
The use of a customized clinical pathways program that helps manage complexity and guide decisions resulted in a sharp decrease in costs per patient in an analysis of stage IV non–small-cell lung cancer.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


The use of a customized clinical pathways program that helps manage complexity and guide decisions resulted in a sharp decrease in costs per patient in an analysis of stage IV non–small-cell lung cancer.

ERBB2/HER2 mutations appear to be rare but targetable oncogenic drivers in non-small cell lung cancer, according to findings from a small retrospective cohort records analysis.

The LUX-Lung 7 trial found no significant differences between afatinib and gefitinib for patients with EGFR mutation–positive stage IIIb/IV NSCLC.

An IHC assay for ALK status in non-small cell lung cancer tumor tissue predicts crizotinib treatment outcomes and offers a rapid and potentially less expensive alternative to older FISH ALK status assays.
A better delineation of the relationships between lung cancer, COPD, and emphysema may lead to significant improvements in the effectiveness of lung cancer screening programs, and to reductions in the morbidity and mortality associated with these deadly diseases.

The addition of bevacizumab to a first-line regimen of cisplatin and etoposide improved progression-free survival in patients with extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer.

The oral ALK inhibitor ceritinib provided a significant improvement in progression-free survival over platinum-based chemotherapy in patients with previously untreated ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer.

A study just published in Cancer Cell is suggesting a new target for combating KRAS-mediated lung adenocarcinoma.

In my practice, I am constantly being asked how to properly treat scalp involvement in relation to these skin toxicities.

A delay in initiation of adjuvant chemotherapy following resection for non–small-cell lung cancer was not associated with any increase in mortality.

A database analysis shows significant shifts in treatment patterns for elderly patients diagnosed with advanced-stage non–small-cell lung cancer, along with a modest gain in survival since 2000.

Among active or former smokers undergoing lung cancer screening, longer peripheral leukocyte telomere length is associated with an increased risk of lung cancer.

Non-small cell lung cancer can acquire resistance to immune checkpoint blockade agents through evolutionary culling of tumor clones harboring the mutations for cell surface neoantigens that are recognized by patients’ immune T cells.
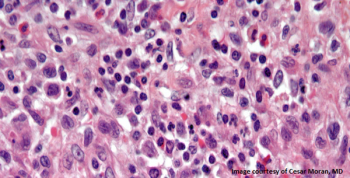
A 38-year-old woman presents with multiple pulmonary nodules. After further assessment a biopsy is performed. What is your diagnosis?

In this interview we discuss the use of liquid biopsies in lung cancer, the pros and cons compared with tissue biopsies, and how they can be used to help make treatment decisions.

Pembrolizumab was associated with clinically meaningful improvements in health-related quality of life compared with platinum-based chemotherapy in NSCLC patients.

The PD-L1 inhibitor atezolizumab significantly improved overall survival compared with docetaxel across subgroups of patients with non–small-cell lung cancer.

Second-line treatment with osimertinib resulted in significantly better progression-free survival compared with chemotherapy alone in patients with EGFR-T790M positive NSCLC, according to the results of the AURA3 trial.

Patients treated with first-line ceritinib had a 45% reduction in the risk for progression of advanced ALK-positive NSCLC compared with chemotherapy.

In this slide show we highlight some of the top news on lung cancer in 2016, including an immunotherapy approval from the FDA, and studies on depression in lung cancer patients, serious side effects to watch for when using immunotherapies, and more.

An updated prognostic tool incorporating gene alteration data could help guide clinical management of patients with non–small-cell lung cancer.

Cabozantinib alone or in combination with erlotinib improved survival outcomes among patients with advanced EGFR wild-type non–small-cell lung cancer.

Researchers at UC San Francisco have recently discovered genetic mutations in a protective protein called Capicua (CIC). The scientists demonstrated that there is a disproportionate frequency of mutated CIC in human lung cancers that have metastasized.

At the 11th Annual New York Lung Cancer Symposium, held on November 12, 2016, in New York City, Roman Perez-Soler, MD, spoke about what is currently understood about resistance to EGFR-targeted therapies and how to treat this population of patients.

Speaking at the 11th Annual New York Lung Cancer Symposium, held on November 12, 2016, in New York City, Howard (Jack) West, MD, medical director of the thoracic oncology program at the Swedish Cancer Institute in Seattle, laid out the available treatment options for patients with treatment-naïve, EGFR-positive NCSLC cancer.