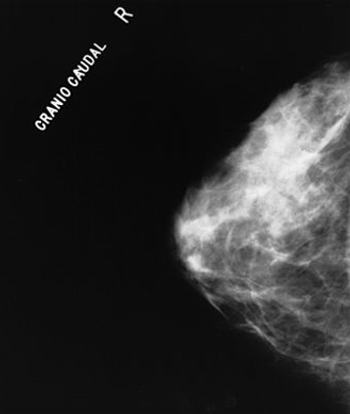
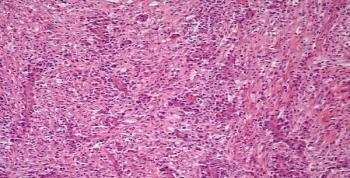
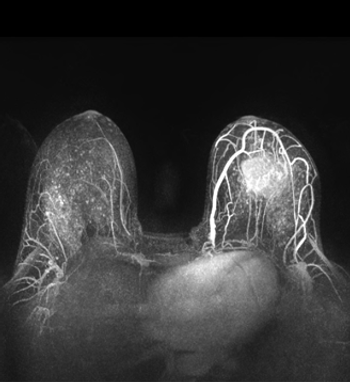
The biologic rationale for the initial evaluation of preoperative chemotherapy or neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with early-stage breast cancer was based on experimental and clinical observations regarding primary tumor cell growth and dissemination.