A Japanese study supports the use of nab-paclitaxel for previously treated non–small cell lung cancer based on noninferiority end points being met.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


A Japanese study supports the use of nab-paclitaxel for previously treated non–small cell lung cancer based on noninferiority end points being met.

Trastuzumab deruxtecan treatment demonstrated strong antitumor activity for patients with HER2-overexpressing NSCLC, regardless of HER2 expression levels, according to interim findings from the phase 2 DESTINY Lung-01 trial.
Results of the phase 1 CHRYSALIS trial demonstrated the safety and efficacy of amivantamab in patients with previously treated non–small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations.
This ongoing study supports the continued development of AXL inhibition with bemcentinib in order to extend the efficacy of immunotherapy in biomarker-selected refractory non—small cell lung cancer, according to Matthew G. Krebs, MB ChB, FRCP, PhD.

Follow up data from KEYNOTE-799 demonstrated a high overall response rate with no new safety signals for patients with unresectable, locally advanced, stage III non-small cell lung cancer.
Encouraging survival end points are observed with BMS-986012 plus nivolumab in immune checkpoint inhibitor–naïve SCLC, according to data presented at the 2020 World Conference on Lung Cancer.
Results from the 2020 World Conference on Lung Cancer Singapore demonstrated the feasibility of using STK11 mutations and immune-related adverse events as response predictors in patients with non–small cell lung cancer.
An updated analysis presented at the 2020 World Conference on Lung Cancer Singapore expanded on data investigating pembrolizumab in the treatment of patients with PD-L1–positive NSCLC without sensitizing EGFR/ALK alterations.
“With recent advances in early detection of lung cancer, biomarker testing, and personalized treatment planning, effective patient-provider communication is more important than ever for short- and long-term survivorship,” said Kelly Clark, MA.

Supporting previously reported data, updated results of the phase 3 KEYNOTE-189 trial indicate that overall survival is significantly improved when pembrolizumab is added to platinum-based chemotherapy in the frontline treatment of patients with metastatic nonsqamous NSCLC.

A new study presented at the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer's 2019 conference may have found a model for lung cancer screening which improves on lung cancer screening guidelines from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force.
In this phase III trial, investigators assessed the clinical efficacy and safety of durvalumab with or without tremelimumab with etoposide and carboplatin or cisplatin chemotherapy followed by durvalumab with or without tremelimumab maintenance therapy compared with EP alone as first-line treatment in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer.
Video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) results in fewer in-hospital complications and a shorter length of stay compared with open surgery in patients with early-stage lung cancer.
In a phase I trial, researchers demonstrated that KRAS inhibitor AMG 510 demonstrated safety and antitumor activity in advanced NSCLC patients.

Combination immunotherapy with nivolumab plus ipilimumab was examined as a first-line therapy for patients with advanced non–small-cell lung cancer. Results were presented at the International Associate for the Study of Lung Cancer 2019 World Conference on Lung Cancer.

Data presented at the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer 2019 World Conference on Lung Cancer suggested tumor mutational burden may not be associated with the efficacy of pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy or placebo plus chemotherapy.

Little research has been done on these complications commonly found in lung cancer.
Researchers focused on a subset of patients with high tumor mutational burden using a 20-mutation-per-megabase threshold and found significant improvement in progression-free survival and overall survival.
Findings from the upcoming International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer 2019 World Conference on Lung Cancer show camrelizumab and chemotherapy showed survival benefits for patients with metastatic or otherwise advanced non-squamous non–small-cell lung cancer.
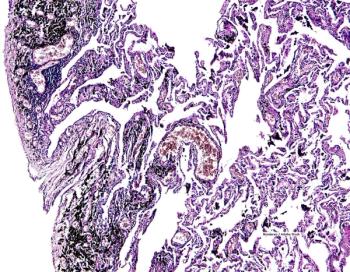
In recent years, advances in the molecular analysis of tumors and pathologic investigation have improved understanding of an ambit of lung cancer types.
Four or more biopsies proffer little additional benefit, found a study presented at the IASLC 19th World Conference on Lung Cancer.
Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy failed to improve survival compared with pembrolizumab alone in patients with non–small-cell lung cancer.
Two presentations at the IASLC WCLC 2018 discussed the evidence on treating breathlessness with pharmacologic vs nonpharmacologic therapy.

Participating in a 12-week physical exercise and psychosocial intervention improved the functional capacity of patients with advanced-stage lung cancer, which may result in improvement in quality of life, according to the results of a study presented at the World Conference on Lung Cancer.

Treating patients with early-stage, resected, node-positive non–small-cell lung cancer with customized chemotherapy based on BRCA1 expression levels did not increase overall survival rates.

Quality of life was not improved with the use of early palliative care for patients recently diagnosed with malignant pleural mesothelioma, according to data presented at the World Conference on Lung Cancer.

Small-cell lung cancer patients with high tumor mutation burden treated with immunotherapy had greater objective response rate, progression-free survival, and overall survival compared with patients with medium or low tumor burden.

In this interview we discuss a new trial involving the antibody-drug conjugate IMMU-132 as well as the future of chemotherapy in the treatment of lung cancer.

A high number of patient life-years are lost to regulatory delays for drug approvals, according to an analysis presented at the 2015 World Conference on Lung Cancer.

Patients with stage IV squamous cell lung cancer positive for an EGFR gene copy number biomarker saw a survival benefit when adding cetuximab to chemotherapy.