
Maintenance therapy with a new immunomodulator agent called MGN1703 improves progression-free survival over placebo in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer, according to a new study presented at the ESMO 2012 Congress.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Maintenance therapy with a new immunomodulator agent called MGN1703 improves progression-free survival over placebo in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer, according to a new study presented at the ESMO 2012 Congress.

The FDA has approved the multikinase inhibitor regorafenib (Stivarga) to treat patients with colorectal cancer that has metastasized following previous treatment.

To the Editor: We appreciated the commentaries by Drs. Duda, Glimelius, and Willet on our paper “Current Perspectives on Preoperative Integrated Treatments for Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer: A Review of Agreement and Controversies” (August issue of ONCOLOGY).
A new oral treatment is showing promise in relapsed, refractory colorectal cancer. Patients given TAS-102, an antitumor agent, showed improved survival and reduced risk of death compared to those given a placebo.
Researchers in Germany have found that longer-term follow-up would still lower risk of colorectal cancer development among patients who had an adenoma detected and removed.

In populations in whom there has been a focus on the important components of rectal cancer management, 5-year survival is better in rectal cancer than in colon cancer, which was not the case in the past. Total mesorectal excision (TME) is one of many important components of current management.

As we look forward, we suggest that the priority should be to further our understanding of the tumor’s interactions with its microenvironment and with the immune system. We think that such an understanding will be critical for advances in locally advanced rectal cancer therapy.

The preferred integrated treatment modality for locally advanced rectal cancer is preoperative radio(chemo)therapy followed by total mesorectal excision, though certain aspects of this standard are still debated.

The FDA has approved aflibercept (Zaltrap) to be used with the chemotherapy regimen FOLFIRI in the treatment of adults with metastatic colorectal cancer.
The new diagnostic test to detect KRAS gene mutations, will facilitate speedier assessment of the KRAS mutation status of a patient’s tumor to allow for an earlier treatment decision to use cetuximab or to go on with another treatment.
Two studies demonstrate that a “liquid biopsy”, using plasma or blood samples can be used to detect the acquired resistance and potentially measure disease progression.

Schrader and colleagues provide four compelling examples of the power of genetic testing to impact medical management for probands and their family members.

In this article, we use a case-based approach to focus on the hereditary aspects of the most common GI cancers, including pancreatic, gastric, and colon cancer.

A new study from the National Cancer Institute shows that physical activity is associated with lower mortality rates in patients with breast and colon cancers.

Three papers published today show that aspirin, taken daily, may prevent cancer, and could even treat certain cancers.

This article reviews the main issues that must be considered in metastatic colorectal cancer from the surgical oncology and medical oncology perspectives, respectively.

Combined-modality therapy has rendered disease-free an increasing number of patients who were previously considered to be incurable. Still, despite myriad advances in imaging, and in surgical and therapeutic modalities, many patients who undergo resection of limited metastatic disease with curative intent ultimately relapse.

In their article in this issue of ONCOLOGY, authors Bartlett and Chu discuss a very provocative suggestion that the possibility exists to cure patients with advanced colorectal cancer.

Reporting interim findings from a multi-institutional assessment of more than 50,000 people 50 to 69 years of age, COLONPREV Study Group investigators from Spain have concluded colonoscopy is better than fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) at detecting adenomas.
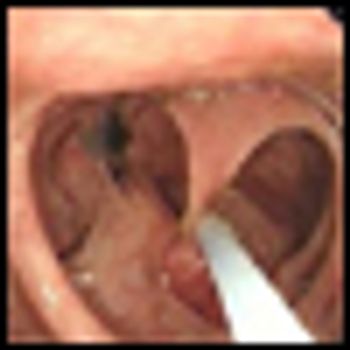
A multi-institutional, NCI-funded retrospective study in the New England Journal of Medicine highlights the significant long-term benefit of colonoscopic polypectomy in preventing death from colon cancer, with polypectomy cutting the incidence of colon cancer–related mortality in half compared with the general population.

Researchers at Vanderbilt University Medical Center have found that eating omega-3 fatty acids regularly can result in prevention of colon polyp formation. The 33% reduced risk of colorectal adenomas was seen in women, but not in men.

In this interview, Dr. David Ahlquist, gastroenterologist and professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester in Minnesota, discusses early detection methods of colorectal cancer, touching on sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopies, fecal blood testing, and in particular, stool DNA screening.

Metastatic melanomas that harbor the V600E mutation in the BRAF gene respond rapidly to vemurafenib (Zelboraf), the BRAF V600E inhibitor. But While vemurafenib results in a response in about 80% of melanoma patients, the clinical response among CRC patients is not greater than 5%.

A study published earlier this month in the New England Journal of Medicine, identifies specific colorectal tumors that are less responsive to chemotherapy. Researchers at the University of Magdeburg show that the hypermethylation of the transcription factor AP-2 epsilon (TFAP2E) gene results in lower expression of the TFAP2E protein and upregulation of the DKK4 gene, a gene which has been previously associated with resistance to the chemotherapy fluorouracil.

Treatment for patients with locally advanced, resectable rectal cancer has clearly evolved, with significant refinements in preoperative assessment, surgical technique, and use of preoperative chemoradiation.