
Although the combination of CA-125 and HE4 appears indicated for use in symptomatic patients or in patients with an adnexal mass, there is no evidence that it would be indicated as a screening test in asymptomatic patients.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Although the combination of CA-125 and HE4 appears indicated for use in symptomatic patients or in patients with an adnexal mass, there is no evidence that it would be indicated as a screening test in asymptomatic patients.
Results from the phase III GOG 240 trial, presented at ASCO, showed the addition of bevacizumab (Avastin) to standard chemotherapy improved overall survival by nearly 4 months in women with advanced or relapsed cervical cancer.
Biennial visual inspection with acetic acid (vinegar) screening by trained public health workers significantly reduced cervical cancer mortality in a large cluster-randomized controlled trial conducted among thousands of women from poor neighborhoods in Mumbai, India.
Women diagnosed with endometrial cancer at age 50 or younger had a fourfold increased risk for a subsequent colorectal cancer diagnosis, according to a historical cohort study published recently in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.

Therapy for recurrent ovarian cancer is not curative, and presumed overall survival benefits of standard strategies are uncertain and often based on low-level evidence. Treatment toxicity and patient quality of life should be considered at all points during disease management.

It is important to help patients with recurrent ovarian cancer recognize and acknowledge when further therapy is likely to be futile. For some patients this might occur very early in their disease course, while for others it may be after many years of treatment.

Emerging therapies in the management of ovarian cancer have resulted in a shift in paradigm, including in the appropriate time to institute therapy, and in the selection of therapy. This review focuses on chemotherapy and emerging biologic agents that present a therapeutic option for patients with recurrent ovarian cancer.
A novel therapy has shown activity in the treatment of difficult-to-treat, advanced, platinum-resistant ovarian cancer. The drug, DMUC5754A, is part of a new class of drugs called antibody-drug conjugates.

In this interview we discuss HPV-associated cancers, which are on the rise, and the low vaccination coverage for HPV with Edgar Simard, PhD, MPH, senior epidemiologist of surveillance research, who studies the impact of prevention and screening on cancer incidence at the American Cancer Society.


A large collaborative sequencing study using data from the Cancer Genome Atlas shows basal-like breast cancers share similar genetic origins and features with serous ovarian tumors.
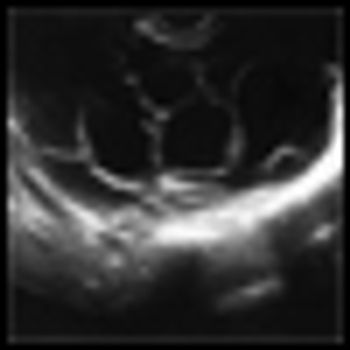
In updated guidelines, the USPSTF concludes that there is still no adequate evidence of a mortality benefit from routine ovarian cancer screening using transvaginal ultrasonography or CA-125 testing.

Researchers have found that tumors with multiple cancer genomes and the downregulation of the LRP1B gene are associated with chemotherapy resistance among patients with the high-grade serous ovarian cancer.
A new study finds that baseline testing for HPV can better predict long-term negative cervical cancer outcomes compared to a Pap smear.

Lori Smith addresses a side effect that affects 88 percent of women treated for cervical cancer with radiation: vaginal stenosis.

Lori Smith discusses the side effect of incontinence in women being treated for GYN malignancies.
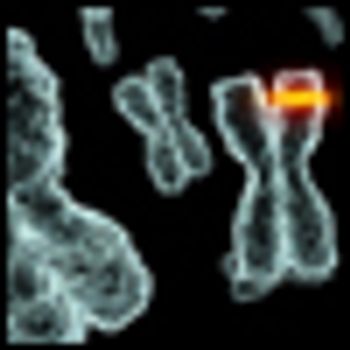
A study published today details a scoring system that may predict which ovarian cancer patients responded to first-line platinum chemotherapy based on a DNA-repair pathway-focused score. The score is based on a gene expression profile of 23 DNA-repair genes that normally function to repair platinum-induced DNA damage.

Selumetinib, a small-molecule MEK inhibitor, controlled recurrent low-grade serous ovarian cancer in 81% of patients treated. Current first-line defense against this disease (surgery followed by cytotoxic chemotherapy) has met with limited success.

Cancer Network interviews two prominent ovarian cancer researchers from both sides of the Atlantic on the role of PARP inhibitors and the challenges of developing ovarian cancer therapies.

This article reviews the trials that have been conducted with PARP inhibitors in epithelial ovarian cancer, fallopian tube cancer, and primary peritoneal cancer, and places the impact of those results in the larger context of PARP inhibitor development.

Four publications on cancer treatment during pregnancy were published last week in the journal Lancet, serving as new treatment guidelines for chemotherapy and surgery in pregnant patients with solid tumors and hematologic malignancies.

The development of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors as a new class of anticancer agents has created a tremendous amount of hope in the ovarian cancer community, especially in the high-risk, difficult-to-screen, hereditary ovarian cancer population.

Ovarian cancers account for more than 50% of gynecologic cancer deaths. This is attributable to the late stage of the disease at diagnosis.

A new study has made a step forward toward better characterization of sporadic ovarian tumors by identifying their DNA repair protein expression profile.

Coffee is emerging as a protective agent against a number of diseases, including cancer. A study published last week shows that women who drank more than four cups of coffee per day cut their risk of endometrial cancer by 25% compared with those who drank less than one cup per day.