate-specific antigen levels who do not have any highly effective treatment options, says Anthony D’ Amico, MD, PhD.
The partial clinical hold on a phase 1 study assessing NX-2127 in those with B-cell malignancies comes after the developer communicated intent to the FDA to move to a different manufacturing process.

The Hispanic Breast Cancer Clinic at Northwestern Memorial Hospital includes a social worker, nurse practitioners, a medical oncologist, a radiation oncologist, and surgeons, says Claudia Tellez, MD.

The goal of creating the Hispanic Breast Cancer Clinic at Northwestern Memorial Hospital is to establish a safe space for Hispanic patients, says Claudia Tellez, MD.
Preliminary overall survival data with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and chemotherapy in recurrent ovarian cancer in the phase 3 ATALANTE trial appear to warrant further analysis.
Investigators are assessing rhenium obisbemeda as a treatment for breast cancer harboring leptomeningeal metastases as part of the phase 1/2a ReSPECT-LM trial.
Data from a phase 2 trial support lenalidomide plus rituximab as a novel treatment strategy for patients with previously untreated mantle cell lymphoma.

Several factors may contribute to the low Hispanic breast cancer population at Northwestern Memorial Hospital, including a lack of resources and a focus on other disease types.
Results from the phase 2 THIO-101 trial demonstrate disease control in all 19 patients with non–small cell lung cancer who received second-line THIO plus cemiplimab.
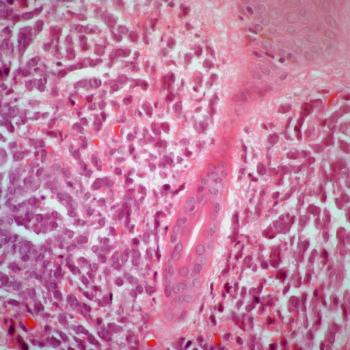
Adding all-trans retinoic acid to chemotherapy does not appear to improve complete remission rates compared with chemotherapy alone in patients with NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia.
Survival following relapse appears to be shorter in patients with stage III colon cancer harboring KRAS exon 2 and BRAF V600E mutations regardless of microsatellite stability status.
Patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer who receive trilaciclib appear to experience lower rates of hematologic adverse effects than those who are not treated with the agent.
Treatment with dostarlimab plus chemotherapy followed by dostarlimab appears to improve outcomes among patients with advanced endometrial cancer and mismatch repair deficient disease in the phase 3 RUBY trial.
Data from a retrospective study spotlight a need for more effective first-line and second-line clinical management strategies to improve outcomes in patients with lower-risk myelodysplastic syndrome.

Data from a systematic review highlight a significantly higher risk of any bleeding and major bleeding in patients with treatment-naïve chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with a second generation Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
More than half of resected patients with muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma achieve a pathologic response with durvalumab plus neoadjuvant cisplatin/gemcitabine in the phase 2 SAKK 06/17 trial.

Financial constraints and a lack of education among some patients and providers must be addressed to improve the real-world use of certain prostate cancer therapies, says Neeraj Agarwal, MD.

Investigators of the phase 3 KEYNOTE-671 trial identify no new safety signals with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in those with early-stage non–small cell lung cancer.

Collaboration among surgical specialties allows for safe removal of all visible tumors, thus improving survival in patients with advanced ovarian cancer, says Donal J. Brennan, MB, PhD.
Results from a phase 1 of study of 177Lu-PSMA-617 in combination with pembrolizumab show significant anti-tumor activity with low toxicity in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.

Results from the phase 3 KEYNOTE-966 trial led to the approval of pembrolizumab plus gemcitabine and cisplatin for patients with locally advanced unresectable or metastatic biliary tract cancer.
With the announcement that the supply of 177Lu vipivotidete traxetanis now unconstrained, the targeted radioligand will be available in over 200 centers for patients with prostate cancer.

The FDA has set a Prescription Drug User Fee Act date of April 30, 2024 for tovorafenib as a treatment for pediatric patients with relapsed or progressive low-grade glioma.
Mirvetuximab soravtansine-gynx may have the potential to become a new standard for patients with folate receptor α–positive, platinum-resistant ovarian cancer, experts say.

Novel anti-PSMA monoclonal antibody rosopatamab is capable of carrying a bigger payload of radiation particles, which may potentially reduce doses for patients with prostate cancer, says Neeraj Agarwal, MD.
Patients with breast cancer harboring BRCA1/2 mutations appear to be more likely to undergo mastectomies than those without, according to Zachary Kiss, DO.

Rebecca M. Shulman, MD, and Zachary Kiss, DO, discuss findings from a study evaluating differences in outcomes with radiotherapy and disease characteristics of patients with breast cancer harboring BRCA mutations compared with those without mutated disease.
Data from the phase 3 MIRASOL trial support the European marketing authorization application for mirvetuximab soravtansine as a treatment for folate receptor α–positive, platinum-resistant ovarian cancer.
The regulatory agency has set a Prescription Drug User Fee Act date of April 23, 2024 for N-803 plus BCG as a treatment for BCG-unresponsive, non–muscle invasive bladder carcinoma.