
Holocaust survivors have a small but consistent increase in the risk of developing cancer, in particular colorectal and lung cancers.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Holocaust survivors have a small but consistent increase in the risk of developing cancer, in particular colorectal and lung cancers.

Proton-beam therapy was found to be safe for patients with limited-stage small-cell lung cancer in the first prospective registry study of the therapy, with only a small number of high-grade toxicities.

This video reviews immunotherapy options now available for the treatment of lung cancer across different lines of therapy.

Nivolumab did not extend progression-free survival over chemotherapy in the first-line setting in patients with PD-L1–positive advanced non–small-cell lung cancer, according to results of an open-label phase III trial.

This video highlights a study that tested an alternative maintenance strategy determined by response to induction chemotherapy for patients with advanced non-squamous non–small-cell lung cancer.

A subpopulation of T cells called tissue resident memory cells may be able to determine which cancer patients' immune systems can mount an effective anti-tumor response

The FDA has approved dabrafenib in combination with trametinib for the treatment of BRAF V600E mutated non-small cell lung cancer.

Dr. Kim discusses why non-small cell lung cancer should be considered the paradigm for precision medicine, and how treatment of the disease has changed over the last decade.

Adding nintedanib to pemetrexed/cisplatin improved the progression-free survival of patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma compared with placebo.

In this podcast interview, Dr. Hossein Borghaei discusses some of the latest science presented at ASCO that focuses on immunotherapy in lung cancer.

The PD-L1 inhibitor atezolizumab showed substantial responses as a single-agent treatment in patients with advanced non–small-cell lung cancer with confirmed PD-L1 expression.

Adding palifosfamide to carboplatin and etoposide failed to improve survival over the latter two agents alone in patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer.

The American Society for Radiation Oncology issued a new clinical guideline for the use of stereotactic body radiation therapy in patients with early-stage lung cancer.

Treatment with nivolumab alone and in combination with ipilimumab resulted in durable responses in patients with previously treated small-cell lung cancer.
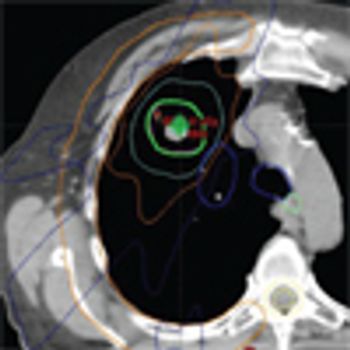
Three randomized trials of SBRT vs surgical resection closed due to poor accrual, but an analysis of patients treated in these trials suggested that SBRT might even be superior to surgery. New trials are underway to further assess the question of whether SBRT can be the definitive treatment for early-stage NSCLC instead of surgery.

In this interview we discuss the role of checkpoint inhibitors in advanced lung cancer and treatment strategies when patients progress.

This video examines how a change to weight-based pembrolizumab dosing in first-line PD-L1–positive lung cancer could save nearly $1 billion in US healthcare costs.

Dr. Karen Reckamp talks about ways to incorporate biomarkers for the treatment of lung cancer with immunotherapy into clinical practice at the 2017 American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting, held June 2–6 in Chicago.

The second-generation ALK-inhibitor alectinib should be the new standard of care for first-line treatment of ALK-positive non–small-cell lung cancer, according to a new study.

The use of prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) reduced the incidence of symptomatic and asymptomatic brain metastases in patients with radically treated stage III NSCLC. The therapy did not, however, improve overall survival, and decreased quality of life.

Lorlatinib exhibits durable responses in patients with ALK-positive non–small-cell lung cancer and robust intracranial activity in those with brain metastases.

Immunotherapy may represent an effective new treatment approach for relapsed mesothelioma patients, according to a new study.

Atezolizumab treatment beyond progression might benefit patients with advanced non–small-cell lung cancer, according to the first report from the randomized phase III OAK trial.

This video examines a phase II trial that studied maintenance pembrolizumab in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer.

Dacomitinib delayed progression of EGFR-positive non–small-cell lung cancer, but led to more adverse events compared with gefitinib.