
By adjusting the sequencing of currently available treatments, improved compliance with therapy is ensured, and novel scientific and clinically relevant hypotheses can be further explored.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


By adjusting the sequencing of currently available treatments, improved compliance with therapy is ensured, and novel scientific and clinically relevant hypotheses can be further explored.

In this interview we discuss the CheckMate 142 trial, which looked at nivolumab and ipilimumab for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer.

Matching targeted therapies to genetic abnormalities harbored by tumor types for which those therapies are not approved by the FDA might expand treatment options for some patients with advanced cancers.

The physical location of the primary tumor predicts survival in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer, according to an analysis to be presented at ASCO.

Combined therapy with trastuzumab and the tyrosine kinase inhibitor lapatinib shows promise against chemotherapy-refractory, HER2-positive colorectal cancers that do not harbor KRAS mutations.

Women who have undergone oophorectomy may be at an increased risk for colorectal cancer, according to the results of a recent study.

A new study suggests that cholesterol levels rather than cholesterol-lowering statin drugs may actually be responsible for the decrease in colorectal cancer risk.

The use of a noninvasive colorectal cancer screening test called a multi-target stool DNA test (mt-sDNA) detected the disease in patients who had previously avoided more invasive screening procedures.

New data indicates that entrectinib has clinical activity in patients with a variety of cancers with gene alterations in NTRK1/2/3, ROS1, or ALK who had never been treated with targeted agents.

Clinicians now have a new tool to better identify colorectal cancer in its early and more treatable state.

Drinking coffee resulted in a more than 25% decreased risk for developing colorectal cancer, according to the results of a new study.
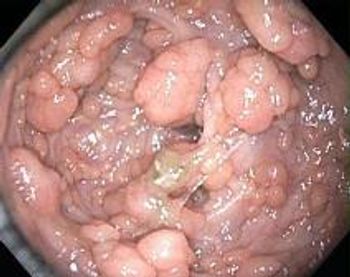
The combination use of sulindac and erlotinib significantly reduced the number of small intestine, or duodenal, polyps present in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis.

A large cohort study showed that the risk of colorectal cancer is increased following a diagnosis of prostate cancer, suggesting colorectal cancer screening should be considered following a prostate cancer diagnosis.
Regular use of aspirin has been linked with a small but significant reduction in the risk for overall cancer, and especially gastrointestinal cancers.

The addition of selective internal radiation therapy with yttrium-90 resin microspheres to standard FOLFOX chemotherapy did not improve progression-free survival in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer, but it did significantly delay disease progression in the liver.

Muscle area decreases significantly during treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer, and lower muscle area is associated with poor survival.

High expression levels of EGFR ligands epiregulin and amphiregulin are associated with increased benefit from panitumumab in patients with RAS wildtype advanced colorectal cancer.

A combination of four biomarkers may be able to help clinicians identify patients who have a high-risk type of colorectal cancer.

A short-course of preoperative radiation therapy plus consolidated chemotherapy was shown to be as effective as standard preoperative chemoradiation in the treatment of locally advanced rectal cancer.

Here, we review the studies that have explored different treatment regimens, therapeutic sequencing, and biologic inclusions for the treatment of these patients, with neoadjuvant intent. We also describe how we have established our own treatment paradigm for the management of potentially curable metastatic colorectal cancer.

It remains difficult to decipher which patients are appropriate candidates for conversion therapy vs upfront surgery. Therefore, in predicting potential outcomes, several factors should be considered. Here, we will attempt to address such factors and provide insights.

In all other settings, giving chemotherapy just to make us feel better emotionally in exchange for potential harm to the patient is not the right strategy. We need to find better treatments for this new clinical indication.

There is clear proof of principle for adjuvant therapy in patients at high risk for tumor recurrence, such as those with resected metastatic colorectal cancer. For that reason, this strategy has been largely adopted, especially using 5-FU– and oxaliplatin-based regimens, thereby mirroring the approach in resected stage III colon cancer.

The use of a reduced preparation CT colonography increased participation in colonography as a method of population screening for colorectal cancer, according to the results of a large Italian study.

Paid sick leave benefits could alleviate some of the financial burden patients with colorectal cancer incur during treatment and boost their job retention.