
We are speaking with Maximilian Diehn, MD, PhD, on developing genomics-based biomarkers to identify the presence of cancer cells for prognosis and predicting response to cancer therapies.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


We are speaking with Maximilian Diehn, MD, PhD, on developing genomics-based biomarkers to identify the presence of cancer cells for prognosis and predicting response to cancer therapies.

Two studies of the new HER2 selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor ONT-380 showed the drug has promising activity in HER2-positive breast cancer and especially in patients with central nervous system metastases.

T-DM1 improved survival in women with HER2-positive breast cancer, even after treatment with two or more other HER2-targeted therapies including trastuzumab and lapatinib.

Women with early-stage breast cancer treated with breast-conserving therapy had significantly improved 10-year overall survival compared with women who underwent mastectomy without radiation therapy.

A preclinical study looking at ER-positive breast cancer indicated that tamoxifen response was improved by reducing levels of the enzyme APOBEC3B and worsened by increasing levels of the enzyme.

Women with advanced endocrine-resistant breast cancer who had PIK3CA mutations in their circulating tumor DNA had an almost 4-month progression-free survival improvement when adding the PIK3CA inhibitor buparlisib to fulvestrant.

The addition of carboplatin to a neoadjuvant chemotherapy regimen resulted in improvements in disease-free survival for women with triple-negative breast cancer.

MRI can detect a larger tumor burden than detected by mammography alone, potentially changing treatment, according to a recently published study.

Among local treatment options for early breast cancer patients, mastectomy plus reconstruction has the highest rate of complications and is highest in cost.
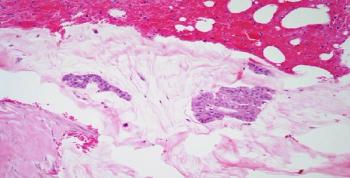
A 49-year-old woman is found to have a breast mass. After a biopsy is performed, what is your diagnosis?

The addition of denosumab to adjuvant hormonal therapy in postmenopausal breast cancer patients improves disease-free survival compared with placebo.

Patients with breast cancer who still had residual disease after undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy and surgery had improved survival outcomes with the addition of adjuvant capecitabine to standard treatment.

Premenopausal women with luminal A breast tumors received no benefit from treatment with adjuvant chemotherapy.

Breast cancer survivors with therapy-related leukemia were found to have personal and family histories that suggested an inherited risk for cancer.
Ahead of SABCS we discuss the biology and treatment of ductal carcinoma in situ, as well as research into prognostic indicators that could help guide treatment decisions.

Survival of women initially diagnosed with stage IV breast cancer has improved in the last 20 years, according to results of a retrospective cohort study.

Cancer survivors treated with anthracycline-based chemotherapies exhibited poorer performance of certain cognitive skills.
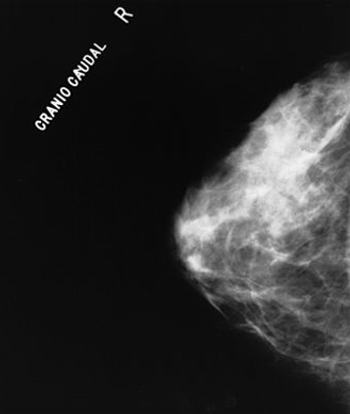
Women who previously had a false-positive mammogram or biopsy are at higher risk for developing breast cancer for at least 10 years, according to a new study.

In this interview we discuss the new American Cancer Society breast cancer screening guidelines and find out how they stack up with other recommendations for mammography screening.

Serum matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) and HER2 extra-cellular domain (HER2-ECD) might be predictive biomarkers for the metastasis of breast cancer to the brain, according to a case-control study.

Dual HER2 blockade with trastuzumab and lapatinib was no better than trastuzumab alone in producing pathologic complete responses in metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer patients in the neoadjuvant setting, according to a new study.
Researchers have developed a blood-based assay that detects ESR1 mutations in circulating tumor DNA and could predict treatment failure in breast cancer patients.
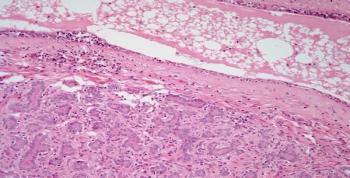
A 31-year-old woman presents with a nodule in the breast. After further evaluation, a biopsy is performed. What is your diagnosis?

The use of afatinib failed to show a benefit in HER2-positive breast cancer patients with progressive brain metastases.
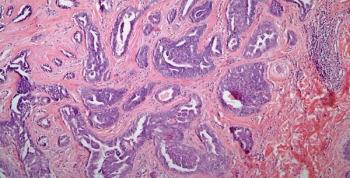
A 43-year-old woman presents with a lesion in the right nipple. After further evaluation, a biopsy is performed. What is your diagnosis?