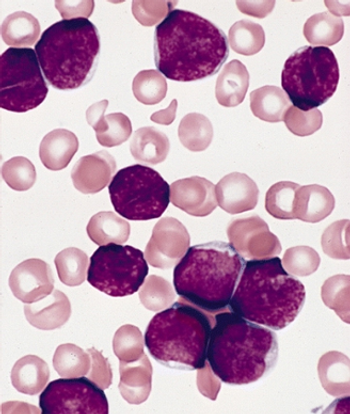
Long-term outcomes of patients treated for pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) with modern treatment protocols are good, with an overall low risk for serious long-term side effects.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Long-term outcomes of patients treated for pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) with modern treatment protocols are good, with an overall low risk for serious long-term side effects.

The FDA has approved the drug belinostat to treat patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma.

Measuring changes in levels of BCR-ABL in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) can help predict treatment outcomes and disease progression, according to a new study.
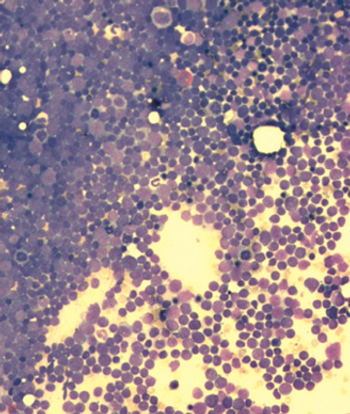
Researchers have identified Down syndrome as a risk factor for infection-related mortality among pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
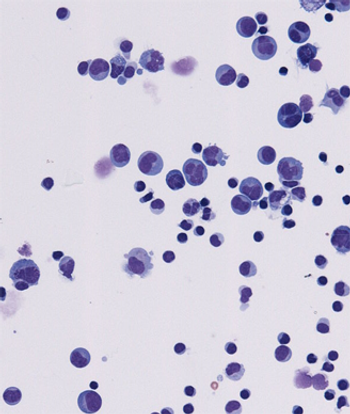
A novel inhibitor of CD19 was well tolerated and showed promising activity in patients with relapsed or refractory B-lineage non-Hodgkin lymphoma, according to a phase I study.

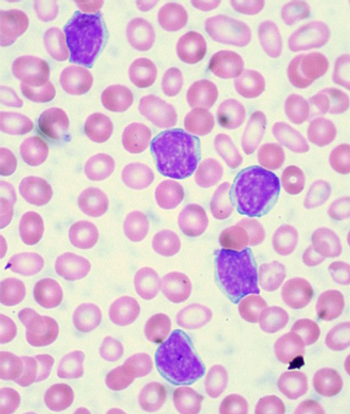
A phase II trial of the selective spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) inhibitor GS-9973 showed substantial biologic activity in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
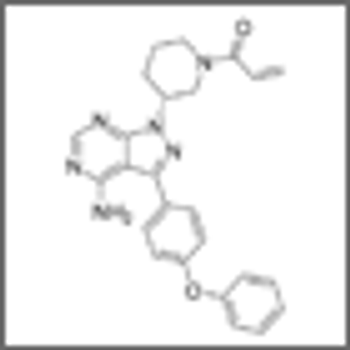
Ibrutinib substantially increased progression-free survival and overall survival over ofatumumab in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), according to the results of the RESONATE trial.

As part of our coverage of the 2014 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, we discuss the pros and cons of follow-up imaging in lymphoma.

The new drug volasertib, which is in trials for the treatment of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), has been granted orphan drug designation by the FDA.

Obesity or underweight status at diagnosis can influence outcomes in pediatric ALL patients, but a new study shows that the risk can be mitigated if weight status changes following treatment induction.

A novel agent known as BL-8040 will enter phase I/II testing for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia, according to BioLineRx, the company developing the drug.

A rare subtype of disease known as atypical chronic myeloid leukemia (aCML) has been shown to be clinically distinct from a related condition known as unclassifiable myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasm.

The FDA has approved siltuximab (Sylvant) for the treatment of multicentric Castleman disease, a disorder of the lymph nodes that is similar to lymphoma and often treated with chemotherapy and radiation.

Using both clinical and molecular markers, researchers have created a simple prognostic index for patients with cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
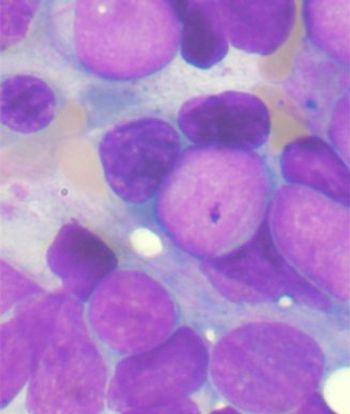
New trial results show that a novel, oral metabolic inhibitor has demonstrated early activity in relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML), according to data presented at the annual meeting of the American Association of Cancer Research.
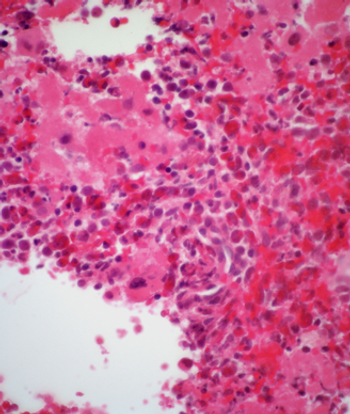
A subgroup of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cells that were “sticky,” or adherent to plastic, showed higher expression levels of BCR-ABL and were more resistant to treatment with the tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib.
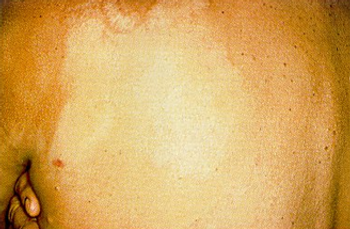
A phase II trial of mogamulizumab showed that the agent has meaningful antitumor activity in patients with relapsed peripheral T-cell lymphoma and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, and acceptable toxicity.

MolecularMD and Novartis are working on a diagnostic test to help determine which chronic myeloid leukemia patients may be candidates to stop taking nilotinib.

Although the cure rate remains high in women who present with bulky mediastinal stage I–II HL, the challenge remains to balance efficacy and minimize long-term toxicities.

Contrary to some previous research as well as popular belief, living underneath or near to power lines as a child may not have any notable effect on childhood leukemia risk, according to a new case-control study conducted in the United Kingdom.

Researchers have identified distinct pre-leukemic hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients.
A score based on an epigenetic signature of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) is highly prognostic for patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), according to a new study.

The FDA has approved ibrutinib (Imbruvica) as a single-agent treatment for previously treated patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), under the FDA’s accelerated approval program.
The combination of idelalisib with rituximab improved survival in relapsed CLL, and idelalisib also showed antitumor activity as a single agent in patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma.