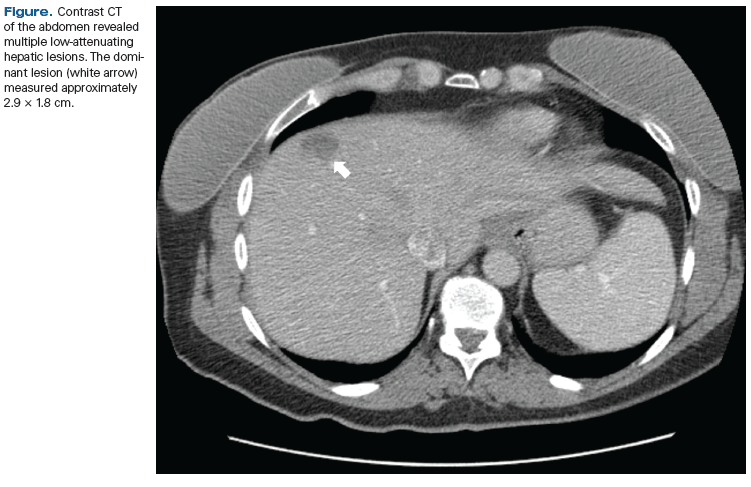
A large study found that while the risk of dying from breast cancer after a DCIS diagnosis is quite low, it is on par with that of women diagnosed with small, invasive breast tumors, and that aggressive DCIS treatment does not produce better results.