Though the results still need to be confirmed, researchers suggested these findings indicate a need to better understand how BMI affects the biology, progression, and treatment efficacy of breast cancer.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Though the results still need to be confirmed, researchers suggested these findings indicate a need to better understand how BMI affects the biology, progression, and treatment efficacy of breast cancer.

Researchers found that breast cancer survivors who were prescribed adjuvant endocrine therapy and regularly performed moderate physical activity reported better health-related quality-of-life.
Researchers suggested that these findings support using minimal residual disease as a major stratification variable in all clinical trials to be conducted in patients with triple negative breast cancer.
These study results suggested that a longer time to surgery does not lower overall survival for women with early-stage breast cancer who had to delay operations due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The study evaluating atezolizumab in combination with paclitaxel compared to placebo plus paclitaxel did not meet its primary end point of progression-free survival in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer.

Researchers specifically suggested that the 86-SNV score could be incorporated into breast cancer risk prediction models for patients carrying a pathogenic variant in BRCA1, BRCA2, and CHEK2.

Marking the first US applications for pembrolizumab in breast cancer, the applications are based on data from the KEYNOTE-355 and KEYNOTE-522 trials, respectively.
A Yale study found that states with expanded Medicaid diagnosed women with breast cancer at an earlier stage of disease and was associated with a reduced number of uninsured patients when compared to non-Medicaid expansion states.
The findings indicated that a fasting mimicking diet is safe and effective as an adjunct to chemotherapy in women with early breast cancer.

The study results confirmed that the triple-negative breast cancers emergence among young compared with elderly patients can be completely different entities.
Findings suggested that conventional mammography screening performance metrics underestimate the interval cancer rate of a mammography screening episode.

Researchers highlighted the importance of recognizing the environmental and biological factors that contribute to the development of PTSD, which can help inform clinical care and potentially reduce PTSD comorbidity.

The combination demonstrated a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in pathological complete response for the treatment of individuals with early triple-negative breast cancer, regardless of PD-L1 expression.

A recent study demonstrated the validity of current breast cancer testing panels for use in African American women and provides a basis for increased referral of this patient population for cancer genetic testing.

Payment models with shared-savings components, such as the Oncology Care Model, may be associated with fewer visits and lower costs in certain cancer settings in the first year.
A study found that a 6-month follow-up examination was recommended for women found to have BI-RADS 3 lesions after previous recommendations suggested a year follow-up was safely sufficient.
A recent examination of older adults with cancer found accelerated losses in differing sarcopenia measures existed before and after a cancer diagnosis.
An analysis of women in Sweden found that mammography screening reduces the rate of advanced and fatal breast cancers, regardless of changes in treatment regimens.
Insulin resistance was found to be 1 factor that contributes to the worse prognosis in breast cancer between black and white women, potentially through direct effects of insulin on the tumor insulin receptor.
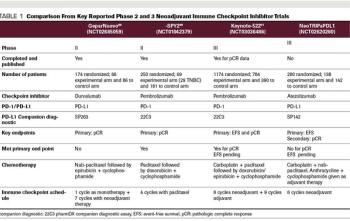
Experts review the current landscape and potential use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy with additional novel agents for patients with localized TNBC.

This study analyzed the full prevalence and spectrum of partner and localizer BRCA2 (PALB2) germline mutations in China, focusing on the associations between these PALB2 germline mutations and breast cancer risk.

The results from this random-effects meta-analysis suggested that dietary fiber intake may decrease the risk of breast cancer, including both premenopausal and postmenopausal breast cancers.

A recent study led by led by King's College London and Public Health England examined 1.4 million patients of cancer via the National Cancer Registry and found that early GP referrals led to longer survival rates for patients.
The breast cancer expert discussed the implications of this approval, as well as the data that led to the approval of sacituzumab govitecan-hziy.
This study found a substantial difference in the number of agents available for use in the metastatic and adjuvant settings for non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, and colon cancer.