Lung Cancer
Latest News
Latest Videos
CME Content
More News

In CheckMate -078, nivolumab yielded superior OS compared with docetaxel in previously treated NSCLC, regardless of PD-L1 expression and tumor histology.

Treatment with the second-generation EGFR TKI dacomitinib resulted in improved overall survival over gefitinib in patients with NSCLC and activating EGFR mutations.
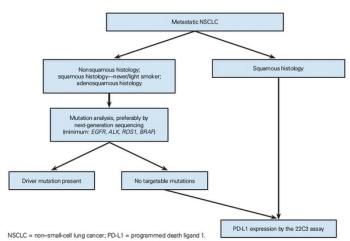
Newly Diagnosed Lung Cancer: Which Molecular Tests Are Needed for Optimal Treatment Decision Making?
In this article, an approach to the diagnostic evaluation of patients with newly diagnosed advanced NSCLC is suggested, in an attempt to identify the best treatment options.

An avelumab combination therapy shows promise against ALK-driven lung cancers, but another was neither safe nor effective in non–ALK-driven cases.

Cell-free DNA, used to guide treatment of advanced lung cancer, may become a tool for early detection, based on analysis of participants in the Circulating Cell-free Genome Atlas study.

Researchers in Hong Kong found dacomitinib was associated with longer OS than gefitinib in patients with advanced EGFR+ NSCLC.

Among former heavy smokers, the risk for lung cancer remains significantly increased compared with never-smokers, even more than 25 years since quitting.

In this video, Apar Ganti, MD, highlights recent advances and studies presented at ASCO 2018 on management of NSCLC and SCLC with ICIs and targeted agents.

Weekly patient symptom self-reports, filed using an online tool, allowed timely detection of lung cancer relapses and prolonged patient survival.
In this video, Dr. Leena Gandhi discusses KEYNOTE-042, a study of pembrolizumab vs chemotherapy in NSCLC (abstract LBA4), and other key ICI trials reported at ASCO 2018.

Corticosteroid medications are associated with poorer outcomes of therapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors for patients with lung cancer.

Administering pembrolizumab before EGFR TKIs may be inappropriate for TKI-naive patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC.

Adding pembrolizumab to pemetrexed and carboplatin for advanced nonsquamous NSCLC is associated with improved overall survival at 24 months.

Alectinib was generally better tolerated and associated with better outcomes vs crizotinib in ALK mutation–positive non–small-cell lung cancer.

Pembrolizumab represents a new standard first-line treatment option for PD-L1–expressing advanced/metastatic NSCLC, according to KEYNOTE-042 investigators.

Combining the ALK inhibitor with this immunotherapeutic agent had an acceptable safety profile and yielded an ORR of 85.7%, South Korean investigators reported.

A simple blood draw to evaluate cfDNA might one day be used for early-stage lung cancer screening-if the mutational “noise” of normal aging can be addressed.

The addition of atezolizumab to chemotherapy was associated with superior PFS but did not improve preliminary OS.

Obese patients survived longer during immune checkpoint blockade for metastatic lung cancer compared with underweight patients and those who lost weight during treatment.

Pembrolizumab has shown activity against some lung cancer metastases in the brain, but responses can be discordant with extracranial tumor responses.

Activating oncogene mutations do not predict lung tumor responses to immune checkpoint blockade, ImmunoTarget investigators found.

An analysis of patient-reported outcomes showed that osimertinib yielded a longer time to deterioration compared with chemotherapy in patients with advanced non–small-cell lung cancer.

Alectinib offered significantly improved outcomes over standard chemotherapy in patients with ALK-positive non–small-cell lung cancer who had progressed on crizotinib therapy.

Neoadjuvant nivolumab combo proved safe while yielding high response rates in patients with NSCLC.

In KEYNOTE-189, a pembrolizumab/chemo combination yielded OS and PFS benefits in patients with advanced NSCLC.