
Chadha et al are to be commended for their excellent review of repeat breast-conservation therapy after isolated in-breast local failures. We will briefly review several important points already made by the study authors.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Chadha et al are to be commended for their excellent review of repeat breast-conservation therapy after isolated in-breast local failures. We will briefly review several important points already made by the study authors.

Breast-conservation therapy (BCT) is a well-characterized treatment for early-stage breast cancer that has been studied for decades. The risk of local recurrence following BCT for invasive breast cancer ranges from 8.8% to 14.3% at 20 years.

October marks National Breast Cancer Awareness month, now in its 25th year, a time to contemplate important advances and milestones as well as future research needs.

In the US, breast cancer is the most common invasive cancer in women, with more than 200,000 diagnosed with the disease each year.

In about 30% of U.S. women who receive a diagnosis of early breast cancer, the cancer will progress to metastatic disease, but in the developing world, most cancer is initially diagnosed at an advanced stage, said William Gradishar, MD, director of medical breast oncology at the Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center, at Northwestern University, Chicago.

Thanks to the tireless efforts of the breast cancer community, October and breast cancer are tightly bound with the ubiquitous pink ribbon. But the awareness campaign places a heavy emphasis on prevention, detection, and early diagnosis. For women with metastatic breast cancer, there is a sense that the “pink parade” has intentionally passed them by even though an estimated 465,000 annual deaths from breast cancer worldwide occur because of metastatic disease.

Breastfeeding reduces breast cancer risk among women with a family history of breast cancer, according to a study. Observational studies suggest a relationship between lactation and premenopausal breast cancer risk.

Final results from a phase II study of an enhanced version of Herceptin upheld the emerging benefits previously seen with this novel approach in HER2-positive breast cancer.

Current evidence does not support the routine use of breast MRI in women with newly diagnosed breast cancer, according to Monica Morrow, MD, chief of the breast service, department of surgery, at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center.

Researchers suggest routine screening of breast cancer patients for disruptions.

Newly published data in the August 20, 2009, issue of The New England Journal of Medicine affirm 5-year upfront use of letrozole (Femara) following surgery as an optimal treatment approach vs tamoxifen for postmenopausal women with early-stage breast cancer (hormone-receptor positive).

Black women who are diagnosed with breast cancer have a higher probability of dying from the disease than white women, regardless of their estrogen receptor status, according to research from the National Cancer Institute (NCI).

E-Updates in the Adjuvant Treatment of Breast Cancer, Volume 2Updates on Chemotherapeutic Options and Targeted Therapies

They are supposed to be the standard bearers of the body’s defense against disease. But when it comes to cancer, some macrophages are traitors, helping rather than fighting the enemy. They attach to metastatic tumor cells, as they do to other threats. But rather than destroying metastatic cells, these macrophages enable their growth.

WASHINGTON, DC-Two separate new drug applications, for the treatment of relapsed ovarian cancer and advanced breast cancer, failed to win the approval of FDA’s Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee.

In a follow-up study, Christopher I. Li, MD, PhD, and colleagues have reconfirmed their finding that migraine headaches are associated with a lower risk of breast cancer.

For every 1000 women aged 40 to 74 years who participated in screening, 3.9 diagnosed with breast cancer died compared with 5.0 among those who did not participate. The absolute benefit in terms of reduced deaths due to mammography screening, therefore, is about one in 1000.
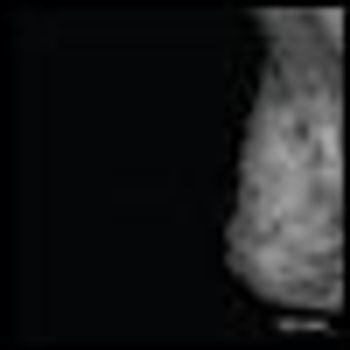
This feature examines the case of a patient with newly diagnosed breast cancer in the setting of a first-trimester pregnancy presenting to our multidisciplinary breast cancer clinic.

Research by the International Breast Cancer Study Group furthers knowledge on how anti-estrogen agents affect cognitive function and memory.

ORLANDO-RIBBON-1 results demonstrate that bevacizumab (Avastin) can be added to nearly any standard chemotherapy regimen for metastatic breast cancer, although the jury is still out on how meaningful the additional treatment is for overall survival.

Washington, DC-The idea of universal healthcare coverage was a crowd pleaser at the 2009 Annual Advocacy Training Conference of the National Breast Cancer Coalition, but expert panelists agreed that making that dream into a reality will take time and perseverance.

Two proteins could become important prognostic markers for long-term survival in breast cancer patients, according to researchers at Seattle’s Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center.

After it was reported that 25 labs in Quebec incorrectly identified markers for hormone therapy in 15% to 20% of breast cancer patients, the Canadian Breast Cancer Network called for urgent action to implement systemic changes in national standards for breast cancer testing.

Cell surface coating may play a major role in the spread of breast cancer to the brain, according to a study out of Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York. Three genes-COX2, HB-EGF, and ST6GALNAC5-have been found to mediate the metastasis of breast cancer to the brain, reported lead author Joan Massagué, PhD, and colleagues (Nature online, May 6, 2009)

Merck KGaA of Darmstadt, Germany, has initiated a global phase III trial of BLP25 liposome vaccine (L-BLP25, Stimuvax) in patients with hormone receptor–positive, locally advanced, recurrent or metastatic breast cancer.