
Adjuvant chemotherapy is underutilized in elderly patients with stage III colon cancer, despite improved long-term survival after treatment.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!



Adjuvant chemotherapy is underutilized in elderly patients with stage III colon cancer, despite improved long-term survival after treatment.

In this interview we discuss the role of genetic testing in patients with colon cancer.

No difference in time to recurrence, recurrence-free survival, or overall survival were noted for patients with rectal cancer who underwent one of three different preoperative radiotherapy regimens.

Completing a course of preoperative radiotherapy prior to undergoing surgical resection for rectal cancer was associated with improved survival compared with patients who had an incomplete course of radiotherapy.

Young and middle-aged patients diagnosed with colon cancer were more likely to receive postoperative chemotherapy compared with their older-age counterparts, according to the results from a recent cohort study.

A study found that normal-weight women should be evaluated for metabolic health to reduce their risk for colorectal cancer.

We spoke with Dr. Luis Diaz about his recent presentation on immunotherapy in colorectal cancer at the 2017 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium, held January 19–21 in San Francisco.

The immune checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab showed durable responses and disease control in a group of heavily pretreated patients with DNA mismatch repair deficient/microsatellite instability high (MSI-H) metastatic colorectal cancer.

Using immunohistochemistry to measure the expression of certain target enzymes-cox-2 and 15-prostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH)-in premalignant colorectal adenomas, researchers were able to get significant predictive and prognostic information in patients treated with the cox-2 inhibitor celecoxib for prevention of colorectal adenomas.

The addition of the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib to irinotecan and cetuximab prolonged progression-free survival and resulted in a higher disease control rate than treatment with irinotecan and cetuximab alone in patients with BRAF-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer.

Certain patient-reported outcomes including fatigue and emotional support are associated with survival outcomes in patients with early-stage colorectal cancer.

Advanced colorectal cancer patients with BRAF mutations have markedly worse prognosis than non-mutant patients, according to a large analysis. Post-progression survival in particular is worse among BRAF-mutant patients.

Patients with metastatic colorectal cancer who engaged in more hours of physical activity at the time of their diagnosis had improvements in both progression-free and overall survival compared with patients who had less physical activity.

Non-aspirin NSAIDs are more effective than other options for colorectal chemoprevention in individuals with previous colorectal neoplasia, according to a new meta-analysis. Low-dose aspirin, however, is a safer option, and offers the best risk-benefit profile.

More than 15% of patients with early-onset colorectal cancer may harbor mutations to cancer susceptibility genes, suggesting a need for genetic counseling and a multigene panel.
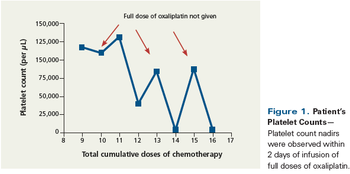
A 44-year-old patient with a history of stage IIB colorectal cancer at the hepatic flexure, invading the duodenum and pancreas, was initially diagnosed in September 2005 and received modified Whipple surgery and 8 cycles of adjuvant chemotherapy with capecitabine and oxaliplatin every 3 weeks.

In the United States, approximately 20% of patients with colorectal cancer present with distant metastasis at diagnosis. In 25% of cases, the peritoneal cavity is the only site of metastatic disease, which is not indicative of a generalized systemic disease, as is the case with lung or liver metastases.

The occurrence of colon cancer on the right vs left side of the colon is a prognostic factor for all stages of the disease.

Patients with peritoneal metastatic colorectal cancer had significantly shorter overall survival compared with patients with other isolated sites of metastases.

The expansion of healthcare in Massachusetts in 2006 was associated with increased rates of resection for patients with colorectal cancer.
Colonoscopy screening is modestly effective for preventing colorectal cancer in patients aged 70 to 74, but the benefits may begin to diminish after that.

If you’ve been in oncology long enough, you’ve likely seen the patient who presents with metastatic disease, gets first-line therapy, progresses, switches to second-line therapy, progresses again, and so on, with their cancer becoming increasingly more resistant to therapy.

A set of genes that are more likely to be mutated in African-Americans vs Caucasians with colorectal cancer appears to increase the risk of metastases and relapse in mutant versions.

In this interview we discuss the GeneFx Colon test (or the ColDx assay), which can helpful identify patients with low- or high-risk stage II colon cancer.

A gene expression microarray-based assay was able to successfully identify patients with stage II colon cancer who are at high risk for recurrence.