
This Medical News Minute outlines efforts by a number of advocacy groups and medical associations urging the CMS to abandon proposed reimbursement cuts to low-dose CT screening for lung cancer.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!

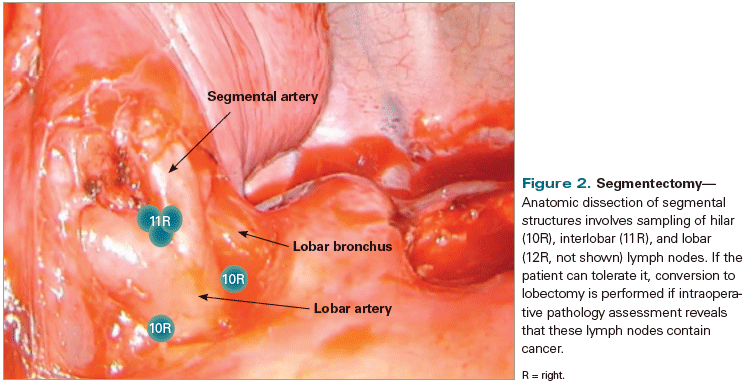

This Medical News Minute outlines efforts by a number of advocacy groups and medical associations urging the CMS to abandon proposed reimbursement cuts to low-dose CT screening for lung cancer.

I currently have a 68-year-old patient with EGFR-mutated adenocarcinoma of the lung, who presented with metastatic disease to the brain, liver, and bone in late 2014.

The addition of selumetinib to docetaxel failed to improve progression-free and overall survival in patients with KRAS-mutated locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC.

The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved atezolizumab (Tecentriq®, Genentech) for treating chemotherapy-refractory, metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), Genentech announced.

Adding pembrolizumab (Keytruda) to first-line chemotherapy improves response and survival rates among patients with previously-untreated advanced PD-L1-positive non-small cell lung cancer.

The use of the PD1 inhibitor nivolumab appeared to be feasible and safe in a small study of patients with untreated, stage I–IIIa non–small-cell lung cancer.

Patients diagnosed with early-stage lung cancer who are also diagnosed with depression have an increased risk of mortality, according to a prospective, observational study.

The US Food and Drug Administration has approved a plasma sample label extention for the T790M companion diagnostic blood test, cobas® Mutation Test v2.

Combining two cancer immunotherapies to target both the interleukin 10 (IL-10) and programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) receptors has yielded promising early results for some patients with renal cell carcinoma and non-small cell lung cancer.

Researchers in Texas are now reporting they have developed drug-loaded synthetic nanoparticles that can distinguish lung cancer cells from healthy cells.
A 34-year-old woman presents with a coin lesion in the right upper lobe of the lung. What is your diagnosis?

US soldiers and veterans will be at the forefront of a new nationwide integrated proteogenomic lung tumor screening program aimed at boosting enrollment in clinical trials and hastening the development of targeted anticancer therapies.

Although the overall incidence of programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) inhibitor-related pneumonitis is rare, the serious adverse event may occur more commonly in certain solid tumor types like non–small-cell lung cancer and renal cell carcinoma.

Researchers from China have discovered a way to offset the brain complications of leptomeningeal metastases in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.

Automated computer analysis of pathology slide images can more accurately predict lung cancer patient prognosis than can human pathologists, according to researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine.

In a phase III trial, Opdivo (nivolumab) did not meet its primary endpoint, a disappointment to researchers and patients.
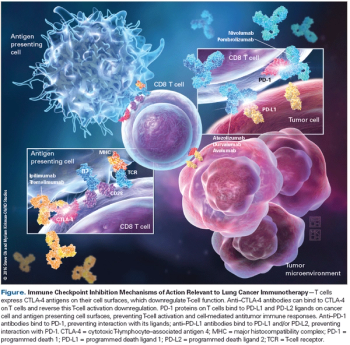
Immune checkpoint inhibitors have changed the treatment paradigm for patients with lung cancer, bringing about the most promising outcomes we have seen in a long time.

Immune checkpoint inhibitors are a reality for the treatment of patients with NSCLC, and if approved for SCLC, would be a treatment breakthrough we have not seen for decades.

The combination of pemetrexed and gefitinib offered improved progression-free survival in East Asian patients with advanced nonsquamous NSCLC and activating EGFR mutations.

Transgenomic, Inc. has announced the commercial availability of assays to detect EGFR C797S mutation, a mechanism of acquired lung tumor resistance to third-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer.

A trial showed that KRAS wild-type NSCLC patients fare better with regimens containing erlotinib, while KRAS-mutated patients had better outcomes without erlotinib.

Virginia Cancer Specialists reported they have enrolled the first patient in a new advanced lung cancer clinical trial for patients with ALK-positive locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer.

Prescribing nivolumab only to patients with programmed cell death ligand 1-positive (PD-L1+) tumors improves its cost-effectiveness.

ALK-targeting agents such as crizotinib may work most effectively in lung cancer patients with ALK variant 1.
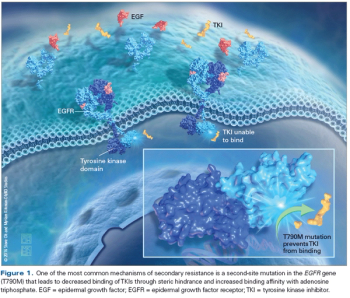
In this article, we review the available literature addressing the competing treatment strategies in EGFR-Positive Lung Cancer and attempt to clarify best treatment practices, including the emerging role of T790M-directed therapies.