Francisco Castro-Alonso, MD, and colleagues describe the effects of the use of erdafitinib in a patient with metastatic urothelial bladder cancer.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Francisco Castro-Alonso, MD, and colleagues describe the effects of the use of erdafitinib in a patient with metastatic urothelial bladder cancer.
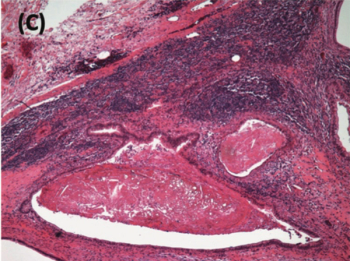
In this edition of Clinical Quandaries, Regina Barragan-Carrillo, MD, and colleagues present a case of an 18-year-old man who has a 1-month history of nonpainful right testicular enlargement.

In this side of the Point/Counterpoint, Drs. Bernard and Flaig state that genomic testing should be routine in the management of prostate cancer patients.

A 65-year-old man presented with locally advanced, high-risk prostate cancer. His medical history was remarkable for type 2 diabetes mellitus, and he was an active smoker with a 27 pack-year history.

In this review, we describe the historical data for chemotherapy in the perioperative and metastatic prostate cancer settings, and the recent trials that are changing the paradigm in support of docetaxel in the upfront setting.

While evidence points to benefit from highly active hormonal agents in prostate cancer with visceral involvement, the usefulness of immunotherapy is much less clear.
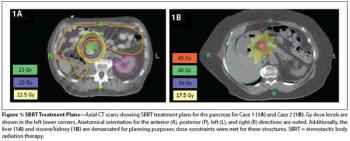
In this edition of our ongoing series, the authors present two cases involving renal cell carcinoma patients treated with SBRT for pancreatic metastases.

A 70-year-old, otherwise healthy man presented to his primary care provider for an annual checkup, at which time a nontender right testicular mass was noted. He denied any symptoms, and his serum alpha-fetoprotein and beta-human chorionic gonadotropin levels were normal.

With the emergence of several new agents for the treatment of advanced prostate cancer, new questions have arisen regarding the optimal sequence or combination of these agents. As we await the results of ongoing and planned clinical trials to answer some of these questions directly, the decision-making process will rely heavily on considerations of side effects and patient characteristics.
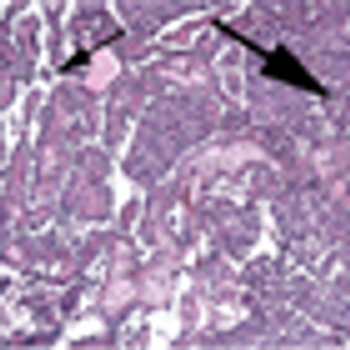
The patient is a 66-year-old male who presented to his primary care physician with a 3-week history of painless gross hematuria. He underwent a renal ultrasound that showed a left kidney mass.

We have entered a period of accelerated drug development and optimism in the care of advanced prostate cancer. The treatment paradigm for these patients is rapidly evolving, with future study needed to define the optimal sequencing and potential combinations of these new agents.

The patient is a 43-year-old man who was initially evaluated at an outside institution for unexplained anemia and who was found to have a large right kidney mass. He underwent a radical nephrectomy for a 19-cm large-cell, poorly differentiated neoplasm, consistent with pleomorphic, epithelioid angiomyolipoma (EAML) with extensive necrosis and cytologic atypia.

Prostate cancer will be diagnosed in one of six men during their lifetimes, and a small portion of these will progress after primary and salvage therapies. For many years, there were few treatment options for these patients after routine hormonal maneuvers, and standard of care since the early 2000s has consisted primarily of docetaxel, which improved survival over the previous first-line therapy mitoxantrone. In recent years, however, new therapies have begun to emerge to treat this devastating form of prostate cancer. This review examines the mechanisms behind these therapeutics and the key trials seeking to validate their clinical use.
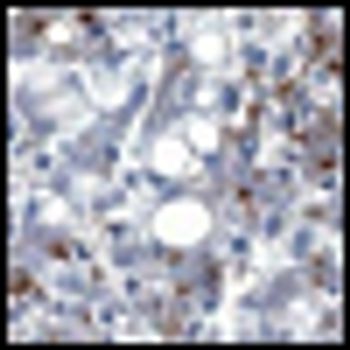
The patient is a 26-year-old woman with a complex oncologic history. At 1 year of age, she was diagnosed with a stage III abdominal neuroblastoma, which was treated, and again at age 9, she had a recurrence of neuroblastoma in the left axilla. She was in her usual state of good health until 18 months ago, when she presented with hematuria and was found to have a right-sided kidney mass.

A 56-year-old woman was referred to our institution for a left nephroureterectomy after the diagnoses of a nonfunctioning left kidney and noninvasive papillary urothelial carcinoma of the distal left ureter (Ta grade 1). Following the procedure, surveillance cystoscopy and computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen and pelvis demonstrated a large bladder tumor with pan-urothelial extension.
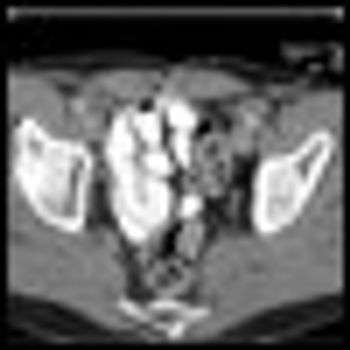
The patient is a 39-year-old man who presents with pelvic lymphadenopathy. He has a history of ureteral reflux disease, recurrent nephrolithiasis, right nephrectomy, ileal loop diversion of the left ureter, and radical cystectomy for “bladder cancer,” which he underwent 3 years ago. The lymphadenopathy was discovered incidentally during recent imaging.

The patient is a 39-year-old Caucasian male who presented with a right renal mass and painless gross hematuria. He underwent a right laparoscopic radical nephrectomy and the final pathology revealed a carcinoid tumor.
Published: December 17th 2021 | Updated:
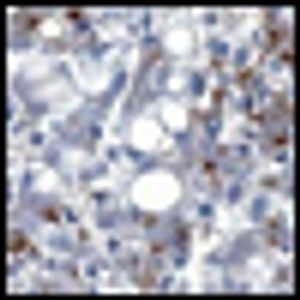
Published: March 22nd 2010 | Updated:
Published: February 19th 2009 | Updated:
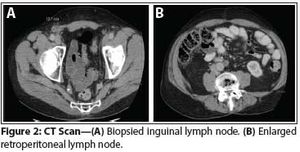
Published: March 15th 2014 | Updated:

Published: November 15th 2013 | Updated:
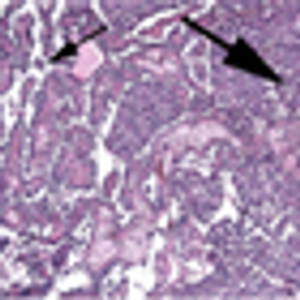
Published: September 15th 2013 | Updated: