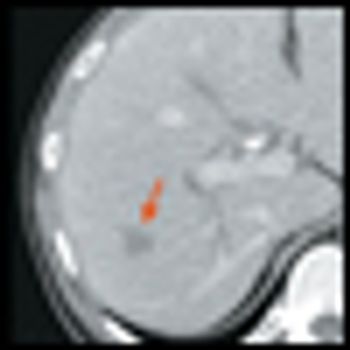
A phase III clinical trial of sunitinib (Sutent) has been stopped early after the drug showed significant benefit in patients with advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. An independent data monitoring committee recommended halting the trial after concluding that sunitinib demonstrated greater progression-free survival compared with placebo plus best supportive care in these patients.