
All News


The combination of the chemotherapy capecitabine with external beam radiation was found to be both safe and effective in treating pain from bone metastases in patients with advanced breast cancer.

The ALSYMPCA phase III clinical trial, recently published, demonstrated that radium-223 dichloride was well-tolerated and resulted in an improvement in overall survival by 3.6 months compared with placebo.

There are risks to privacy and informed consent embedded in the many exciting discoveries of personalized approaches to medicine. These risks vary greatly.

A study published today has linked higher stature in women after menopause with a higher risk of developing any of 19 cancer types.

More than one-third of patients with oropharyngeal cancer were seropositive for HPV16 E6 an average of 6 years prior to their cancer diagnosis compared with less than 1% of healthy controls, a new study has found.

Fat. It isn’t said in polite company, and doctors never use it with patients because it is considered rude and inflammatory. But fat is now a disease. OK-obesity is a disease. The American Medical Association has proclaimed it as such, and now we are free to discuss it unhindered by rules of etiquette.

The community oncology practice is the nation’s headquarters in the war on cancer. Eighty-five percent of all cancer patients receive their treatment in local community oncology practices.

A 40-year-old woman with no significant family history of cancer came to me for a second opinion about her widely metastatic infiltrating gastric cancer.


A pair of studies from the ASCO annual meeting examined bone metastases from lung cancer, with one study finding that survival in patients was poorer in patients with bone metastases, and another study finding that the development of bone metastases could predict subsequent development of metastasis in the brain.

A study of colorectal cancer survivors shows those who consume higher amounts of red and processed meats before a colorectal cancer diagnosis are at higher risk of death from any cause compared to those who eat less of both types of meat.

If you or your loved one had cancer, how would you go about picking their treating oncologist? What would you want to know about their experience in that disease? And if a patient asks you how many cases you have treated with their diagnosis, will you look at them and be totally honest?

Today we speak with Dr. Robert Coleman about several new agents that have shown promise in early-stage clinical trials for ovarian cancer.
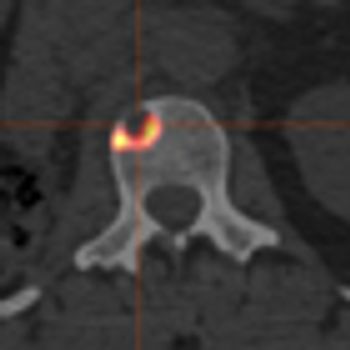
Bone metastases result in poorer outcomes for those patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), who were treated with a molecularly targeted therapy. The results were presented in two separate analyses at the annual ASCO meeting.
Researchers found that the more cost-effective option (surgery vs SBRT) in stage I lung cancer depends on whether the disease is clearly or marginally operable.

Here’s a fun fact: most doctors will be sued at least once during their career. Physicians in high-risk specialties such a surgery have a 99% chance of being sued by age 65; even low-risk specialists have a 75% probability.


A group of cancer and other healthcare advocacy organizations applauded a provision in the Affordable Care Act that requires private insurers to cover the routine medical costs of patients participating in clinical trials. However, many of those patients will continue to face roadblocks to participating in trials unless the federal government provides clear guidance on implementation, the groups said in a recent letter.

The first treatment for a rare tumor called giant-cell tumor of the bone has been approved by FDA. The approval of denosumab (Xgeva) was based on a priority FDA review.

Have you ever read someone’s note in the EMR and noticed it says “normal” in every section under physical exam, when in fact, the patient has had a mastectomy, a markedly enlarged liver, 3+ edema, or (horrors!) an amputation that goes undocumented?
The mTOR inhibitor everolimus failed to prove progression-free survival noninferiority compared with the VEGF-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib when given as first-line treatment in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.

In our commentary, we will address ways to consider this research across the cancer continuum, with a focus on the cancer survivor, highlighting some of the challenges in interpreting the research evidence for translation into clinical practice and noting some research gaps.

Exercise and physical activity are beneficial along the spectrum of care in cancer patients. However, much more research is needed to better understand this association and guide recommendations for patients.

This article will review these intersections of exercise and oncology, discuss the known mechanisms by which exercise exerts its salutary effects, and touch upon the future directions of exercise research in the oncology setting. Finally, recommendations are provided for clinicians to help patients with and without cancer take advantage of the benefits of physical activity.

Collaboration between oncologists and reproductive endocrinologists/infertility specialists not only will improve patient care, but it also will facilitate advances in the field through cooperative research and education.

How often do you refer patients for molecular profiling of a malignant tumor? For which of the following tumor types would you be most likely to recommend molecular profiling? Answer these questions and more.

In the late 1960s, I quickly learned that a large proportion of requests for narcotics in this population were spurious. Patients would simulate renal stone, acute myocardial infarction, and many other painful illnesses in order to obtain narcotic drugs.

The use of magnetic resonance–guided focused ultrasound ablation therapy for the management of painful bone metastases resulted in a high rate of pain response that was rapid, durable, and clinically meaningful, according to an abstract presented at the 2013 ASCO Annual Meeting in Chicago.
