Testing for HPV infections in urine could be an extremely accurate way to exclude the possibility of such infections and screen for cervical cancer.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Testing for HPV infections in urine could be an extremely accurate way to exclude the possibility of such infections and screen for cervical cancer.

ASCO has released a clinical practice guideline on invasive cervical cancer. For the first time, ASCO created the guideline based on resource availability, tailoring recommendations to support basic- or limited-resource settings.

Women who do not engage in regular physical activity have an increased risk of developing cervical cancer, according to a new study

In 2016, it is estimated that there will be 22,280 newly diagnosed cases of ovarian cancer in the United States. Astonishing as it may seem, the lifetime risk for a woman developing ovarian cancer is 1 in 75, with a risk of death related to the disease being 1 in 100 (excluding low malignant potential tumors).

It may be possible to remove deleterious germline BRCA1 mutations through alternative mRNA splicing and prevent drug resistance in some breast and ovarian cancer patients.

NEW ORLEANS – A new type of antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) platform may pave the way to help patients with ovarian cancer and non-small cell lung cancer.

The American Society of Clinical Oncology released a statement calling for the rapid expansion of use of the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine to help protect thousands of people from HPV-associated cancers.

The combination of sentinel lymph node mapping and use of uterine intraoperative restrictive frozen section in patients with low-grade endometrial cancer can reduce the rate of complete lymphadenectomy without reducing the detection of lymphatic metastasis.

Loss of function of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene leads to resistance to therapies targeting the Notch signaling pathway according to a mouse study presented at the 2016 Society of Gynecologic Oncology annual meeting, held in San Diego, March 19-22, 2016.

Combining three markers of homologous recombination deficiency into a single score may improve treatment decisions for women with ovarian cancer, according to a study reported at the 2016 SGO Annual Meeting.
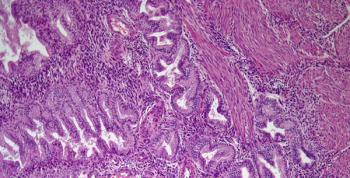
A 42-year-old woman presents with excess uterine bleeding. After a biopsy is performed, what is your diagnosis?

Ovarian cancer is a complex disease, comprised of many forms of degrees of aggression. Statistics for ovarian cancer remain startling and include 21,000 new cases annually in the United States and a staggering 14,000 deaths.

Assignment to a dose-dense regimen of paclitaxel given weekly did not prolong progression-free survival compared with paclitaxel given every 3 weeks in a group of patients with ovarian cancer treated with or without bevacizumab.
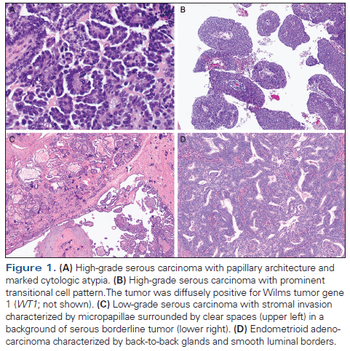
This review focuses on the clinicopathologic and molecular features of epithelial ovarian cancer, with specific attention to genetic predisposition, morphologic challenges, immunohistochemistry, and molecular features.

The movement of ovarian carcinoma histotypes from ill-defined and poorly reproducible clusters of cases to distinct disease entities clearly has beneficial implications for patient management.
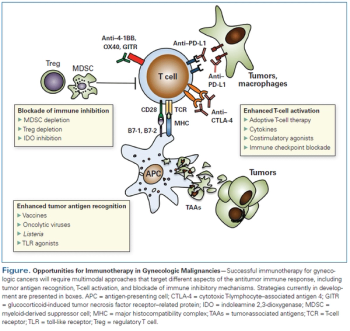
In this review, we will summarize clinical trials that have used various immunotherapeutic strategies, with a particular focus on recently emerging data for new agents and combinations.

Adolescent girls who live in predominantly Hispanic and high poverty communities are more likely to have had at least one HPV vaccine dose compared to girls in low poverty communities and those with different ethnic make up.

The advent of immunotherapy presents us with new treatment approaches in gynecologic cancers, with preliminarily promising outcomes. Multiple clinical trials are currently being conducted to better define the role of immunotherapy. Further investigation is warranted to develop and identify predictive biomarkers.

A mouse study found that resveratrol has a significant antitumor effect in an ovarian cancer model, and also suppressed tumor regrowth following cisplatin.

Women older than 70 received less treatment for ovarian cancer than did their younger counterparts, according to the results of a single-center French study.

Women with chemotherapy-naive advanced ovarian cancer gained significant delays in the progression of their disease when adding nintedanib to carboplatin/paclitaxel.
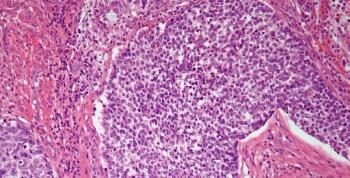
A 47-year-old woman undergoes a hysterectomy and a section of the endometrium is sent for analysis. What is your diagnosis?

The panel reviewed the pertinent literature in vulvar cancer and voted on three variants to establish appropriate use of imaging, adjuvant radiation, including dose, fields, and technique, as well as adjuvant chemotherapy. This report will aid clinicians in selecting appropriate patients for adjuvant treatment and will provide guidelines for the optimal delivery of adjuvant radiation therapy and chemotherapy.

In this interview we discuss sexual health during cancer treatment and some of the disappointments of precision medicine.

A review by the European Medicines Agency shows that the HPV vaccine does not cause complex regional pain syndrome and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome.