
Women with onset of breast cancer over age 65 typically do not qualify for genetic testing, however this study demonstrated that frequency of pathogenic variants and risk of breast cancer is not negligible in this patient population.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!



Abemaciclib, Standard Endocrine Therapy Show Continued Lower Risk in iDFS in High-Risk Early HR+ Breast Cancer

Women with onset of breast cancer over age 65 typically do not qualify for genetic testing, however this study demonstrated that frequency of pathogenic variants and risk of breast cancer is not negligible in this patient population.

“In the current era of effective multimodality therapy for breast cancer, the need for [axillary lymph node dissection] for patients with axillary lymph node metastases must be re-evaluated, even for patients with clinically positive nodal disease,” the study authors wrote.

The FDA approved the use of PD-L1 IHC 22C3 pharmDx as an aid in identifying patients with triple-negative breast cancer who may be appropriate for treatment with pembrolizumab (Keytruda).

The FDA granted accelerated approval to pembrolizumab (Keytruda) in combination with chemotherapy for the treatment of patients with locally recurrent unresectable or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer whose tumors express PD-L1 as determined by an FDA approved test.
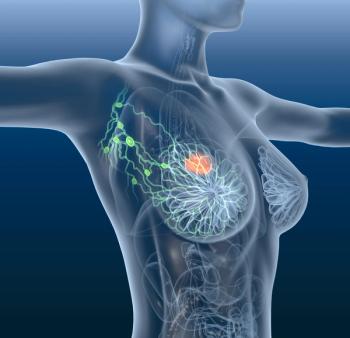
Researchers indicated that there is still a persistent survival disparity that has not narrowed over 2 decades between white and Black patients with inflammatory breast cancer.

A recent study found that automated analyses of CT scans for patients with breast cancer can predict which patients are likely to develop cardiovascular disease in the future.
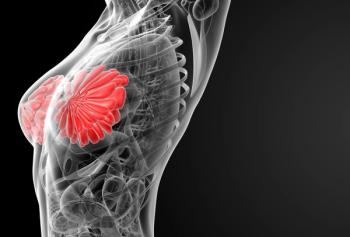
A study presented at the 12th European Breast Cancer Conference suggests women over the age of 70 with breast cancer can tolerate surgery even though they aren’t offered it regularly, but a second abstract suggests these women tend to opt out of this treatment option.

A study revealed that the way data is collected regarding women with benign breast diseases can provide insight into which non-cancerous disorders are likely to become cancerous in the future.

A study led by Jefferson researchers found that not all patients, specifically African American patients and women without private insurance, receive the same breast cancer treatment, specifically the beneficial and more cost-effective hypofractionated whole breast radiation therapy.

According to researchers, these findings “support the hypothesis that regional nodal disease may precede and contribute to the seeding of distant foci.”
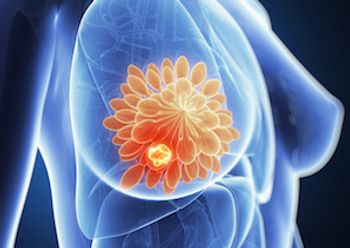
Detection of ESR1 mutations in baseline ctDNA was associated with inferior progression-free survival and overall survival in patients with advanced HR-positive breast cancer treated with exemestane versus fulvestrant.
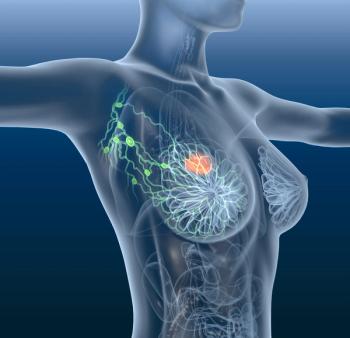
A recent examination of breast cancer subtypes, specifically luminal A and luminal B breast cancer, found that incidence rates from 2010-2016 increased for a number of racial/ethnic and age groups.

Among accredited US cancer centers, hospitals which serve primarily minority patients were found to be as likely as other hospitals to offer the standard of surgical care for early-stage breast cancer.

Natera announced the DARE trial examining Palbociclib to treat patients with advanced breast cancer will use its Signatera molecular residual disease test.
A study published in The BMJ concluded that a single dose of targeted radiotherapy was just as effective as conventional radiotherapy for women with early breast cancer.

The trial did not meet its primary end point of improved invasive disease-free survival in women with hormone receptor-positive HER2-negative early breast cancer who have residual invasive disease after completing neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Findings from the phase 2 FLIPPER trial indicated that frontline fulvestrant (Faslodex) in combination with palbociclib (Ibrance) demonstrated an improvement in PFS at 1 year in patients with endocrine-sensitive HR-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer.

Results from the study suggest that ctDNA testing can be seen as a standard of care test for both common and rare genetic events for patients with breast cancer.
The collective study findings suggested that for risk assessment, the recurrence score needs to be complemented by clinicopathologic parameters for therapy decision making.

The agency indicated that the use of atezolizumab (Tecentriq) and paclitaxel in patients with previously untreated, inoperable, locally advanced, or metastatic triple negative breast cancer was not effective in treating the disease.

Researchers indicated that these findings highlight the need for clinicians to emphasize the importance of both smoking cessation and cancer screening for women who currently smoke.

The new drug application was based on data from a single, pivotal, randomized, controlled, phase 3 study of encequidar for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer.
Researchers from Singapore discussed their own experiences and strategies used to safely manage breast cancer during the COVID-19 pandemic.

A study published in Cancer found that the introduction of generic aromatase inhibitors reduced the decrease trend of adherence to hormonal therapy for patients with breast cancer.
Researchers suggested that these findings support a change of the current screening guidelines for this specific risk group and support MRI screening.