
Citing different studies, two physicians reach different conclusions as to whether ovarian cancer screening is worthwhile.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Citing different studies, two physicians reach different conclusions as to whether ovarian cancer screening is worthwhile.

Physicians must engage and educate patients about significant risk for cardiovascular disease.

Mrs. S. is a 37-year-old Caucasian female who sought care at her home institution overseas during a period of several months for complaints of esophageal reflux, constipation, early satiety, increasing abdominal girth, and fatigue.

Postmenopausal women at average risk of ovarian cancer may benefit from ROCA (Risk of Ovarian Cancer Algorithm), a new ovarian cancer screening strategy that combines information about trends in CA-125 blood test results and age, followed by transvaginal ultrasound (TVU) as needed and referral to a gynecologic oncologist. Results of a prospective multicenter trial of ROCA were reported at the 44th annual meeting of ASCO (abstract 5003). Results of ROCA testing were used to categorize women as low risk (requiring a repeat CA-125 test in 1 year); intermediate risk (repeat CA-125 test in 3 months); or high risk (TVU and referral to a gynecologic oncologist, who decides, based on clinical findings and the TVU result, whether the patient needs to undergo surgery).

Postmenopausal women who regularly use painkillers have lower estrogen levels, which could lead to a decreased risk of breast or ovarian cancer.

Of the predominant gynecologic cancers, cancer of the uterine cervix is the least common, with only 11,270 new cases anticipated in the United States in 2009. Nevertheless, approximately 4,070 women die of cancer of the uterine cervix annually in the United States.

Cervarix has won FDA approval for the prevention of cervical pre-cancers and cervical cancer associated with HPV-16 and HPV-18 for use in girls and young women (ages 10-25), according to GlaxoSmithKline.

The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved GlaxoSmithKline’s human papillomavirus bivalent (types 16 and 18) vaccine, recombinant (Cervarix) for the prevention of cervical precancers and cervical cancer associated with oncogenic human papillomavirus (HPV) types 16 and 18 for use in girls and young women (aged 10–25).

Comparative uptake of two radiotracers allows characterization of tumor.

Ovarian cancer is the most deadly gynecologic malignancy. In the US alone, an estimated 21,500 new cases will be diagnosed in 2009, and an estimated 14,600 women will die from this disease.

The Society of Gynecologic Oncologists (SGO) has published the first in a series of four papers on a variety of cervical cancer issues and topics that were the focus of its Forum “The Future Strategies for Cervical Cancer Prevention: What Do We Need to Do Now to Prepare,” held last September in Chicago.

The final analysis of the largest efficacy trial of a cervical cancer vaccine was published July 25, 2009, in The Lancet. The study, involving 18,644 women, confirmed GlaxoSmithKline’s Cervarix is highly effective at protecting against the two most common cervical cancer–causing human papillomavirus (HPV) types, 16 and 18. The study also showed that the vaccine provides cross-protection against HPV types 31, 33, and 45, the three most common cancer-causing virus types beyond 16 and 18.

Imaging with MR and/or PET/CT can help physicians figure out appropriate treatment for cervical cancer patients as well as prevent unnecessary therapy, according to a new study.
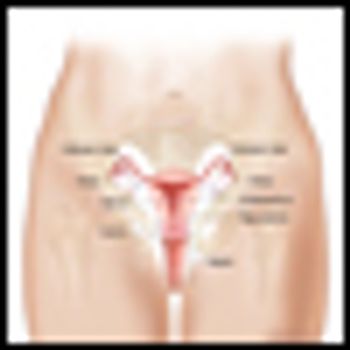
Endometrial cancer is the most common gynecologic malignancy, with an estimated 40,100 cases and 7,470 deaths in 2008. This malignancy represents 6% of all cancers, and 3% of cancer deaths in women. Endometrial cancer is more prevalent in older women, with an incidence of 1 in 142 for women 40 to 59 years old, increasing to 1 in 81 women over 70 years old.[1] Median age at diagnosis is 62.[2] The mortality of endometrial cancer has decreased from 4.18 to 4.12 per 100,000 from 1991 to 2004.

Published analyses combining groups of patients with different risk profiles have created confusion surrounding patient selection for adjuvant treatment after surgery for endometrial cancer. As a result, no randomized trial has demonstrated a survival benefit with the addition of adjuvant radiation

In this issue of ONCOLOGY, Diavolitsis et al have provided an excellent overview of the literature and state of our understanding of the role of adjuvant therapy in the treatment of endometrial cancer.

Results from an 8-year trial involving more than 130,000 women published in The New England Journal of Medicine (360:1385-1394, 2009) demonstrate that in low-resource settings, a single round of human papillomavirus (HPV) testing significantly reduces the numbers of advanced cervical cancers and deaths, compared with Pap testing or visual inspection with acetic acid (VIA). This was the first randomized controlled trial to measure incidence of cervical cancer and associated rates of death as the primary outcomes, using different tools for screening.

Diffusion-weighted MRI added to standard T2-weighted scans can help spot cervical cancer in its early stages. A preliminary study from the Institute of Cancer Research in London determined that DWI can spot tumors missed by T2 imaging and bolster management options for women who wish to preserve reproductive organs.

Patients with endometrial cancer who have minimally invasive robotic-assisted hysterectomies tend to have quicker surgeries and shorter hospital stays compared with patients who have similar laparoscopic surgical procedures, according to new research from The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer–James Cancer Hospital and Solove Research Institute.

BD Diagnostics recently announced that it received US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Premarket Approval for the BD FocalPoint GS Imaging System.
Given that in the 21st century many believe 70 years of age is the new 60 and 80 years of age is the new 70, any article on ovarian cancer in the elderly depends on one’s definition of elderly. To put this in a 21st century perspective, in a thoughtful article on aging in The New Yorker (“The Way We Age Now,” April 30, 2007), Atul Gawande points out, “for most of our hundred-thousand-year existence-all but the past couple of hundred years-the average life span of human beings has been 30 years or less (research suggests that subjects of the Roman Empire had an average life expectancy of 28 years).

Conventional therapy for advanced-stage ovarian cancer-ie, aggressive cytoreductive surgery followed by aggressive chemotherapy-was established more than 3 decades ago [Editor’s note: See Dr. Schwartz’s article, “Cytoreductive Surgery in the Management of Ovarian Cancer,” in last month’s issue of ONCOLOGY]. Since that time, no prospective randomized trials have been reported to confirm the efficacy of this treatment strategy.

The standard management for advanced-stage ovarian cancer was established in the mid-1970s. At a 1974 National Cancer Institute Consensus Conference on Ovarian Cancer, Griffiths presented data supporting the role for aggressive cytoreductive surgery as the first step in the management of this disease, followed by cytotoxic chemotherapy.

The first phase III study of its kind has found that vaginal brachytherapy—in which a radioactive cylinder is inserted into the vagina—is as effective at preventing the recurrence of higher-risk endometrial cancer as external-beam radiation therapy, has fewer side effects, and results in a better quality of life for patients (abstract LBA5503).

Although vulvar cancer is relatively rare, accounting for less than 5% of all cancers of the female genital organs, lymph node metastasis associated with vulvar carcinoma is a common event and occurs in about 25% of cases.[1] The presence and number of lymph node metastases is the single most important prognostic factor in vulvar cancer and a critical component to the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) staging system, as well as a major determinant in the need for adjuvant therapy