
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a clonal myeloproliferative disorder resulting from the neoplastic transformation of the primitive hematopoietic stem cell.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a clonal myeloproliferative disorder resulting from the neoplastic transformation of the primitive hematopoietic stem cell.

Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine recently published a study in Nature Communications explaining that the rate at which genetically mutated cancer cells grow may help explain why some CLL patients develop treatment resistance.

A 5-year analysis of the DASISION trial showed that dasatinib continued to offer better responses than imatinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia.

The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted accelerated approval of nivolumab (Opdivo) based on overall response rate (ORR) in classical Hodgkin lymphoma patients.

A phase II study of the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax has shown that a large majority of patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia responded to treatment with the drug.

The early 21st century has brought with it significant improvements in survival from most common hematologic malignancies for patients aged 65 years or older, but these increases still lag behind those of 50- to 59-year-olds.

Chronic myeloid leukemia patients had a significantly increased prevalence of prior malignancies and autoimmune disorders compared with the general population.

Blood transfusions play a key role in managing complications of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL), involving unique blood product strategies.

The addition of pegylated interferon-ɑ2b to dasatinib yielded promising results in a small trial of newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia patients.

Genentech and Astex Pharmaceuticals will collaborate in a clinical trial of a combination hypomethylating and immune checkpoint blockade therapy for patients with acute myeloid leukemia.

The efficacy of ponatinib in patients with newly diagnosed CML compared with imatinib remains to be established, as a randomized phase III trial was terminated early due to concerns regarding arterial occlusive events with ponatinib.
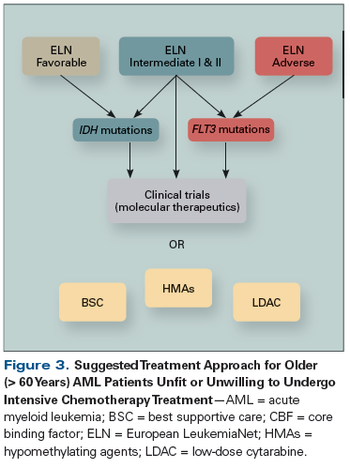
We review here the state of the art of diagnosis and treatment of AML and provide insights into the emerging novel biomarkers and therapeutic agents that are anticipated to be useful for the implementation of personalized medicine in AML.

Recent advances in mantle cell lymphoma include: (1) identification of new pathways to target, (2) novel therapeutics to treat patients with relapsed/refractory disease, and (3) monitoring of minimal residual disease and adoption of a maintenance therapy approach to prevent relapses post induction or post stem cell transplantation.

Receipt of EBRT for CTCL varies by sociodemographic factors and the centers where patients receive their care. Among those receiving EBRT, there are variations in dose, and median survival may vary by race. Further research is needed to assess differences in receipt, outcomes, and dose.

A rapid reduction in BCR-ABL transcript levels and the halving time of those levels are predictive of better outcomes in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia.

Overall, the future of patients with MCL is promising, since therapeutic options have widened. The implementation of universal aggressive treatment is challenged by novel regimens, targeted agents, the use of MRD to guide treatment decisions, and new trials that will directly compare transplant vs non-transplant approaches.

We are ready to move beyond a “one-size-fits-all” approach in AML and join our colleagues treating other malignancies, such as lung cancer, in moving towards a personalized medicine approach.

On April 11, 2016, The US Food and Drug Administration approved a new agent for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.

A first-in-man phase I study of CUDC-907, which targets both histone deacetylase and PI3K enzymes, has shown promise in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma or lymphoma.

The long-term use of romidepsin in a dose-sparing regimen to treat cutaneous T-cell lymphoma may be a useful strategy to try to prolong disease response.

A significant number of children who have completed treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukemia may be experiencing anxiety or depression, according to a new study.

Patients with acute myeloid leukemia who have undergone autologous stem cell transplantation and survived without disease recurrence for at least 2 years are still at risk for late recurrences.

Patients with CML who are treated with dasatinib commonly experience lymphocytosis, and the condition is associated with higher response rates and increased survival in patients who are refractory or intolerant of imatinib.

The injectable drug APO866, designed to induce apoptosis, did not have efficacy against cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, according to the results of small study.

Elevated levels of TGF-α and IL-6 in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients were predictive of failure to achieve molecular response.