
A study showed that tumors of younger patients with early-onset colorectal cancer differ from the tumors of those diagnosed later in life, both genetically and epigenetically.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


A study showed that tumors of younger patients with early-onset colorectal cancer differ from the tumors of those diagnosed later in life, both genetically and epigenetically.

Blocking the MAPK pathway through treatment with dabrafenib and trametinib resulted in meaningful clinical activity in a subset of patients with BRAF V600-mutated metastatic colorectal cancer.
The USPSTF recently issued a draft recommendation advising the use of aspirin to prevent cardiovascular disease and colorectal cancer in certain patients aged 50 to 69 years.
A payment system for colonoscopies offering full insurance coverage at low-priced facilities and cost sharing at high-priced alternatives reduced spending with no increase in complications.

Consumption of four or more cups of coffee a day was associated with a reduced risk for colon cancer recurrence and death in patients with stage III disease.

A new scoring system may help to identify patients at low risk for colorectal cancer who could forego screening with colonoscopy.

Patients diagnosed with colorectal cancer at younger ages are more likely to have an underlying hereditary syndrome than older patients, according to a new study.

The use of BEAMing technology on circulating DNA to identify multiple mutations in real time could help guide treatment in colorectal cancer patients.

Our future goal should be to increase the resectability of patients with colorectal cancer and peritoneal metastases by improving selection criteria and by referring early, but also by using systemic therapies in the neoadjuvant setting.
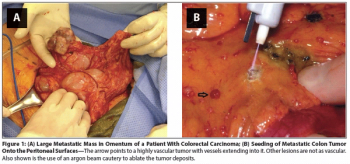
This review focuses on the underlying rationale for the use of cytoreductive surgery plus hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (CS + HIPEC) in the treatment of patients with primary gastrointestinal tumors with metastatic peritoneal disease.

It is clear that in a subset of patients with GI malignancies, particularly the low-grade appendiceal neoplasms, CS + HIPEC can result in improved outcomes and in some cases, long-term remission and occasionally cure.

Though the United States has seen a decrease in death rates from colorectal cancer, three regions, or "hotspots," continue to experience high rates.

Treatment with FOLFOX plus cetuximab resulted in improved PFS vs FOLFOX alone in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer with “all-RAS” wild-type tumors.

A subgroup analysis of the phase III RECOURSE trial has shown that TAS-102 is effective at improving survival in patients with both KRAS wild-type or mutant metastatic colorectal cancer.

Two phase III trials have confirmed the benefit of regorafenib, an oral multikinase inhibitor, in patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer.

Large proportions of lung and colorectal cancer patients believe that surgery will cure their cancer, according to results of a new population-based study.

Adding the oral NK1 antagonist aprepitant to an oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy regimen effectively reduced nausea and vomiting in colorectal cancer patients.

A new study has found that in patients diagnosed with metastatic colorectal cancer, a low BMI could be a poor prognostic factor.

Ahead of the ESMO World Congress on Gastrointestinal Cancer, we are discussing the use of maintenance therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer with Axel Grothey, MD.

Measuring ERCC1 and TS gene expression could help physicians better manage metastatic colorectal cancer patients with the most beneficial chemotherapy.

Using simulation modeling, researchers found that higher adenoma detection rates were linked with lower lifetime colorectal cancer incidence and mortality.

Aspirin use after a colorectal cancer diagnosis was independently associated with improved rates of both cancer-specific and overall survival.

Treating patients with unresectable colorectal liver metastases with radiofrequency ablation and chemotherapy resulted in improved long-term overall survival.

Neoadjuvant mFOLFOX6 plus radiation improved pathologic complete response in advanced rectal cancer patients compared with 5-FU/radiation or mFOLFOX6 alone.

Increased levels of vitamin D were associated with improved overall survival rates in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated as part of CALGB/SWOG 80405.