The regular use of aspirin reduced the risk for pancreatic cancer by almost 50%, according to the results of a Chinese study.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


The regular use of aspirin reduced the risk for pancreatic cancer by almost 50%, according to the results of a Chinese study.

The Pancreatic Cancer Action Network is aiming to improve the lives of patients diagnosed with the third-leading cause of cancer-related death with a new precision drug trial.

These guidelines review the use of radiation, chemotherapy, and surgery in borderline and unresectable pancreas cancer. Radiation technique, dose, and targets were evaluated, as was the recommended chemotherapy, administered either alone or concurrently with radiation. This report will aid clinicians in determining guidelines for the optimal treatment of borderline and unresectable pancreatic cancer.

Researchers are reporting they have identified ERCC3 as a new target for pancreatic cancer and demonstrated the effects are extremely strong in a molecularly defined subset of patients.

The ESPAC-4 trial found that adding capecitabine to gemcitabine in patients with resected pancreatic cancer resulted in an improved estimated 5-year survival rate.

Use of hypofractionated chemoradiation prior to pancreatoduodenectomy resulted in similar resection rates and outcomes vs standard fractionation.

Annual screening of people at high risk for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) because of CDKN2A mutations was relatively successful and allowed for the detection of disease in time to perform surgery.

For the first time, researchers suggest that underlying genetic mutations may cause pancreatic adenocarcinoma tumors to stiffen up and produce a dangerous thickening and scarring of the tissue around them.

Researchers have identified two species of bacteria linked with periodontal disease in healthy individuals that are associated with a risk of developing pancreatic cancer.

Higher preoperative levels of serum albumin were significantly associated with greater overall survival among patients undergoing resection of pancreatic adenocarcinoma.

An integrated genomic analysis has found that pancreatic cancer can be divided into four specific subtypes based on molecular characteristics. This division could help guide treatment decisions and future research avenues into this difficult malignancy.

Pancreatic cancer patients who received adjuvant therapy at a high-volume center had superior overall survival vs patients who were treated in a community setting.

Nanoliposomal irinotecan combined with fluorouracil/leucovorin improved overall survival in metastatic pancreatic cancer patients who have already been treated with gemcitabine.

The developer of evofosfamide announced that two phase III trials of the agent in advanced soft-tissue sarcoma and in advanced pancreatic cancer did not meet their primary endpoints.

A retrospective cohort study showed that socioeconomic variables including race, marital status, insurance status, and geography are associated with rates of resection for early-stage pancreatic cancer. Most of these factors, however, were not associated with survival following resection.
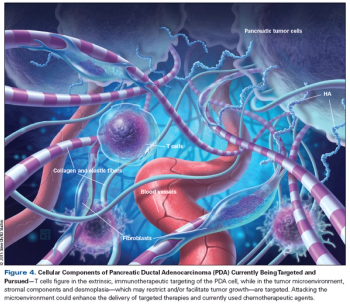
This article reviews the current treatment paradigms for metastatic disease, focusing on ways to ameliorate symptoms and lengthen survival. We then summarize recent advances in our understanding of the molecular and cellular aspects of pancreatic cancer.

The ultimate benefit to patients will come from a demonstration of clinically worthwhile benefits of new drugs that have been tested in well-designed and adequately powered clinical trials performed in an expedited fashion.

The FDA has approved the combination of irinotecan liposome injection plus 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin for the treatment of metastatic pancreatic cancer in patients who previously progressed on gemcitabine-based chemotherapy.
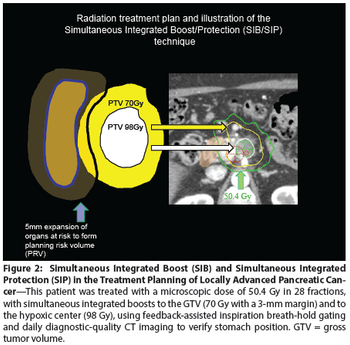
Five randomized trials involving patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer illustrate most clearly the substantial degree to which standard therapies are limited in their effectiveness.

The FDA has granted a priority review for MM-398 as a second-line treatment for metastatic pancreatic cancer after the drug demonstrated improved survival.

Researchers have discovered a protein encoded by the GPC1 gene present on cancer exomes that may be used as a diagnostic tool to detect early pancreatic cancer.

Patients with treatment-naive metastatic pancreatic cancer assigned to treatment with gemcitabine plus rigosertib did not have any improvement in tumor response or survival compared with treatment with gemcitabine alone.

The presence of an abdominal blood clot may be a sign of cancer and may also be associated with poor survival for patients with pancreatic or liver cancers.

Metformin, a common drug for type II diabetes, did not improve the survival of patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
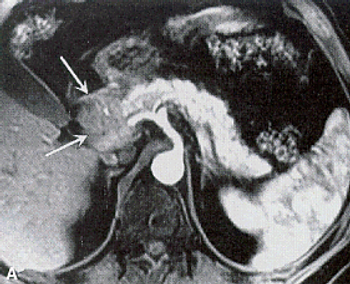
An MRI screening program for individuals at high risk for pancreatic cancer may be effective, according to the results of a short-term study.