
A recent study that gave hormone therapy to ovarian cancer patients with severe menopausal symptoms revealed that the treatment had a beneficial survival effect.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


A recent study that gave hormone therapy to ovarian cancer patients with severe menopausal symptoms revealed that the treatment had a beneficial survival effect.

In this interview we discuss the latest on HPV vaccines for cancer prevention and some of the struggles countries face in achieving widespread adoption.
An investigational vaccine has shown activity as a therapeutic treatment for high-grade pre-cancerous cervical lesions caused by the human papillomavirus.

Here we discuss the advantages and pitfalls of HIPEC in advanced ovarian cancer, as well as current data and ongoing prospective trials.

The evidence suggests that few centers offer IP therapy routinely. Why? The answer may be that oncologists simply don’t know what to do. There have been three completely distinct regimens, none of which has been used in the outpatient setting.

Based on the currently available scientific evidence, HIPEC should not be considered a standard therapeutic option after optimal cytoreduction in advanced ovarian cancer, nor should it be offered outside of a clinical trial.

A small study showed that treatment with the anti-PD-1 immunotherapy nivolumab was able to produce complete responses in patients with advanced platinum-resistant ovarian cancer.

Beta-blockers were associated with increased overall survival in women with epithelial ovarian cancer, according to a retrospective study.

Government-subsidized breast cancer and cervical cancer screening will no longer be available through Planned Parenthood clinics in Texas beginning September 1, 2015.

Testing women for non-BRCA gene mutations that can confer breast or ovarian cancer risk has clinical management consequences for both the women and their family members.

Women younger than 35 with low-grade serous carcinoma of the ovary or peritoneum or those who still had persistent disease at the completion of primary therapy were found to have worse disease outcomes.

A study has found that mutations in the genes RAD51C and RAD51D confer risk for epithelial ovarian cancer, causing approximately one in every 90 high-grade and one in every 120 epithelial ovarian cancer occurrences.
According to a recent study, the use of oral birth control pills has prevented 200,000 cases of endometrial cancer over the last 10 years.

Despite trials showing a benefit when combining IP and IV chemo for ovarian cancer, fewer than 50% of eligible patients are currently receiving this treatment.

The FDA has granted Orphan Drug Designation to the immunotherapy DPX-Survivac, which is in development for the treatment of ovarian cancer.

Fertility preservation for patients diagnosed with early-stage cervical cancer is feasible and has gained acceptance within the gynecologic oncology community.

A group of several ovarian cancer patients have either called or visited me in my office recently to ask for information and validation to begin a vaccine clinical trial on a tropical island in the Atlantic.

Ovarian cancer progression may be driven by the activation of an endoplasmic reticulum stress response factor that disrupts the function of dendritic cells and, subsequently, antitumor fighting T cells.

Detection of cervical lesions among young women has decreased since the introduction of HPV vaccines and guidelines calling for reduced cervical cancer screening.

The addition of bevacizumab to carboplatin/paclitaxel chemotherapy increases progression-free survival in advanced/recurrent endometrial cancer patients.


A phase III trial found that primary chemotherapy resulted in similar survival compared with primary surgery in newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer patients.

Preoperative albumin level and number of extended cytoreductive procedures in ovarian cancer patients predicted the likelihood of surgical complications.
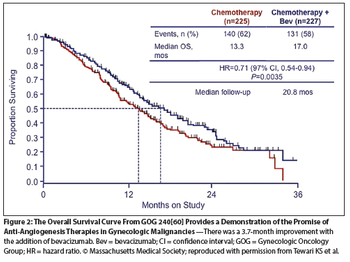
The purpose of this paper is to provide a review of site-specific treatment options that involve the targeting of angiogenesis in gynecologic malignancies.

In order for there to be a truly clinically significant breakthrough in targeted therapy, we need to further explore the tumorigenesis of gynecologic malignancies and identify the initiators and true drivers of these cancers.