
This article focuses on the recent debate regarding when-or whether-patients with ovarian cancer should undergo aggressive surgical resection.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!



This article focuses on the recent debate regarding when-or whether-patients with ovarian cancer should undergo aggressive surgical resection.

Whether advanced ovarian cancer should be treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy or primary debulking surgery is one of the most debated topics in gynecologic oncology.

Surgical debulking of epithelial ovarian carcinoma has been a mainstay of therapy for more than 50 years-since the approach was first advocated by Meigs in 1934.[1] In 1968, Munnell[2] introduced the idea of the "maximum surgical effort”-essentially the removal of as much cancer as possible.
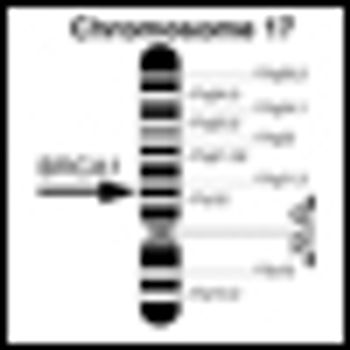
The results of a study that tracked BRCA mutation carriers suggest that women who inherit BRCA gene mutations develop cancer at a younger age than women in the previous generation. The study is published on-line today in the journal Cancer.

The European Society of Gynaecological Oncology (ESGO) biennial meeting is taking place in Milan, Italy, and will run from September 11-14, 2011.

Last week the FDA cleared the use of blood tests for two proteins, HE4 and CA-125; biomarkers that together can be used to estimate risk for ovarian cancer in women who present with a pelvic mass.
A phase II trial of BIBF 1120 (Vargatef) in women with relapsed ovarian cancer that were previously treated with chemotherapy showed that BIBF 1120 given as maintenance therapy resulted in improved progression-free survival rates.
Researchers at the BC Cancer Agency in Vancouver and colleagues have just published the results of a phase II study showing that olaparib (AZD2281), an oral PARP inhibitor, may be effective in treating non-BRCA-related ovarian cancer patients.
Cabozantinib (cabo), formerly known as XL184, has recently shown unprecedented activity against bone metastases in prostate cancer patients in a phase II trial.

Many doctors do not properly adhere to current guidelines for offering breast and ovarian cancer counseling and testing services to their female patients, according to a new study from the Division of Cancer Prevention and Control at the CDC.

Two large-scale phase III trials that add bevacizumab to standard chemotherapy regiments in advanced ovarian cancer have reported results at this year's American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).

Live coverage of the ASCO session on PARP inhibitors and DNA repair, with speakers Michael Kastan, Judy Garber, and Elisabeth Plummer.
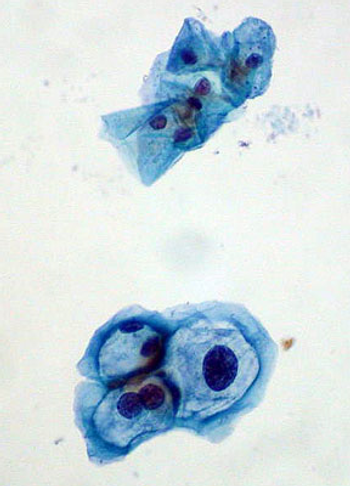
One of the highlights of the released abstracts is “Cervical cancer risk for 330,000 women undergoing concurrent HPV testing and cervical cytology in routine clinical practice” (J Clin Oncol 29: 2011 (suppl; abstr 1508). The large-scale study showed the effectiveness of human papillomavirus (HPV) testing alone or in combination with cytology testing for identifying women at high-risk for cervical cancer development.
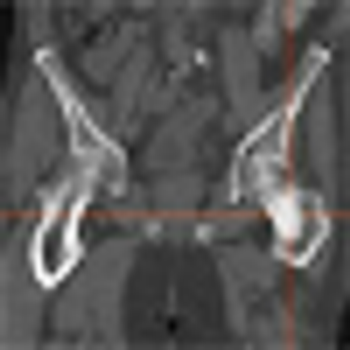
Data from a phase II study of cabozantinib (XL184) in patients with advanced solid tumors show that the drug has activity in both bone and soft tissue. The study evaluated the efficacy and safety of cabozantinib compared to placebo in 9 different solid tumor types including breast, lung, ovarian, and prostate.

A recent study demonstrated that the novel oral Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor, olaparib, provided a significant improvement in progression-free survival for women with serous ovarian cancer when used as a maintenance therapy.

Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted infection in the United States, with approximately 20 million people currently infected and an additional 6.2 million infected each year, despite increased media attention to HPV as a cause of cervical cancer and the availability of a vaccination to reduce HPV-associated cervical cancer.

The Swiss pharmaceutical company Roche and Roche Group member Genentech have announced that addition of bevacizumab (Avastin) to chemotherapy improved progression-free survival over chemotherapy alone in the phase III OCEANS ovarian cancer study, meeting the study’s primary endpoint.

The article by Dr. Echarri Gonzalez and her colleagues regarding intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy for women with epithelial ovarian cancer provides a comprehensive yet practical review of the critical questions surrounding the use of IP chemotherapy.

In 2006, after a third consecutive large-scale US phase III trial conducted by the Gynecologic Oncology Group (GOG) confirmed that use of intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy in optimally resected stage III epithelial ovarian cancer results in superior overall survival (OS) and/or progression-free survival (PFS),[

Epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) spreads prominently within the peritoneal cavity. In fact, we now know that high-grade serous cancers are often of tubal origin, and their presentation as tubo-ovarian masses renders it likely that intraperitoneal spread occurs as an early event in their clinical evolution.

Early results from the ICON7 trial suggest that adding bevacizumab (Avastin) to standard chemotherapy in women with newly diagnosed ovarian cancer reduces the risk of disease progression during the first year of treatment.

Investigators from the German Cancer Research Center in Heidelberg reported on the effects of LMV-601 on cultured human cervical cells. LMV-601 is a phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C (PC-PLC) inhibitor.

With the increased use of human papillomavirus vaccines such as Gardasil and Cervarix, the medical community is likely to see a decrease in cases of genital warts and other complications caused by several HPV strains. But it may be a decade or two before oncologists can expect to see a decline in cervical cancer rates attributable to the use of these relatively new vaccines.

Current advances in the field of medicine have aided in the early detection and treatment of cancer, leading to an increased rate of survivorship among cancer patients after an initial diagnosis.

Human papilloma virus often lurks in cervical tissue, and it can cause cancer there. But the infection is also often benign, particularly among young women. Biomarkers of transformation are proving useful in helping cytologists to decide when a suspicious-looking Pap result is truly a sign of trouble.