
Results from the phase II SORAML trial indicated that adding sorafenib to standard chemotherapy for younger patients with acute myeloid leukemia was effective, but also resulted in increased toxicity.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Results from the phase II SORAML trial indicated that adding sorafenib to standard chemotherapy for younger patients with acute myeloid leukemia was effective, but also resulted in increased toxicity.

Many chronic myeloid leukemia patients who discontinue second-line dasatinib maintain a deep molecular response, according to a new study.

The presence of the gene KIR2DL5B was found to be associated with outcomes in patients with chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia, according to a new study.

The use of reduced-intensity conditioning HSCT as a method to maintain remission was effective in a select group of older patients with acute myeloid leukemia.

In Hodgkin lymphoma survivors, both mean heart radiation dose and cumulative dose of anthracyclines significantly predicted cardiovascular disease.

In patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), a prospective, long-term study has found that hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) and drug therapy yielded similar 10-year survival outcomes.

The combination of chemotherapy with the TKI ponatinib was an effective treatment for patients with newly diagnosed Ph-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Allogeneic HSCT may be the best treatment option in older patients with acute myeloid leukemia who obtain first complete remission after induction chemotherapy.

A new risk assessment score more accurately reflects the probability of dying from chronic myeloid leukemia than do existing scoring systems.

Treatment with intermittent imatinib is feasible among elderly CML patients who are stable responders to the drug, according to a new study.

GM-CSF was associated with lower transplantation-related and cumulative mortality among patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.

The antibody-drug conjugate brentuximab vedotin is effective as a frontline therapy for Hodgkin lymphoma patients over age 60 who are unfit for chemotherapy.

Data taken from EUROCARE showed large variations in survival rates from several hematologic malignancies across European countries, with lower survival in Eastern Europe and higher survival in Northern and Central Europe.

New research showed that it appears to be feasible to treat low- and high-risk patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia with the chemotherapy-free regimen of all-trans retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide.

In this interview, researchers discuss their analysis of a specific type of acute myeloid leukemia.

Anti-diabetic drugs could help eradicate leukemic stem cells in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) patients, according to a new study.

Nonbiological factors such as insurance and marital status and county-level income were found to independently affect the survival of younger patients with AML.

Treatment with a short course of vemurafenib was effective and rapid in patients with relapsed or refractory hairy-cell leukemia, resulting in overall response rates of over 95%.

A new laboratory study shows that inhibiting the uptake of certain dipeptides could represent a novel therapeutic approach to inhibiting chronic myeloid leukemia proliferation.

Risk for leukemia was significantly lower among children in Taiwan who were infected with the enterovirus compared with children who were not infected.

A complex high-dose combination therapy is tolerable and effective in patients with aggressive B-cell lymphoma that has spread to the central nervous system.

Our standard therapies for peripheral T-cell lymphoma may cure a subset of patients, and thus far novel agents have not changed the outcomes for the majority.

This article evaluates the most up-to-date peer-reviewed published work on the treatment of peripheral T-cell lymphoma, and offers a glimpse into the current upfront clinical trial landscape for patients affected by this uncommon disease.
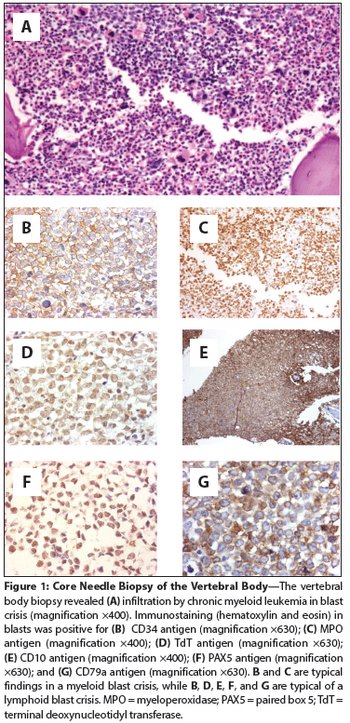
A 45-year-old man with a known history of rheumatic fever and aortic valve replacement 15 years earlier presented with the chief complaint of a 1-month history of progressive, intense, nonmechanical lumbar pain.

Ponatinib yielded complete cytogenetic responses in most patients with newly diagnosed chronic-phase CML, but the risk of vascular events suggests other agents should first be considered.