
The kinase inhibitor fruquintinib offered improved outcomes vs placebo as a third- and fourth-line treatment in advanced non–small-cell lung cancer.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


The kinase inhibitor fruquintinib offered improved outcomes vs placebo as a third- and fourth-line treatment in advanced non–small-cell lung cancer.

Substantial variation in treatment patterns can explain geographic differences in survival outcomes in patients with lung cancer, according to a UK study.

Maintenance therapy with pazopanib significantly prolonged progression-free survival in patients with extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer, but with toxicity.

Nivolumab offers extended overall survival benefit vs docetaxel in patients with advanced non–small-cell lung cancer, according to an analysis with 3 years of follow-up.

ASCO recently released a clinical practice guideline on the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma, including recommendations on diagnosis, staging, and treatment with chemotherapy, surgical cytoreduction, and radiation therapy.

The FDA has expanded the approval of afatinib (Gilotrif) to include the first-line treatment of metastatic non–small-cell lung cancer patients whose tumors have non-resistant EGFR mutations, including three newly identified substitution mutations.

The EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor osimertinib showed promising efficacy and manageable toxicity in patients with advanced NSCLC and CNS metastases.

Nearly two-thirds of older patients with stage III lung cancer do not receive any treatment, according to a new study.

An individual risk–based approach could identify more people eligible for lung cancer screening, and thus prevent more early deaths, compared with USPSTF criteria.

The combination of exosomal RNA and cell-free DNA improved the sensitivity of blood-based liquid biopsy for EGFR mutation detection in non–small-cell lung cancer compared with standard circulating tumor DNA.

The combination therapy increased the attraction of immune cells to fight non-small cell lung cancer and also boosted the response to immune checkpoint inhibitors.
In this slide show we highlight some of the top news on lung cancer in 2017, including FDA approvals, a new standard of care for ALK-positive lung cancer, increased risk with vitamin B supplements, and more.

Results from a recent study show that some differences exist in NSCLC gene expression from African Americans and European Americans, which could be leveraged to improve patient outcome in both populations.

Treatment with anamorelin significantly increased lean body mass and improved anorexia symptoms in patients with advanced non–small-cell lung cancer, according to a new study conducted in Japan.

The early integration of oncology and palliative care enhanced coping strategies and improved QOL for patients newly diagnosed with incurable lung or GI cancer.

A new study suggests that the protein NFS1 provides a central protection for cancer cells against oxygen and that it may be possible to leverage this discovery into a new lung cancer treatment.

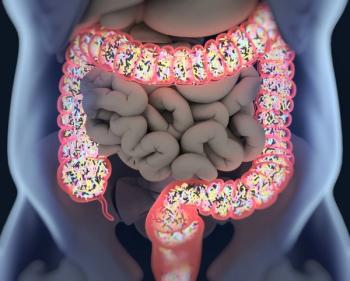
The gut microbiome affects the efficacy of PD-1 immune checkpoint blockade immunotherapy against melanoma and other cancers, according to a pair of recent studies.

Researchers report on the development of a blood-based assay that could potentially provide an earlier warning of small cell lung cancer relapse by improving diagnostic lead-time compared with CT scan.

The LMWH enoxaparin failed to improve overall or progression-free survival in small-cell lung cancer patients, in spite of improved rates of venous thromboembolism.

Researchers analyzed samples from 1,122 patients with advanced-stage NSCLC and discovered that 92.9% of tumors from harbored multiple changes in cancer-related genes in addition to the EGFR driver mutation.

The addition of bevacizumab to adjuvant chemotherapy failed to improve survival outcomes in patients with surgically resected early-stage NSCLC.

Poizotinib, once abandoned as a general EGFR inhibitor, recently demonstrated tumor shrinkage in patients with an EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation.

This peer-to-peer exchange highlights results of a study that tested whether analyzing circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) during treatment with chemoradiotherapy could predict outcomes in patients with localized lung cancer.

The FDA approved alectinib as first-line therapy for ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer based on results of the ALEX study, which showed significant improved PFS compared with crizotinib.

Data presented at the recent World Conference on Lung Cancer show that pembrolizumab improves overall survival in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer whose tumors express high levels of PD-L1.