
The FDA approved the tyrosine kinase inhibitor bosutinib (Bosulif) to treat Philadelphia chromosome–positive chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML).

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


The FDA approved the tyrosine kinase inhibitor bosutinib (Bosulif) to treat Philadelphia chromosome–positive chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML).
A common genetic mutation in BIM appears to play a role in resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and EGFR-mutated NSCLC.

The FDA has approved vincristine sulfate liposome injection (Marqibo) to treat adults with Philadelphia chromosome–negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
A new study finds that adding rituximab maintenance to R-CHOP induction is an effective treatment for older patients with mantle-cell lymphoma.
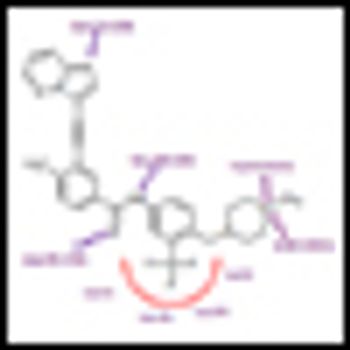
Ariad Pharmaceuticals has asked the FDA for an accelerated approval of the BCR-ABL inhibitor ponatinib, based on promising data from ongoing phase II trials.

Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) encompasses multiple disease entities that differ with regard to marrow morphology, cytochemistry, immunophenotype, pretreatment clinical characteristics, and treatment outcome.

Prognostic factors in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) may be subdivided into those related to patient characteristics and general health condition, and those related to characteristics of the tumor.

Last week the US Food and Drug Administration approved carfilzomib (Kyprolis) to treat patients with multiple myeloma who have received at least two prior therapies, including treatment with bortezomib (Velcade) and an immunomodulatory therapy.
Three-year results from the ENESTnd trial show continued superiority of nilotinib over imatinib in patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) in chronic phase, according to a new paper published online ahead of print in Leukemia in June.
Nilotinib offers good results for patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) in chronic phase who are resistant or intolerant of imatinib, according to 48-month follow-up results of a phase II study.

Observations made in the study of the leukemias have contributed to our understanding of malignancy in general and to our ability to treat cancer patients with drugs.

The article by Drs. Stein and Tallman is an excellent summary indicating that several different approaches may lead to the cure of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL).

The management of patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) has been transformed over the course of the last two decades following the introduction of successful molecularly targeted therapies-all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and arsenic trioxide (ATO)- which act in concert to induce degradation of the PMLRARα oncoprotein formed by the chromosomal translocation t(15;17)(q22;q21).

The treatment of APL in the modern era is a success of modern hematology. In this review we have attempted to plant the seeds of understanding regarding how diagnosis and treatment of APL will be pursued over the next decade.

CancerNetwork speaks with Hagop Kantarjian, MD, M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, who shares his impressions of some of the highlights of this year’s ASCO meeting with regard to hematologic malignancies.
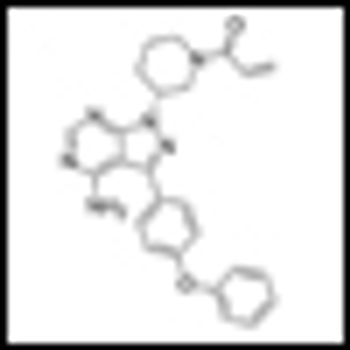
Impressive interim results from a phase Ib/II trial of ibrutinib, a selective Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) were reported at ASCO.
Updated clinical data from the pivotal phase II global PACE trial of ponatinib confirm its impressive antileukemic activity in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia or Philadelphia-chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia at all stages who are resistant or intolerant to dasatinib or nilotinib.
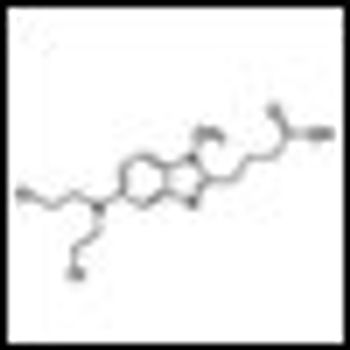
Bendamustine plus rituximab should be considered as the preferred first-line treatment of follicular and indolent lymphomas, and the elderly with mantle cell lymphoma.
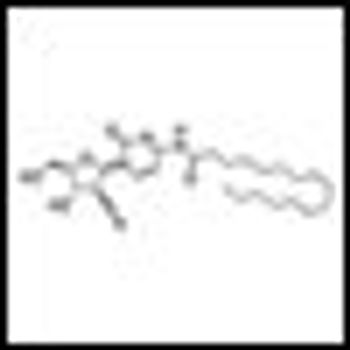
Updated data from an ongoing phase II trial of oral sapacitabine showed that the drug had activity in older patients with myelodysplastic syndromes refractory to front-line hypomethylating agents indicates.
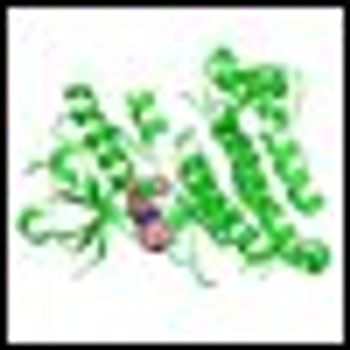
In a phase I study the targeted drug crizotinib, a small molecule inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase and met proto oncogene, delayed or eliminated signs of tumor growth in pediatric patients with aggressive cancers.
A new study has identified independent risk factors for the development of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) including high fetal growth, older age of the mother, low birth order, and male sex. A family history of NHL in either parent or sibling was found to be the strongest risk factor.
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania have identified a protein that could be targeted to turn off B-cell lymphomas. The protein, CD19, was found to be a major regulator of B-cell neoplastic growth driven by the MYC oncogene.
Three studies published this week show that lenalidomide improves progression-free and overall survival as a maintenance therapy in multiple myeloma, despite its link to other primary cancers.

Dr. Hoppe and colleagues present a strong case supporting the use of proton therapy (PT) for the treatment of patients with Hodgkin lymphoma (HL).

Proton radiotherapy is here to stay. Despite the high initial cost, the number of proton therapy machines in the United States and elsewhere is increasing rapidly.[1] The major questions now relate to defining and optimizing their appropriate use.