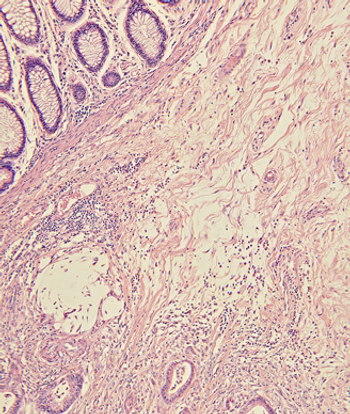
Metastatic colorectal cancer patients had about a 1.5-month increase in overall survival when treated with second-line ramucirumab plus FOLFIRI vs FOLFIRI alone.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Metastatic colorectal cancer patients had about a 1.5-month increase in overall survival when treated with second-line ramucirumab plus FOLFIRI vs FOLFIRI alone.
Patients who had either laparoscopic surgery or open surgery for localized rectal cancer had similar overall survival and disease-free survival rates.

Men with high midlife cardiorespiratory fitness have a lower incidence of lung and colorectal cancer; however, this association was not seen for prostate cancer.
If US colorectal cancer screening is increased to 80% by 2018, a new study predicts a decrease in both cancer incidence and mortality within 20 years.

Although genomic testing can improve the cost-effectiveness of a treatment, assessing the cost-effectiveness of genomic testing outside the context of its impact on treatment is not practical.

The identification and characterization of gene signatures, driver events, and pharmacogenomics in molecularly homogeneous subsets of patients is likely to advance effective drug development strategies in colorectal cancer.

Numerous genomic tests are available for use in colorectal cancer, with a widely variable evidence base for their effectiveness and cost-effectiveness. In this review, we highlight many of these tests, with a focus on their proposed role, the evidence base to support that role, and the associated costs and risks.
Looking at a large group of early-onset colorectal cancer patients, only 1.3% had TP53 mutations, none of whom met criteria for Li-Fraumeni syndrome.

In a large study, it was found that those who ate a vegetarian diet had a lower risk of colorectal cancer compared with their non-vegetarian counterparts.

Bevacizumab as first-line therapy for metastatic CRC equated to an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of more than half a million dollars per QALY.

Patients with lung and colorectal cancer who understood that chemotherapy would not cure them were no less likely to receive chemotherapy at the end of life.

Adding cetuximab to FOLFIRI resulted in improvements in survival and objective response in patients with KRAS codon exon 2 wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer.

The TKI famitinib was associated with a significant PFS improvement in metastatic colorectal cancer patients, according to the results of a phase II study.

The addition of ramucirumab to second-line FOLFIRI resulted in a delay in disease progression and improved survival in metastatic colorectal cancer patients.

Newly diagnosed metastatic colorectal cancer patients with higher vitamin D levels had better outcomes after treatment with chemotherapy and a targeted agent.

Rectal cancer patients who completed neoadjuvant therapy with a clinical complete response had similar 4-year survival rates as patients who opted for surgery.
Initial treatment with FOLFOXIRI plus bevacizumab in metastatic colorectal cancer patients improved survival over FOLFIRI and bevacizumab by more than 4 months.
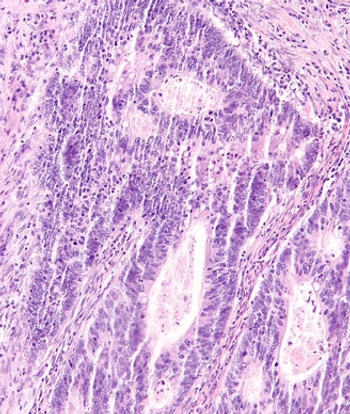
The results of a recent meta-analysis suggest that carriers of the MLH1 or MSH2 mutations associated with Lynch syndrome could delay regular colonoscopies until age 30.

Researchers are estimating that about 3.6% of new cancer cases in 2012 in adults may be attributed to a high BMI, equating to about 481,000 new cancer cases.

A significant proportion of deaths due to colorectal cancer in southern states, and half of deaths due to colorectal cancer nationwide are a result of racial/ethnic, socioeconomic, and geographic disparities.

Researchers have identified a mechanism that could explain how NSAIDs lower the risk of developing intestinal polyps that can transform into colon cancer.

Developing a scoring system for staging patients with hepatic colorectal metastases is important for prognosis and for identifying those who will benefit from additional systemic therapy.

Due to advances in chemotherapy, biologic therapy, and the development of liver-oriented treatment options, the survival of patients with metastatic cancer has more than doubled, and increasing numbers of patients have been cured, even among those with advanced disease.
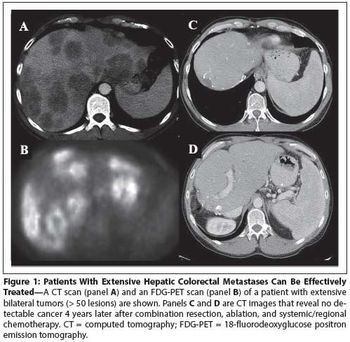
This article will review the current practice of hepatic resection for colorectal liver metastases, including the possibility of combined resection of hepatic metastases at the time of resection of the primary cancer.
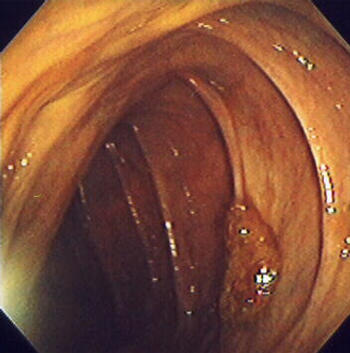
People who underwent genetic and environmental risk assessment evaluating their colorectal cancer risk were no more likely to undergo screening for the disease.