Liver Cancer
Latest News
Latest Videos

More News
The 5-year follow-up results from CheckMate 040 showed consistent responses with nivolumab/ipilimumab in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.
The agency issues a complete response letter for the combination due to deficiencies associated with a manufacturing site inspection.

Adverse Effects Associated with SBRT in Patients With HCC
The panel discusses adverse effects associated with stereotactic body radiation therapy, and the Oncology Brothers provide a recap of the entire discussion.

Treating Transplant-Ineligible Patients With HCC and Liver-Confined Disease
Focusing on liver-directed therapy, the panel provides clinical insights on the treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who have liver-confined disease and are not candidates for transplant.

Overview of Interventional Radiology Treatment Options
Providing the interventional radiologist perspective, Harris Chengazi, MD, gives an overview of available treatment strategies.

The Basics of Radiation Oncology
Radiation oncologists Nina Sanford, MD, and Jeffrey M. Ryckman, MD, provide an overview of treatment modalities, highlighting SRS, SBRT, proton therapy, and how options have improved.
Data from 10 new randomized clinical trials support updated recommendations for various systemic therapy regimens in hepatocellular carcinoma.

Tanios S. Bekaii-Saab, MD, discusses safety profile considerations for patients undergoing treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma, and the Oncology Brothers recap the entire discussion.

Turning the focus to advanced-stage HCC, Tanios S. Bekaii-Saab, MD, offers comprehensive insights on first- and second-line treatment options.

Medical oncologists outline localized therapy options for patients with early- and intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma.
The safety of nivolumab plus ipilimumab among those with hepatocellular carcinoma in the CheckMate-9DW trial appears to be comparable with prior reports.
Investigators are assessing the safety, tolerability, and initial efficacy of BST02 in those with advanced or metastatic liver cancer as part of a phase 1 trial.
At 1 and 2 years, patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and narrow surgical margins experienced encouraging recurrence-free survival rates following adjuvant radiotherapy in the phase 2 RAISE trial.
Duration of response results with pembrolizumab plus lenvatinib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma appear to be ‘promising’ in the phase 3 LEAP-002 trial.
Durvalumab plus bevacizumab and TACE may be a new standard of care in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma eligible for embolization, according to Riccardo Lencioni, MD.

Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and Child-Pugh-B liver function appear to have worse overall survival following treatment with regorafenib in the REFINE trial.

Treatment-emergent adverse effects following therapy with fostrox plus lenvatinib among those with hepatocellular carcinoma appear to be manageable in a phase 1a/2a study.

Govindarajan Narayanan, MD, speaks to the potential time-saving advantages of using the Epione robot for microwave ablation, cryoablation, and other surgical strategies in patients with liver cancer and other tumors.
Use of the surgical Epione robot will save a significant amount of time when performing surgery for patients with liver tumors and potentially other cancers, says Govindarajan Narayanan, MD.

The safety profile of durvalumab plus TACE and bevacizumab in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in the phase 3 EMERALD-1 study appears to consistent with previous findings.
Data from the phase 3 RATIONALE-301 trial appear to support tislelizumab as a potential frontline treatment option for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.

Adding TPST-1120 to atezolizumab and bevacizumab appears to improve progression-free survival compared with atezolizumab and bevacizumab alone in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.

Most adverse effects appear to be grade 1 or 2 among patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and other solid tumors associated with the MYC oncogene receiving OTX-2002 in the phase 1/2 MYCHELANGELO I trial.
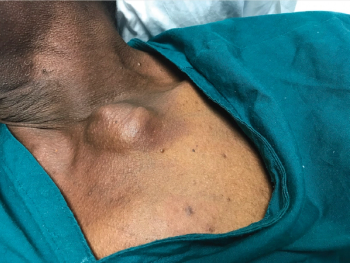
Unusual Initial Presentation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma as a Clavicular Head Mass
Rohit Gupta, MD, et al review a case study of a 70-year-old man who presented with a head mass, and the final diagnosis was hepatocellular carcinoma.
Camrelizumab and rivoceranib appear to be an appropriate novel, first-line regimen for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.